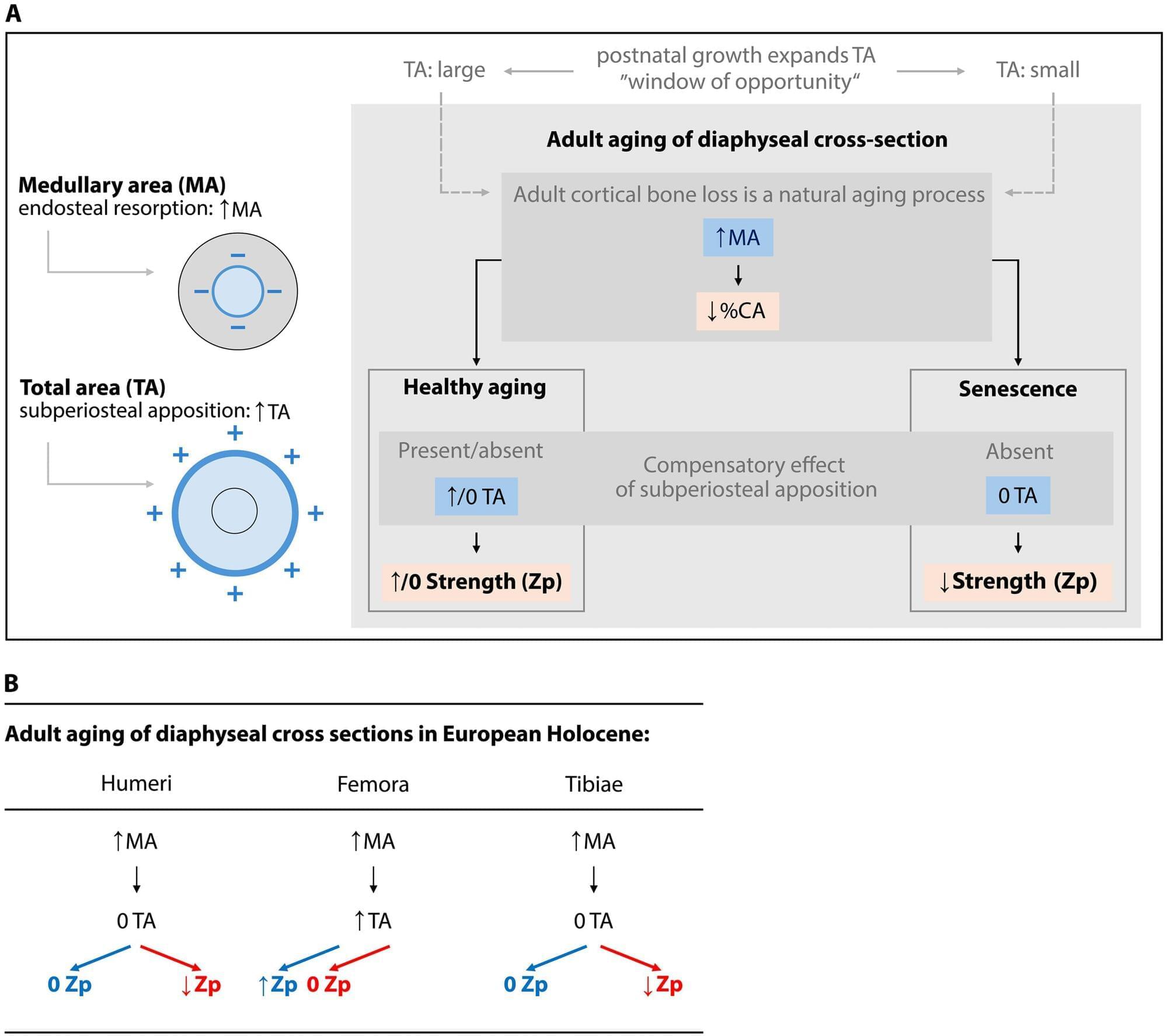
Research led by Vladimír Sládek sheds new light on how bones age, questioning long-standing assumptions that sedentary lifestyles are the primary cause of weakening bone strength in modern humans.
The study analyzed 1,881 adult humeri, femora, and tibiae from European Holocene populations to examine how bone strength and structure change with age. Surprisingly, researchers found that patterns of diaphyseal (shaft) aging were consistent across both Early and Late Holocene adults—despite significant differences in physical activity levels between the two groups. The research is published in the journal Science Advances.
“Our findings suggest that lifestyle differences may not fully explain age-related declines in bone strength,” said Dr. Sládek. “Instead, the biology of bone growth and aging itself plays a critical role.”