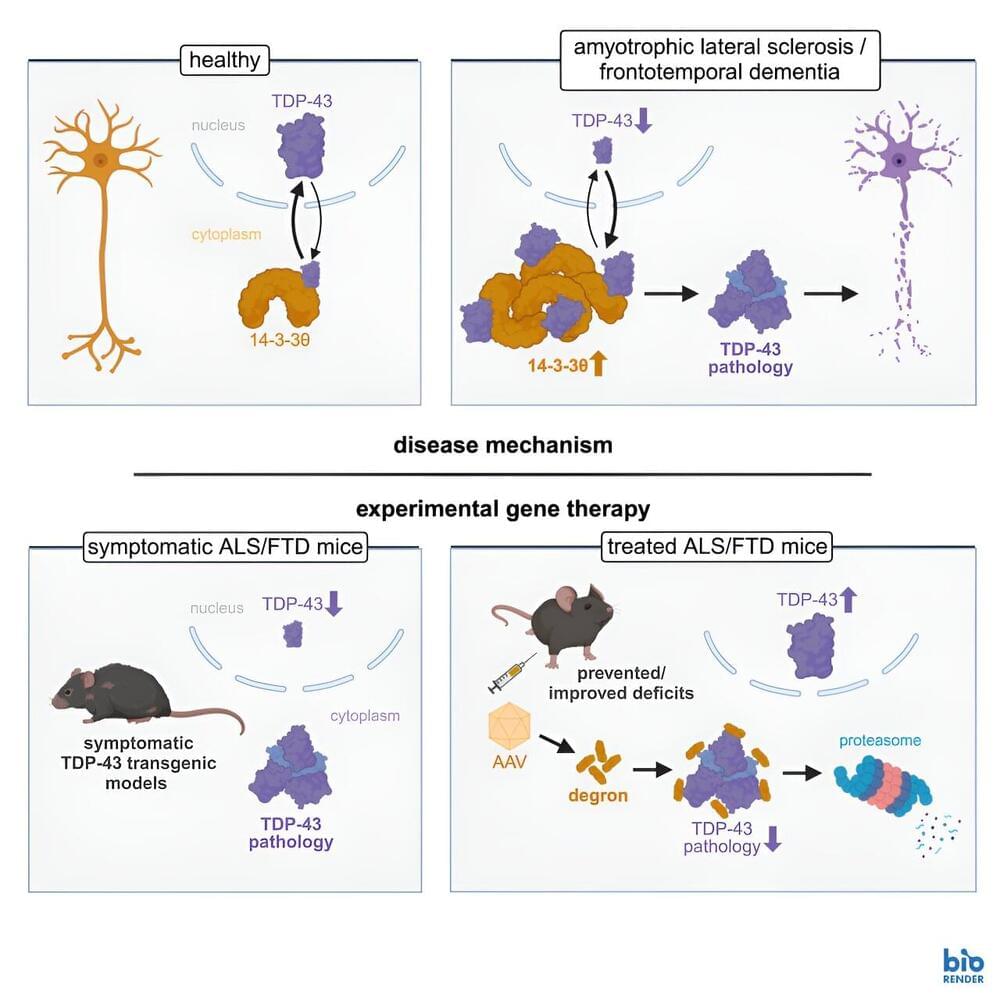
Neurologic immune-related adverse events (nirAEs) following immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for cancer are frequent and varied; a recent study identified risk factors for death after nirAEs.
Recent cohort studies have demonstrated that neurologic immune-related adverse events (nirAEs) following immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy for cancer are frequent, varied, and associated with higher overall survival (NEJM JW Neurol Sep 29 2023 and Neurology 2023; 101:e2472). Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive patients referred to a tertiary center during a 5-year period to characterize the clinical features of nirAEs and identify predictors of ICI response and survival.
The researchers identified 64 patients with confirmed nirAEs, 81% involving the central nervous system (CNS). The vast majority of CNS nirAE patients had encephalopathy, of which 73% were neither seropositive for well-characterized neural autoantibodies, nor had a distinctive encephalitis syndrome, nor had evidence of CNS inflammatory changes. The most common peripheral nervous system (PNS) syndrome was myasthenia and myositis (with or without myocarditis) overlap syndrome. Only 17% of PNS nirAE patients were seropositive. Steroids were given to 91% of nirAE patients after a median of 90 days of symptoms, and 48% received additional immunotherapy. At 1-month follow-up, 72% of nirAE patients showed improvement, 9% had worsened, and 17% had died. Among the 53 patients who survived the first month, median follow-up was 6 months; during follow-up, 30% died, most commonly of cancer progression or cancer-related complications. Death was associated with lung cancer (hazard ratio, 2.