LEDs and their organic counterparts are getting truly tiny. This could be the moment AR and VR companies have been waiting for.



Despite the company’s commitment to making its founder’s dream come true, the virtual reality market is contracting.
Sales of VR headsets and augmented reality glasses in the U.S. plummeted nearly 40% to $664 million in 2023, as of Nov. 25, according to data shared with CNBC by research firm Circana. That’s a much steeper drop than last year, when sales of AR and VR devices slid 2% to $1.1 billion.
The two-year decline underscores Meta’s continuing challenge in bringing the immersive technology out of a niche gaming corner and into the mainstream. While Zuckerberg said, in announcing Facebook’s pivot to Meta in late 2021, that it would likely take a decade to reach a billion users, he may need to start showing more optimistic data to appease a shareholder base that’s been critical of the company’s hefty and risky investments.
Virtual reality, or VR, is not just for fun-filled video games and other visual entertainment. This technology, involving a computer-generated environment with objects that seem real, has found many scientific and educational applications as well.
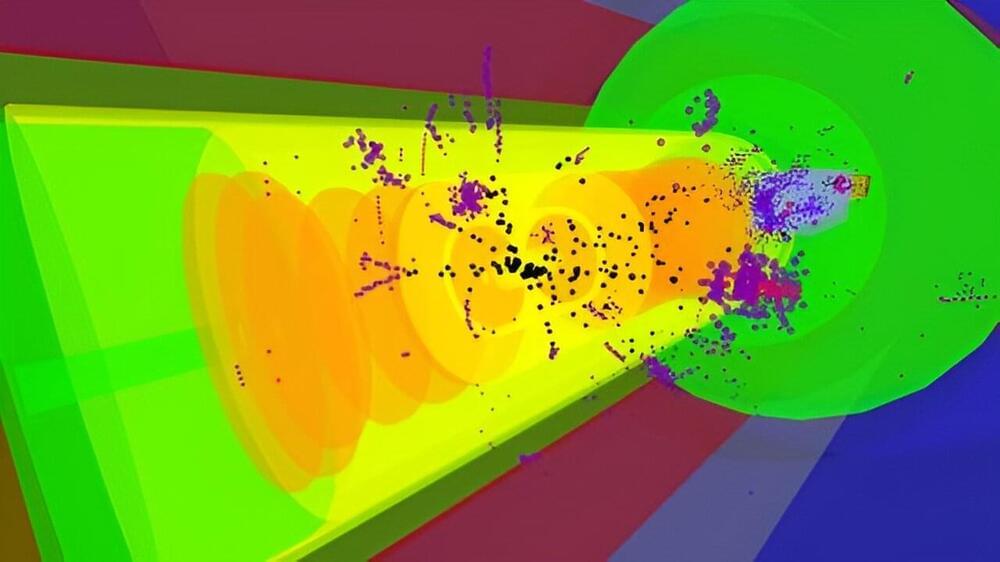
Sean Preins, a doctoral student in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of California, Riverside, has created a VR application called VIRTUE, for “Virtual Interactive Reality Toolkit for Understanding the EIC,” that is a game changer in how particle and nuclear physics data can be seen.
Made publicly available on Christmas Day, VIRTUE can be used to visualize experiments and simulated data from the upcoming Electron-Ion Collider, or EIC, a planned major new nuclear physics research facility at Brookhaven National Lab in Upton, New York. EIC will explore mysteries of the “strong force” that binds the atomic nucleus together. Electrons and ions, sped up to almost the speed of light, will collide with one another in the EIC.

The prevailing scientific paradigm is that matter is primary and everything, including consciousness can be derived from the laws governing matter. Although the scientific explanation of consciousness on these lines has not been realized, in this view it is only a matter of time before consciousness will be explained through neurobiological activity in the brain, and nothing else. There is an alternative view that holds that it is fundamentally impossible to explain how subjectivity can arise solely out of material processes-“the hard problem of consciousness”-and instead consciousness should be regarded in itself as a primary force in nature. This view attempts to derive, for example, the laws of physics from models of consciousness, instead of the other way around. While as scientists we can understand and have an intuition for the first paradigm, it is very difficult to understand what “consciousness is primary” might mean since it has no intuitive scientific grounding. Here we show that worlds experienced through virtual reality (VR) are such that consciousness is a first order phenomenon. We discuss the Interface Theory of Perception which claims that in physical reality perceptions are not veridical and that we do not see the “truth” but that perception is based on evolutionary payoffs. We show that this theory may provide an accurate description of perception and consciousness within VR, and we put forward an experimental study that could throw light on this. We conclude that VR does offer an experimental frame that provides intuition with respect to the idea that “consciousness is first” and what this might mean regarding the perceived world. However, we do not draw any conclusions about the veracity of this notion with respect to physical reality or question the emergence of consciousness from brain function.
Keywords: consciousness; interface theory of perception; perception; presence; real vs. virtual; virtual reality.
Copyright © 2022 Slater and Sanchez-Vives.

In a new study published in Scientific Reports, researchers have uncovered a phenomenon known as the “phantom touch illusion,” where individuals experience tactile sensations without actual physical contact in a virtual reality (VR) setting. This intriguing discovery raises questions about how the brain processes sensory information.
Previous research has shown that our nervous system can differentiate between self-generated touch and touch from external sources, a process often described as tactile gating. This ability helps us understand our interactions with the world around us.
When you perform an action that results in self-touch, your brain anticipates this contact. It knows that the sensation is a result of your own movement. Because of this anticipation, the brain ‘turns down the volume’ on the sensory response. Essentially, it partially “cancels” or gates out the sensation because it’s expected and self-generated. This is why you can’t effectively tickle yourself – your brain knows the touch is coming and reduces the response.
In the exercise, an engineer equipped with a set of virtual reality (VR) goggles is orchestrating the robot’s actions.
Advanced proposition.
Nadia, a cutting-edge humanoid robot, is engineered with a focus on achieving a remarkable power-to-weight ratio and extensive range of motion. This is made possible by leveraging innovative mechanisms and advanced composite materials.
The robot draws its namesake from the renowned gymnast Nadia Comăneci, reflecting the ambitious aim of replicating human range of motion. Funding for Nadia’s development is derived from various sources, encompassing support from the Office of Naval Research (ONR), Army Research Laboratory (ARL), NASA Johnson Space Center, and TARDEC. This diverse funding base underscores the broad interest and recognition of Nadia’s potential applications across military, space exploration, and technological research domains, according to IHMC.
Go to https://buyraycon.com/isaacarthur to get 20 to 50% off sitewide! Brought to you by Raycon.
In the grand theater of the cosmos, amidst a myriad of distant suns and ancient galaxies, the Fermi Paradox presents a haunting silence, where a cacophony of alien conversations should exist. Where is Everyone? Or are we alone?
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-arthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Credits:
The Fermi Paradox Compendium of Solutions & Terms.
Episode 420; November 9, 2023
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Editors: Donagh Broderick.
Graphics by:
Darth Biomech.
Jeremy Jozwik.
Katie Byrne.
Ken York YD Visual.
Legiontech Studios.
Sergio Botero.
Tactical Blob.
Udo Schroeter.
Music Courtesy of:
Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Markus Junnikkala, “Memory of Earth“
Stellardrone, “Red Giant”, “Ultra Deep Field“
Sergey Cheremisinov, “Labyrinth”, “Forgotten Stars“
Miguel Johnson, “The Explorers”, “Strange New World“
Aerium, “Fifth star of Aldebaran”, “Windmill Forests”, “Deiljocht“
Lombus, “Cosmic Soup“
Taras Harkavyi, “Alpha and…”
0:00:00 Intro.
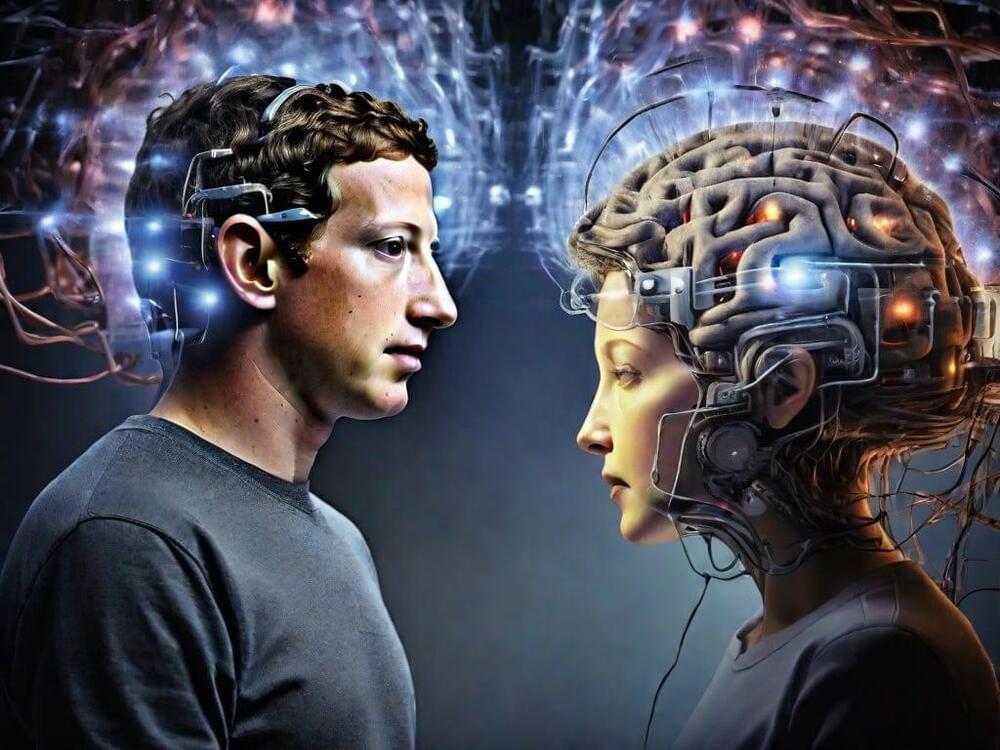

Meta, the parent company of Facebook, has made a groundbreaking development in brain-computer interface technology. They have unveiled an AI system that can decode visual representations and even “hear” what someone is hearing by studying their brainwaves. These advancements in brain-machine interface technology have the potential to transform our relationship with artificial intelligence and its potential applications in healthcare, communication, and virtual reality.
The University of Texas at Austin has developed a new technology that can translate brain activity into written text without surgical implants. This breakthrough uses functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) scan data to reconstruct speech. An AI-based decoder then creates text based on the patterns of neuronal activity that correspond to the intended meaning. This new technology could help people who have lost the ability to speak due to conditions such as stroke or motor neuron disease.
Despite the fMRI having a time lag, which makes tracking brain activity in real-time challenging, the decoder was still able to achieve impressive accuracy. The University of Texas researchers faced challenges in dealing with the inherent “noisiness” of brain signals picked up by sensors, but by employing advanced technology and machine learning, they successfully aligned representations of speech and brain activity. The decoder works at the level of ideas and semantics, providing the gist of thoughts rather than an exact word-for-word translation. This study marks a significant advance in non-invasive brain decoding, showcasing the potential for future applications in neuroscience and communication.
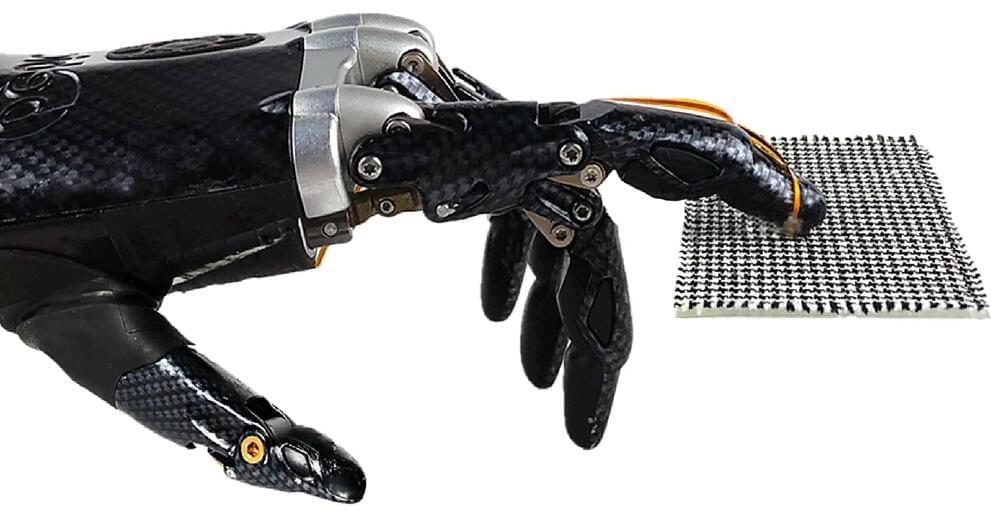

An artificial sensory system that is able to recognize fine textures—such as twill, corduroy and wool—with a high resolution, similar to a human finger, is reported in a Nature Communications paper. The findings may help improve the subtle tactile sensation abilities of robots and human limb prosthetics and could be applied to virtual reality in the future, the authors suggest.
Humans can gently slide a finger on the surface of an object and identify it by capturing both static pressure and high-frequency vibrations. Previous approaches to create artificial tactile sensors for sensing physical stimuli, such as pressure, have been limited in their ability to identify real-world objects upon touch, or they rely on multiple sensors. Creating a real-time artificial sensory system with high spatiotemporal resolution and sensitivity has been challenging.
Chuan Fei Guo and colleagues present a flexible slip sensor that mimics the features of a human fingerprint to enable the system to recognize small features on surface textures when touching or sliding the sensor across the surface. The authors integrated the sensor onto a prosthetic human hand and added machine learning to the system.

Throughout history, sonar’s distinctive “ping” has been used to map oceans, spot enemy submarines and find sunken ships. Today, a variation of that technology – in miniature form, developed by Cornell researchers – is proving a game-changer in wearable body-sensing technology.
PoseSonic is the latest sonar-equipped wearable from Cornell’s Smart Computer Interfaces for Future Interactions (SciFi) lab. It consists of off-the-shelf eyeglasses outfitted with micro sonar that can track the wearer’s upper body movements in 3D through a combination of inaudible soundwaves and artificial intelligence (AI).
With further development, PoseSonic could enhance augmented reality and virtual reality, and track detailed physical and behavioral data for personal health, the researchers said.