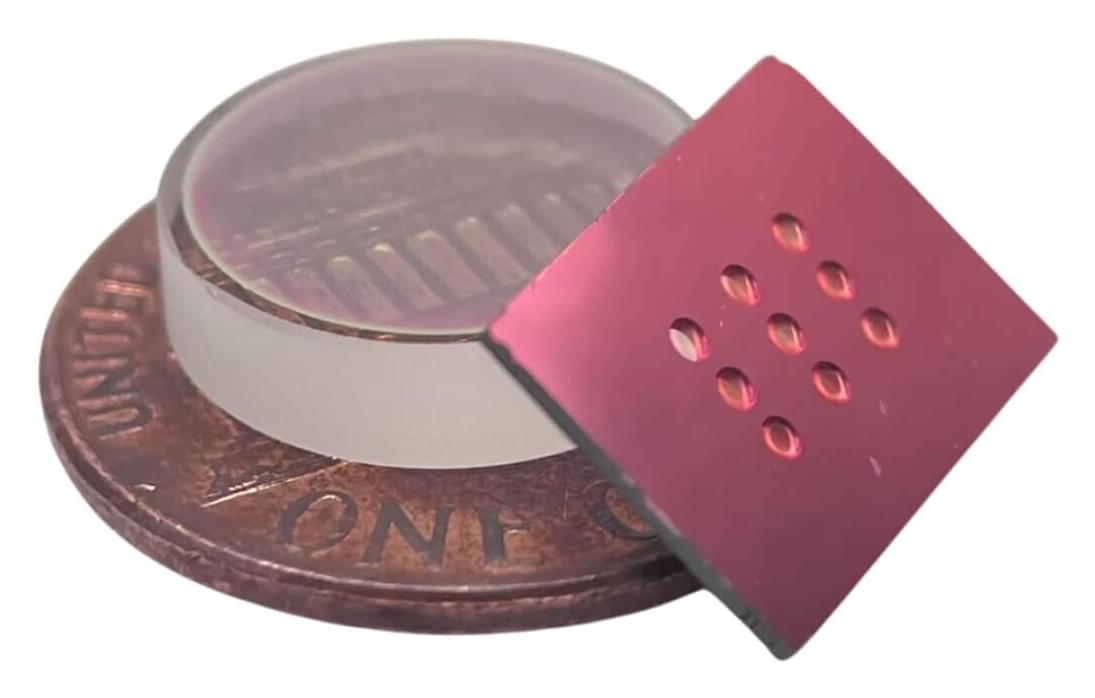
Researchers in the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Faculty of Arts and Sciences have devised a new way to make some of the smallest, smoothest mirrors ever created for controlling single particles of light, known as photons. These mirrors could play key roles in future quantum computers, quantum networks, integrated lasers, environmental sensing equipment, and more.
A team from the labs of Marko Lončar, the Tiantsai Lin Professor of Electrical Engineering at SEAS; Mikhail Lukin, the Joshua and Beth Friedman University Professor in the Department of Physics; and Kiyoul Yang, assistant professor of electrical engineering at SEAS; have described their new method for making high-performance, curved optical mirrors in a study published in Optica.
Using two such mirrors to trap light between them, the team demonstrated state-of-the-art optical resonators that can control light at near-infrared wavelengths, which is important for manipulating single atoms in quantum computing applications.