New research suggests that creative hobbies and skills help keep brain networks healthier as we age.

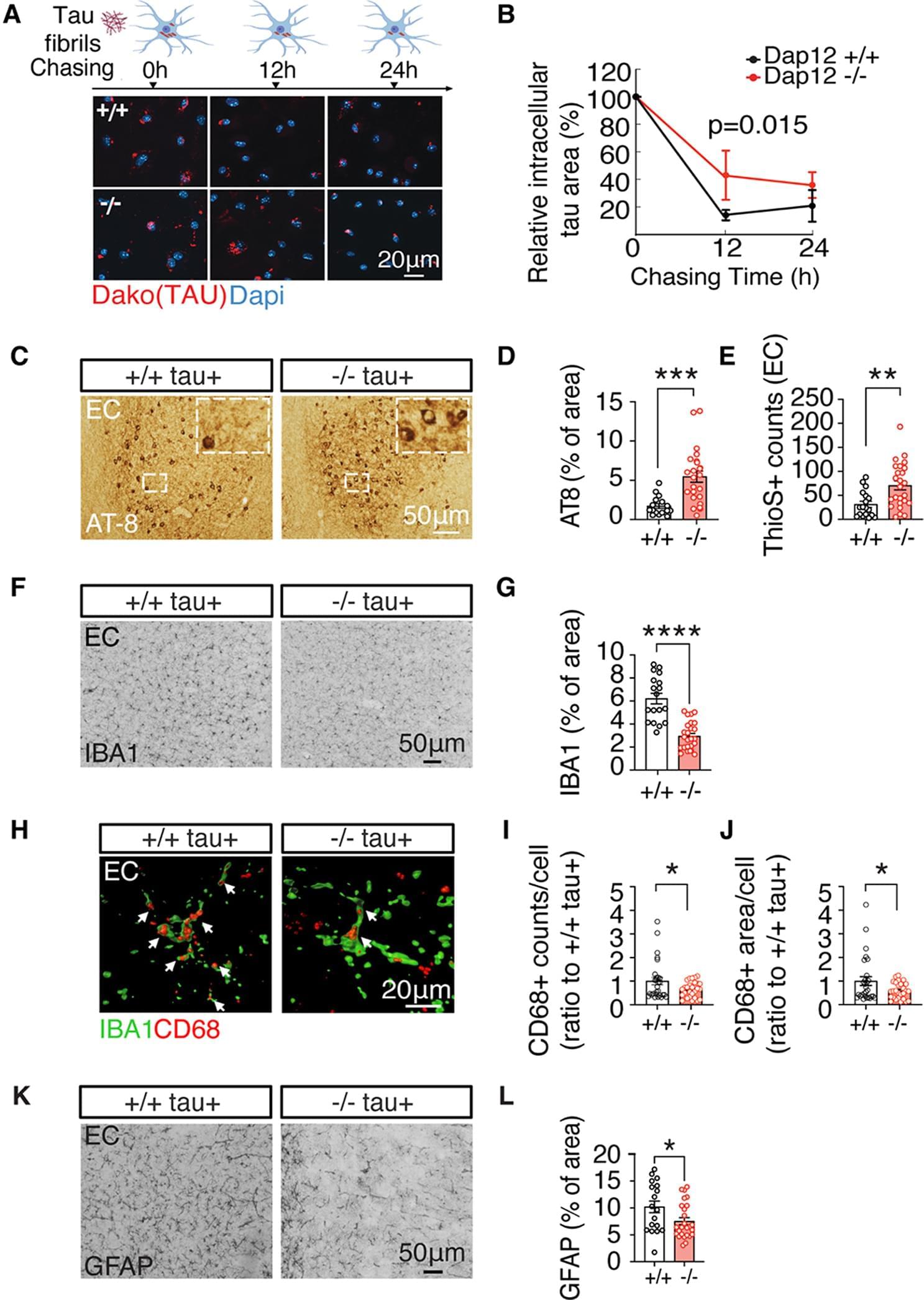
How DAP12 deletion enhances brain resilience in female tauopathy mice.
Microglia selectively expresses DAP12 (DNAX-activation protein 12), which, plays a crucial role in microglial immune responses.
Previously, it was show that tauopathy mice lacking DAP12 exhibit higher tau pathology but are protected from tau pathology-induced cognitive deficits but the mechanism remains elusive.
The authors in this study show that tau processing in primary microglia is reduced by Dap12 deletion, while, tau pathology increased in female tauopathy mice, with minimal effects on males. However, brain inflammation, synapse loss, and demyelination are reduced by Dap12 deletion indicating enhanced resilience to tau toxicity.
The authors also show that elevated SLIT2 levels and demyelination in tauopathy and is reversed by Dap12 deletion. The author s also found correlation of SLIT2 expression and tau pathology in AD brain tissue. https://sciencemission.com/DAP12-deletion-reduces-neuronal-SLIT2
Background Pathogenic tau accumulation drives neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Enhancing the aging brain’s resilience to tau pathology would lead to novel therapeutic strategies. DAP12 (DNAX-activation protein 12), highly and selectively expressed by microglia, plays a crucial role in microglial immune responses. Previous studies have shown that tauopathy mice lacking DAP12 exhibit higher tau pathology but are protected from tau pathology-induced cognitive deficits. However, the exact mechanism behind this resilience remains elusive. Methods We investigated the effects of DAP12 deletion on tau pathology, as well as tau-induced brain inflammation and neurodegeneration, in homozygous human Tau P301S transgenic mice. In addition, we conducted single-nucleus RNA sequencing of hippocampal tissues to examine cell type-specific transcriptomic changes at the single-cell level.
The journey “Up from Eden” could involve humanity’s growth in understanding, comprehending and appreciating with greater love true and wisdom, shaping a future worth living for.
AI is accelerating faster than human biology. What happens to humanity when the future moves faster than we can evolve?
Oxford philosopher Nick Bostrom, author of Superintelligence, says we are entering the biggest turning point in human history — one that could redefine what it means to be human.
In this talk, Bostrom explains why AI might be the last invention humans ever make, and how the next decade could bring changes that once took thousands of years in health, longevity, and human evolution. He warns that digital minds may one day outnumber biological humans — and that this shift could change everything about how we live and who we become.
Superintelligence will force us to choose what humanity becomes next.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/



Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qp0rCU49lMs.
Thank you for listening ❤ Check out our sponsors: https://lexfridman.com/sponsors/cv9485-sb.
See below for guest bio, links, and to give feedback, submit questions, contact Lex, etc.
*GUEST BIO:*
Michael Levin is a biologist at Tufts University working on novel ways to understand and control complex pattern formation in biological systems.
*CONTACT LEX:*
*Feedback* — give feedback to Lex: https://lexfridman.com/survey.
*AMA* — submit questions, videos or call-in: https://lexfridman.com/ama.
*Hiring* — join our team: https://lexfridman.com/hiring.
*Other* — other ways to get in touch: https://lexfridman.com/contact.
*EPISODE LINKS:*
Michael Levin’s X: https://twitter.com/drmichaellevin.
Michael Levin’s Website: https://drmichaellevin.org.
Michael Levin’s Papers: https://drmichaellevin.org/publications/
- Biological Robots: https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00880
- Classical Sorting Algorithms: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.05375
- Aging as a Morphostasis Defect: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38636560/
- TAME: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.10346
- Synthetic Living Machines: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abf1571
*SPONSORS:*
To support this podcast, check out our sponsors & get discounts:
*Shopify:* Sell stuff online.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/shopify-cv9485-sb.
*CodeRabbit:* AI-powered code reviews.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/coderabbit-cv9485-sb.
*LMNT:* Zero-sugar electrolyte drink mix.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/lmnt-cv9485-sb.
*UPLIFT Desk:* Standing desks and office ergonomics.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/uplift_desk-cv9485-sb.
*Miro:* Online collaborative whiteboard platform.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/miro-cv9485-sb.
*MasterClass:* Online classes from world-class experts.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/masterclass-cv9485-sb.
*PODCAST LINKS:*


The study unexpectedly identified a significant role for a group of enzymes known as agmatinases, which convert the metabolite agmatine into polyamines. These enzymes appear to participate in a previously unrecognized “metabolic feedback loop” that helps maintain balanced TOR activity. When agmatinase activity was disrupted, yeast cells grew more quickly but showed signs of premature aging, revealing a trade-off between rapid growth and long-term cell survival.
The team also found that adding agmatine or putrescine (a related compound) supported longevity in yeast and improved growth under specific conditions.
“By showing that agmatinases are essential for healthy aging, we’ve uncovered a new layer of metabolic control over TOR — one that may be conserved in humans,” said Dr. Rallis. “Because agmatine is produced by diet and gut microbes, this work may help explain how nutrition and the microbiome influence aging.”