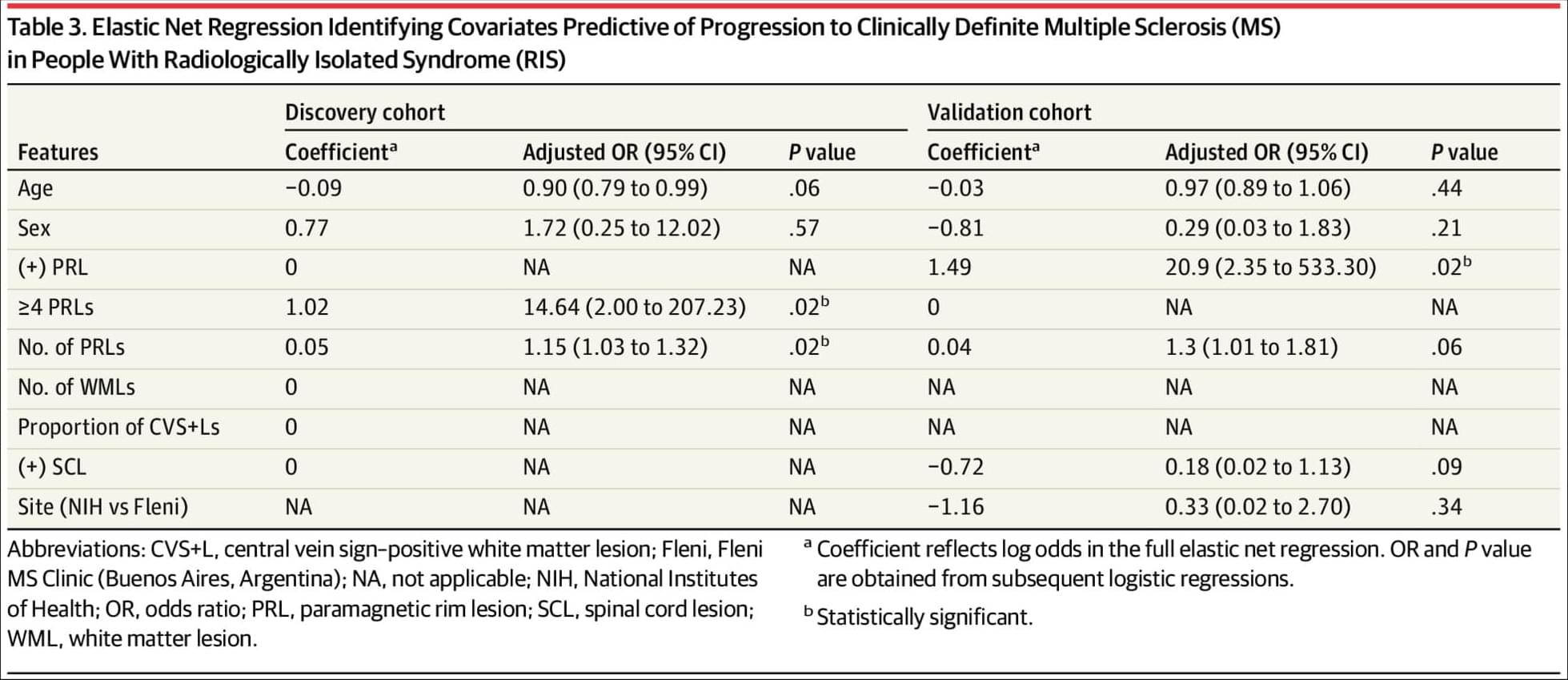
Unraveling the mysteries of how biological organisms function begins with understanding the molecular interactions within and across large cell populations. A revolutionary new tool, developed at the University of Michigan, acts as a sort of tape recorder produced and maintained by the cell itself, enabling scientists to rewind back in time and view interactions on a large scale and over long periods of time.
Developed in the lab of Changyang Linghu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Cell and Developmental Biology and Biomedical Engineering and Principal Investigator in Michigan Neuroscience Institute, the so-called CytoTape is a flexible, thread-like intracellular protein fiber, designed with the help of AI to act as a tape recorder for large-scale measurement of cellular activities.
The research appears in the journal Nature.