Discoveries in the Seidman Lab gave way to a novel treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy


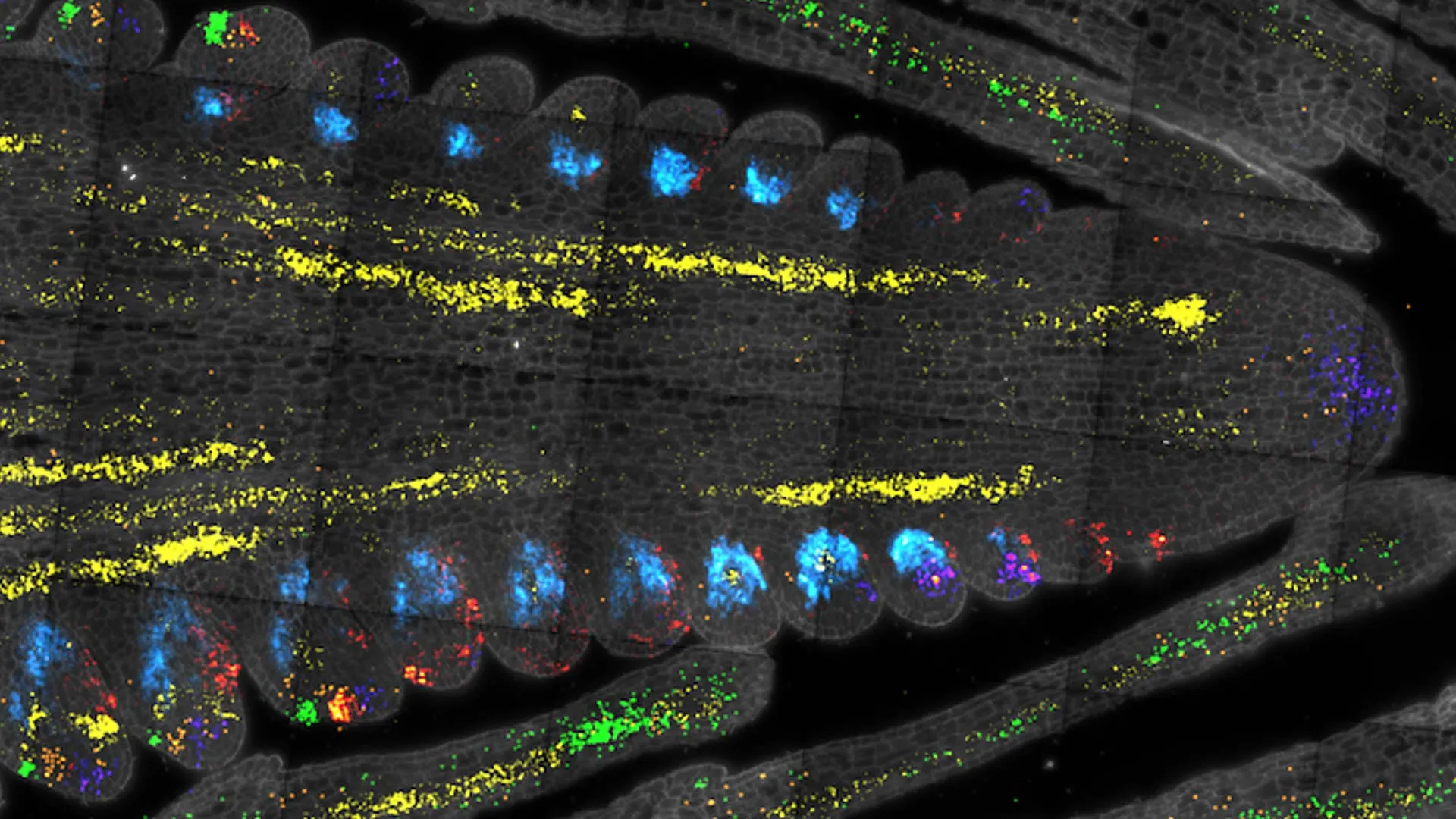
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have cracked open the secrets of plant stem cells, mapping key genetic regulators in maize and Arabidopsis. By using single-cell RNA sequencing, they created a gene expression atlas that identifies rare stem cell regulators, links them to crop size and productivity, and offers a new roadmap for breeding resilient, high-yield plants.
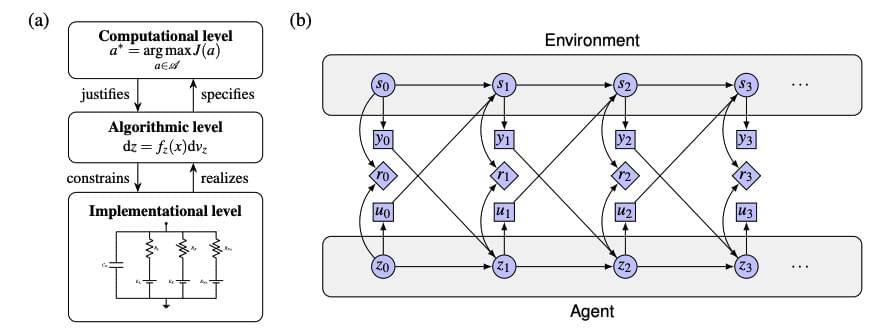
The pursuit of artificial intelligence increasingly focuses on replicating the efficiency and adaptability of the human brain, and a new approach, termed neuromorphic intelligence, offers a promising path forward. Marcel van Gerven from Radboud University and colleagues demonstrate how brain-inspired systems can achieve significantly greater energy efficiency than conventional digital computers. This research establishes a unifying theoretical framework, rooted in dynamical systems theory, to integrate insights from diverse fields including neuroscience, physics, and artificial intelligence. By harnessing noise as a learning resource and employing differential genetic programming, the team advances the development of truly adaptive and sustainable artificial intelligence, paving the way for emergent intelligence arising directly from physical substrates.
Researchers demonstrate that applying dynamical systems theory, a mathematical framework describing change over time, to artificial intelligence enables the creation of more sustainable and adaptable systems by harnessing noise as a learning tool and allowing intelligence to emerge from the physical properties of the system itself.
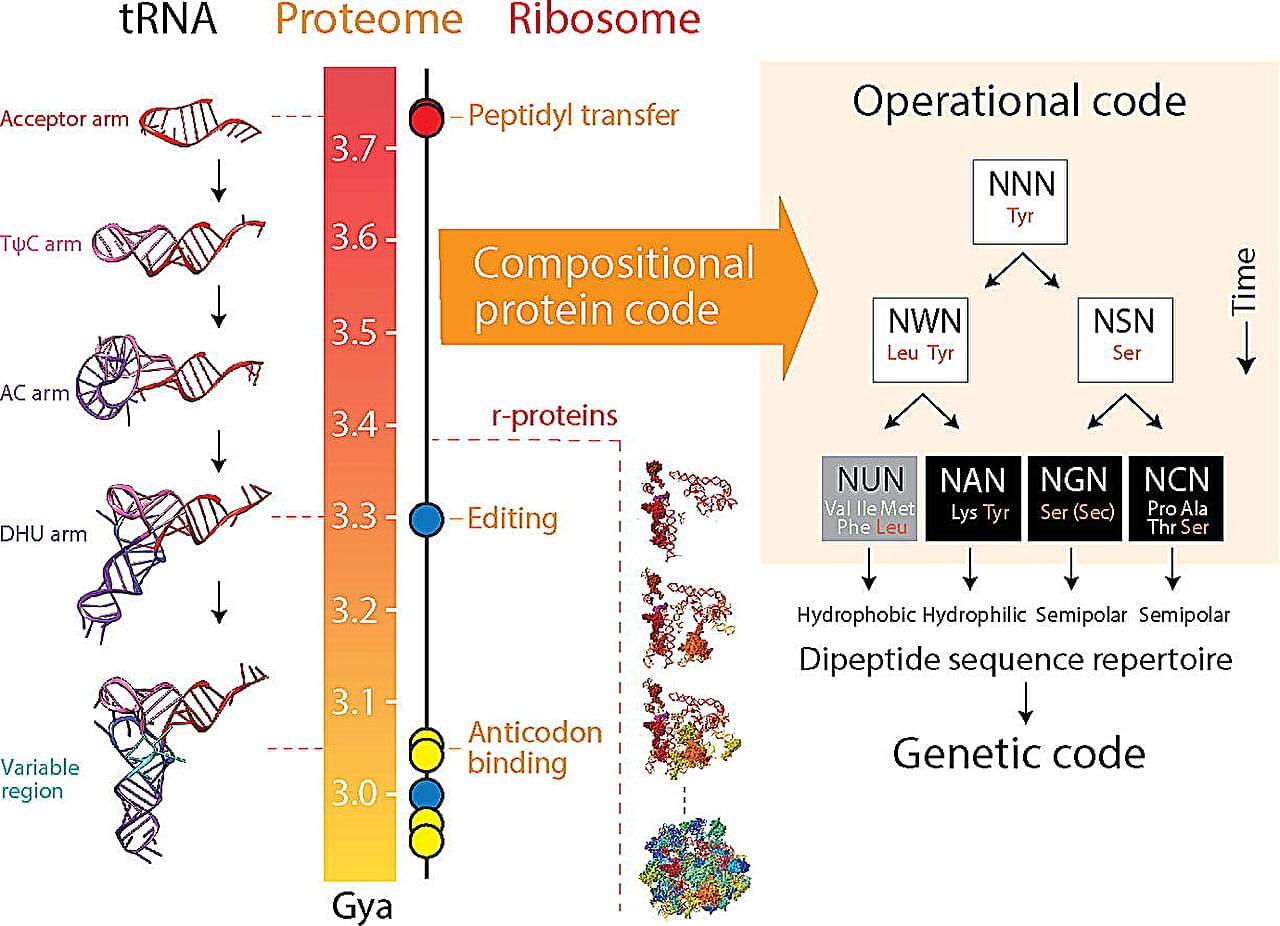
Genes are the building blocks of life, and the genetic code provides the instructions for the complex processes that make organisms function. But how and why did it come to be the way it is?
A recent study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign sheds new light on the origin and evolution of the genetic code, providing valuable insights for genetic engineering and bioinformatics. The study is published in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
“We find the origin of the genetic code mysteriously linked to the dipeptide composition of a proteome, the collective of proteins in an organism,” said corresponding author Gustavo Caetano-Anollés, professor in the Department of Crop Sciences, the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology, and Biomedical and Translation Sciences of Carle Illinois College of Medicine at U. of I.

Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence tool to help scientists better plan gene-editing experiments. The technology, CRISPR-GPT, acts as a gene-editing “copilot” supported by AI to help researchers—even those unfamiliar with gene editing—generate designs, analyze data and troubleshoot design flaws.
The model builds on a tool called CRISPR, a powerful gene-editing technology used to edit genomes and develop therapies for genetic diseases. But training on the tool to design an experiment is complicated and time-consuming—even for seasoned scientists. CRISPR-GPT speeds that process along, automating much of the experimental design and refinement. The goal, said Le Cong, Ph.D., assistant professor of pathology and genetics, who led the technology’s development, is to help scientists produce lifesaving drugs faster.
The paper is published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.

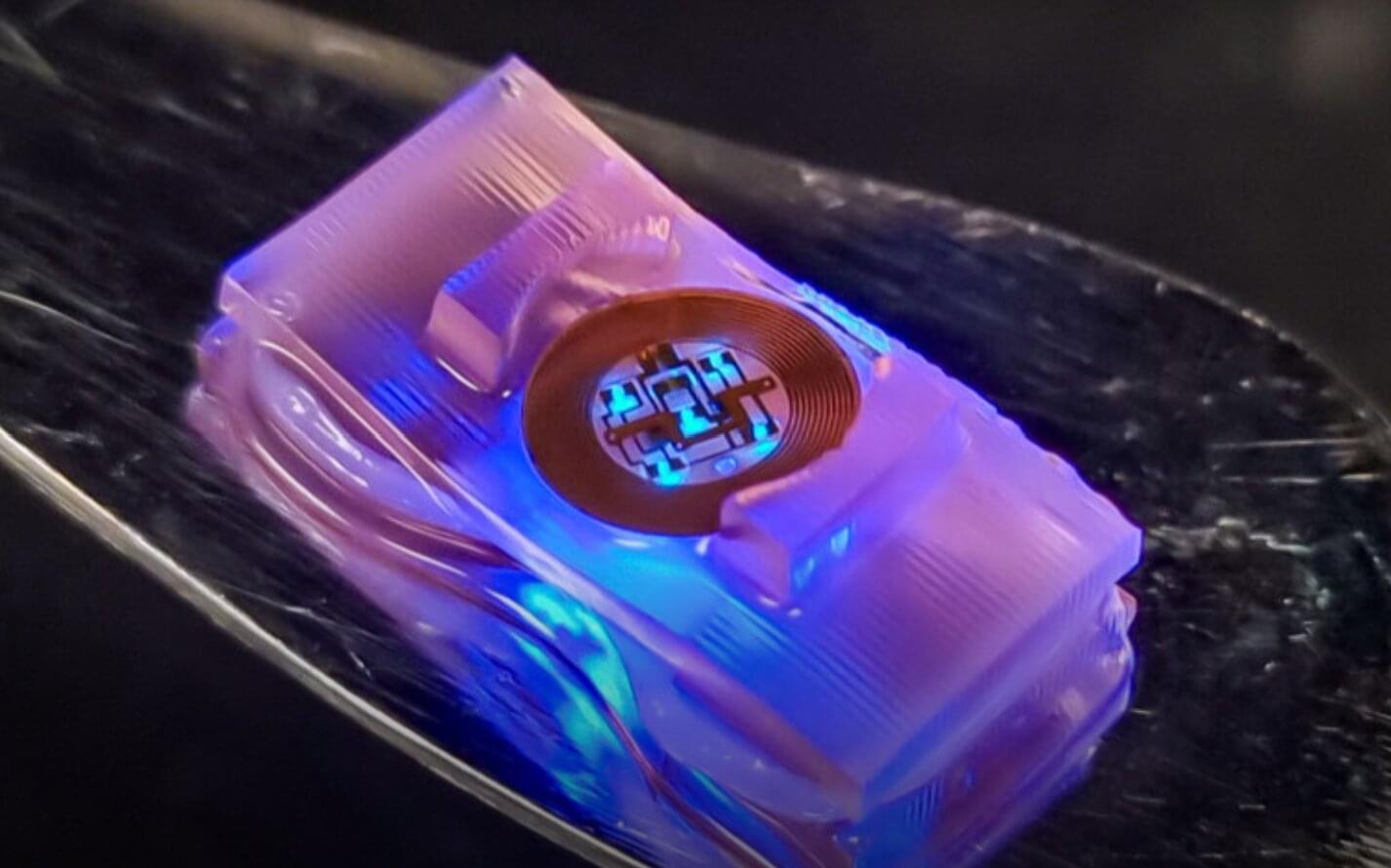
The body movements performed by humans and other animals are known to be supported by several intricate biological and neural mechanisms. While roboticists have been trying to develop systems that emulate these mechanisms for decades, the processes driving these systems’ motions remain very different.
Researchers at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Northwestern University and other institutes recently developed new biohybrid robots that combine living cells from mice with 3D printed hydrogel structures with wireless optoelectronics.
These robots, presented in a paper published in Science Robotics, have neuromuscular junctions where the neurons can be controlled using optogenetic techniques, emulating the neural mechanisms that support human movements.

Researchers at the University of Maine are theorizing that human beings may be in the midst of a major evolutionary shift—driven not by genes, but by culture.
In a paper published in BioScience, Timothy M. Waring, an associate professor of economics and sustainability, and Zachary T. Wood, a researcher in ecology and environmental sciences, argue that culture is overtaking genetics as the main force shaping human evolution.
“Human evolution seems to be changing gears,” said Waring. “When we learn useful skills, institutions or technologies from each other, we are inheriting adaptive cultural practices. On reviewing the evidence, we find that culture solves problems much more rapidly than genetic evolution. This suggests our species is in the middle of a great evolutionary transition.”
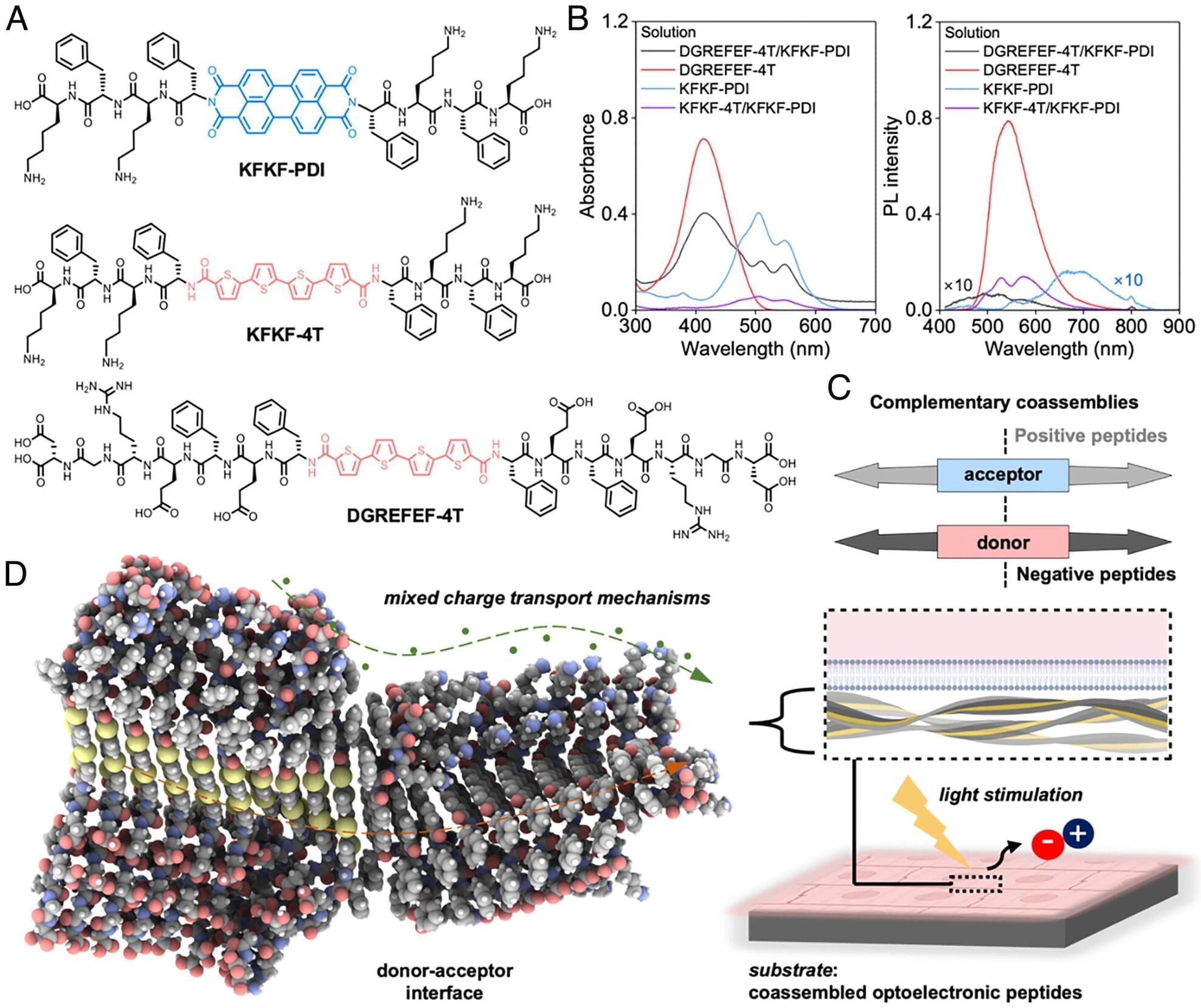
In a new study, University of California, Irvine chemical and biomolecular engineering researchers report the creation of biomolecules that can help grow light-sensitive heart muscle cells in the laboratory. The development enables a biotechnology that could deliver light-triggered signals to the heart, improving its function, without requiring genetic modifications or invasive procedures.
“We show for the first time that light can be converted into cardiac stimulatory cues, with synthetic materials made of biomolecules,” said Herdeline Ann Ardoña, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering. “This can be beneficial for downstream medical applications, such as in cardiac pacemaking technologies, or helping direct therapeutic patient-derived stem cells to better mimic adult heart cell features.”
The findings are reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The paper’s co-first authors are recent Ph.D. graduate Sujeung Lim, and Ze-Fan Yao, previous postdoctoral scholar in the Ardoña Research Group.
