We describe electricity as a flow, but that’s not what happens in a typical wire. Physicists have begun to induce electrons to act like fluids, an effort that could illuminate new ways of thinking about quantum systems.



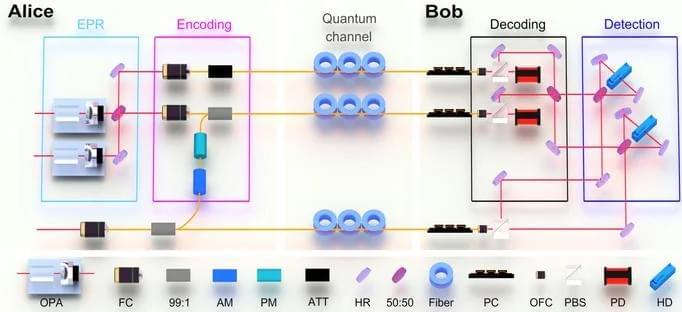
A Chinese research team has reported a pair of advances that could remove two of the biggest technical barriers to building large-scale quantum communication networks, including the generation of ultra-secure encryption keys over 11 kilometers of optical fiber and the validation of the approach at distances up to 100 kilometers, according to China Daily, a state-associated news service.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China said they have demonstrated, for the first time, a scalable core component of a quantum repeater — a long-sought technology needed to extend quantum communication across long distances — while also setting new records for ultra-secure quantum key distribution over fiber networks.
The findings were published in Nature and Science, underscoring their significance within the international research community. Noted Chinese physicist Pan Jianwei led the work.

Once considered an oddity of quantum physics, time crystals could be a good building block for accurate clocks and sensors, according to new calculations.

A long-standing law of thermodynamics turns out to have a loophole at the smallest scales. Researchers have shown that quantum engines made of correlated particles can exceed the traditional efficiency limit set by Carnot nearly 200 years ago. By tapping into quantum correlations, these engines can produce extra work beyond what heat alone allows. This could reshape how scientists design future nanoscale machines.
Two physicists at the University of Stuttgart have demonstrated that the Carnot principle, a foundational rule of thermodynamics, does not fully apply at the atomic scale when particles are physically linked (so-called correlated objects). Their findings suggest that this long-standing limit on efficiency breaks down for tiny systems governed by quantum effects. The work could help accelerate progress toward extremely small and energy-efficient quantum motors. The team published its mathematical proof in the journal Science Advances.
Traditional heat engines, such as internal combustion engines and steam turbines, operate by turning thermal energy into mechanical motion, or simply converting heat into movement. Over the past several years, advances in quantum mechanics have allowed researchers to shrink heat engines to microscopic dimensions.

A team of US researchers has unveiled a device that can conduct electricity along its fractionally charged edges without losing energy to heat. Described in Nature Physics, the work, led by Xiaodong Xu at the University of Washington, marks the first demonstration of a “dissipationless fractional Chern insulator,” a long-sought state of matter with promising implications for future quantum technologies.
The quantum Hall effect emerges when electrons are confined to a two-dimensional material, cooled to extremely low temperatures, and exposed to strong magnetic fields. Much like the classical Hall effect, it describes how a voltage develops across a material perpendicular to the direction of current flow. In this case, however, that voltage increases in discrete, or quantized steps.
Under even more extreme conditions, an exotic variant appears named the “fractional quantum Hall” (FQH) effect. Here, electrons no longer behave as independent particles but move collectively, giving rise to voltage steps that correspond to fractions of an electron’s charge. This unusual collective behavior unlocks a whole host of exotic properties, and has made such states particularly appealing for emerging quantum technologies.
The unveiling by IBM of two new quantum supercomputers and Denmark’s plans to develop “the world’s most powerful commercial quantum computer” mark just two of the latest developments in quantum technology’s increasingly rapid transition from experimental breakthroughs to practical applications.
There is growing promise of quantum technology’s ability to solve problems that today’s systems struggle to overcome, or cannot even begin to tackle, with implications for industry, national security and everyday life.
So, what exactly is quantum technology? At its core, it harnesses the counterintuitive laws of quantum mechanics, the branch of physics describing how matter and energy behave at the smallest scales. In this strange realm, particles can exist in several states simultaneously (superposition) and can remain connected across vast distances (entanglement).

The kind of light you use can reveal very different things about a material. Visible light mainly shows what is happening at the surface. X-rays can probe structures inside. Infrared light highlights the heat a material gives off.
Researchers at MIT have now turned to terahertz light to uncover quantum vibrations in a superconducting material, signals that scientists have not been able to observe directly until now.

Quantum computers are often described as a glimpse of a faster, more powerful future. The catch is that today’s devices are fragile in a way ordinary computers are not. Their biggest headache is decoherence, the gradual loss of the delicate quantum behavior that makes them useful in the first place. When decoherence sets in, it can trigger two common kinds of mistakes: bit flips and phase flips.
A bit flip is the more intuitive problem. A qubit that should represent ‘0’ can unexpectedly behave like ‘1’. A phase flip is stranger but just as damaging. Even if a qubit stays in a superposition, the relationship between its components can suddenly switch, turning a positive phase into a negative one and scrambling the computation.