New research shows CRP, ApoB, and immune diversity may predict biological age better than DNA tests. Learn what they mean and how to improve them.

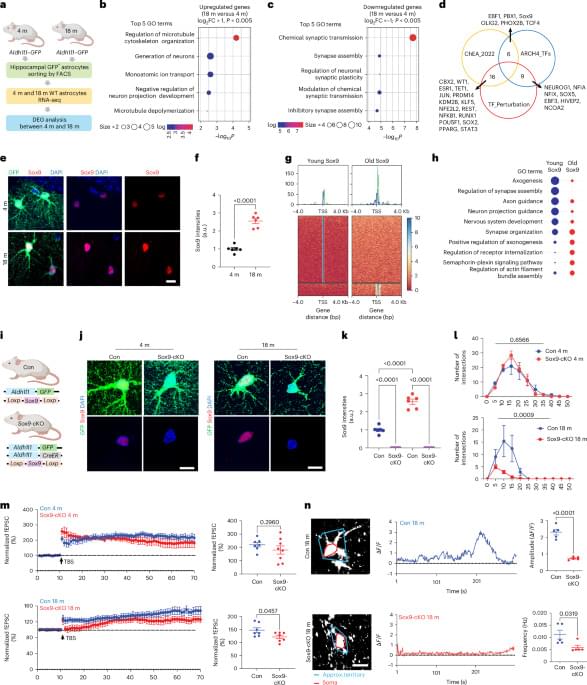
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have discovered a natural mechanism that clears existing amyloid plaques in the brains of mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease and preserves cognitive function. The mechanism involves recruiting brain cells known as astrocytes, star shaped cells in the brain, to remove the toxic amyloid plaques that build up in many Alzheimer’s disease brains. Increasing the production of Sox9, a key protein that regulates astrocyte functions during aging, triggered the astrocytes’ ability to remove amyloid plaques. The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggests a potential astrocyte-based therapeutic approach to ameliorate cognitive decline in neurodegenerative disease.
“Astrocytes perform diverse tasks that are essential for normal brain function, including facilitating brain communications and memory storage. As the brain ages, astrocytes show profound functional alterations; however, the role these alterations play in aging and neurodegeneration is not yet understood,” said first author Dr. Dong-Joo Choi, who was at the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy and the Department of Neurosurgery at Baylor while he was working on this project. Choi currently is an assistant professor at the Center for Neuroimmunology and Glial Biology, Institute of Molecular Medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston.
Astrocytes are associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. We found that the transcription factor Sox9 functions to enhance astrocytic phagocytosis of Aβ plaques via MEGF10, and this clearance of plaques is associated with the preservation of cognitive function in mouse models.
A team of scientists have developed a simple method for automated manufacturing of lung organoids which could revolutionize the development of treatments for lung disease. These organoids, miniature structures containing the cells that real lungs do, could be used to test early-stage experimental drugs more effectively, without needing to use animal material.
In the future, patients could even have personalized organoids grown from their own tissue to try out potential treatments in advance.
“The best result for now—quite simply—is that it works,” said Professor Diana Klein of University of Duisburg-Essen, first author of the article in Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.
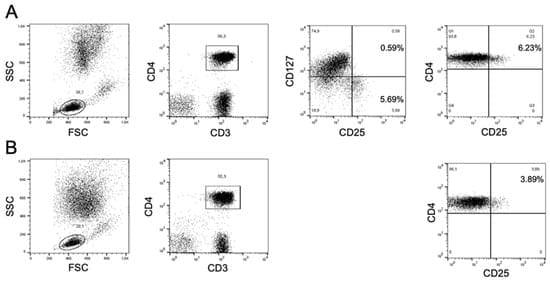
New-generation mRNA and adenovirus vectored vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are endowed with immunogenic, inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Recently, BioNTech developed a noninflammatory tolerogenic mRNA vaccine (MOGm1Ψ) that induces in mice robust expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T (Treg) cells. The Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 is identical to MOGm1Ψ except for the lipid carrier, which differs for containing lipid nanoparticles rather than lipoplex. Here we report that vaccination with BNT162b2 led to an increase in the frequency and absolute count of CD4posCD25highCD127low putative Treg cells; in sharp contrast, vaccination with the adenovirus-vectored ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine led to a significant decrease of CD4posCD25high cells.

Protein homeostasis, or proteostasis, is essential for cellular proteins to function properly. The buildup of abnormal proteins (such as damaged, misfolded, or aggregated proteins) is associated with many diseases, including cancer. Therefore, maintaining proteostasis is critical for cellular health. Currently, genetic methods for modulating proteostasis, such as RNA interference and CRISPR knockout, lack spatial and temporal precision. They are also not suitable for depleting already-synthesized proteins. Similarly, molecular tools like PROTACs and molecular glue face challenges in drug design and discovery. To directly control targeted protein degradation within cells, we introduce an intrabody-based optogenetic toolbox named Flash-Away integrates the light-responsive ubiquitination activity of the RING domain of TRIM21 for protein degradation, coupled with specific intrabodies for precise targeting. Upon exposure to blue light, Flash-Away enables rapid and targeted degradation of selected proteins. This versatility is demonstrated through successful application to diverse protein targets, including actin, MLKL, and ALFA-tag fused proteins. This innovative light-inducible protein degradation system offers a powerful approach to investigate the functions of specific proteins within physiological contexts. Moreover, Flash-Away presents potential opportunities for clinical translational research and precise medical interventions, advancing the prospects of precision medicine.

Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have discovered a natural mechanism that clears existing amyloid plaques in the brains of mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease and preserves cognitive function. The mechanism involves recruiting brain cells known as astrocytes, star shaped cells in the brain, to remove the toxic amyloid plaques that build up in many Alzheimer’s disease brains. Increasing the production of Sox9, a key protein that regulates astrocyte functions during aging, triggered the astrocytes’ ability to remove amyloid plaques. The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggests a potential astrocyte-based therapeutic approach to ameliorate cognitive decline in neurodegenerative disease.
“Astrocytes perform diverse tasks that are essential for normal brain function, including facilitating brain communications and memory storage. As the brain ages, astrocytes show profound functional alterations; however, the role these alterations play in aging and neurodegeneration is not yet understood,” said first author Dr. Dong-Joo Choi, who was at the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy and the Department of Neurosurgery at Baylor while he was working on this project. Choi currently is an assistant professor at the Center for Neuroimmunology and Glial Biology, Institute of Molecular Medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston.
Astrocytic Sox9 overexpression in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models promotes Aβ plaque phagocytosis and preserves cognitive function.
The human body depends on accurate genetic instructions to keep its cells working properly. Cancer begins to form when these instructions become disrupted. As genetic mistakes build up over time, cells can lose their normal limits on growth and start multiplying in an uncontrolled way. Chromosomal abnormalities – numerical and structural defects in chromosomes – are often one of the earliest changes that push healthy cells toward becoming cancerous.
Researchers in the Korbel Group at EMBL Heidelberg have created a new AI-based tool that gives scientists a way to closely examine how these chromosomal abnormalities develop. The insights gained from this approach may eventually clarify some of the earliest steps that lead to cancer.
“Chromosomal abnormalities are a main driver for particularly aggressive cancers, and they’re highly linked to patient death, metastasis, recurrence, chemotherapy resistance, and fast tumor onset,” said Jan Korbel, senior scientist at EMBL and senior author of the new paper, published in the journal Nature. “We wanted to understand what determines the likelihood that cells undergo such chromosomal alterations, and what’s the rate at which such abnormalities arise when a still normal cell divides.”
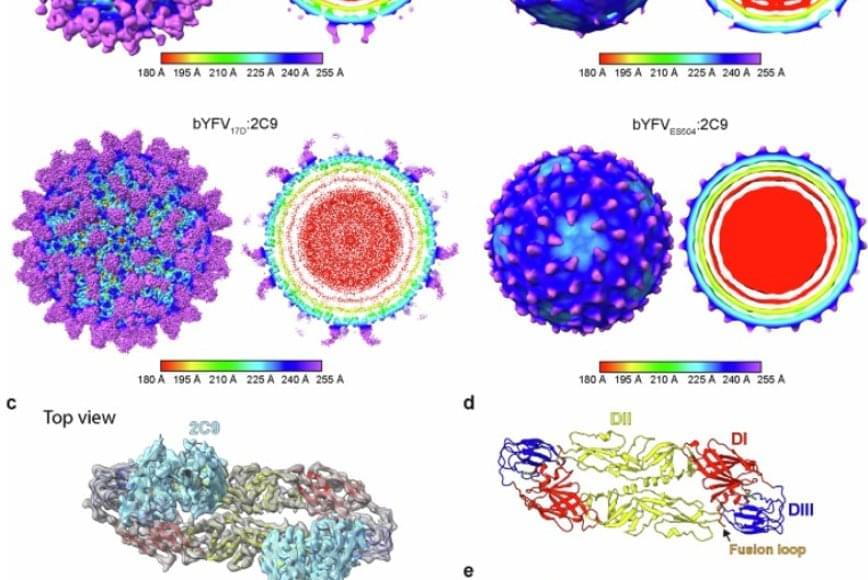
Integrated genomic and transcriptomic profiling of glioblastoma reveals ecDNA-driven heterogeneity and microenvironmental reprogramming.
Tang et al. provide a comprehensive genomic and transcriptomic characterization of extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) in glioblastoma. They reveal that EGFR ecDNA shapes transcriptional subtypes and reprograms the tumor microenvironment by stabilizing metabolically active tumor-associated macrophages. These findings uncover mechanistic links between ecDNA architecture and glioblastoma progression, highlighting potential therapeutic vulnerabilities.
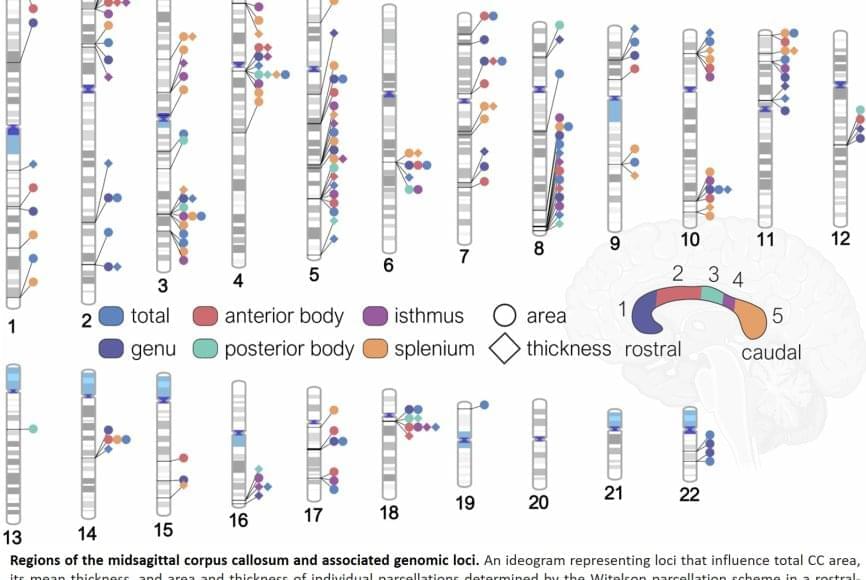
The corpus callosum is critical for nearly everything the brain does, from coordinating the movement of our limbs in sync to integrating sights and sounds, to higher-order thinking and decision-making. Abnormalities in its shape and size have long been linked to disorders such as ADHD, bipolar disorder, and Parkinson’s disease. Until now, the genetic underpinnings of this vital structure remained largely unknown.
In the new study, published in Nature Communications, the team analyzed brain scans and genetic data from over 50,000 people, ranging from childhood to late adulthood, with the help of a new tool the team created that leverages artificial intelligence.
“We developed an AI tool that finds the corpus callosum in different types of brain MRI scans and automatically takes its measurements,” said co-first author of the study. Using this tool, the researchers identified dozens of genetic regions that influence the size and thickness of the corpus callosum and its subregions.
The study revealed that different sets of genes govern the area versus the thickness of the corpus callosum—two features that change across the lifespan and play distinct roles in brain function. Several of the implicated genes are active during prenatal brain development, particularly in processes like cell growth, programmed cell death, and the wiring of nerve fibers across hemispheres.
Notably, the study found genetic overlap between the corpus callosum and the cerebral cortex—the outer layer of the brain responsible for memory, attention, and language—as well as with conditions such as ADHD and bipolar disorder.
For the first time, a research team has mapped the genetic architecture of a crucial part of the human brain known as the corpus callosum—the thick band of nerve fibers that connects the brain’s left and right hemispheres. The findings open new pathways for discoveries about mental illness, neurological disorders and other diseases related to defects in this part of the brain.
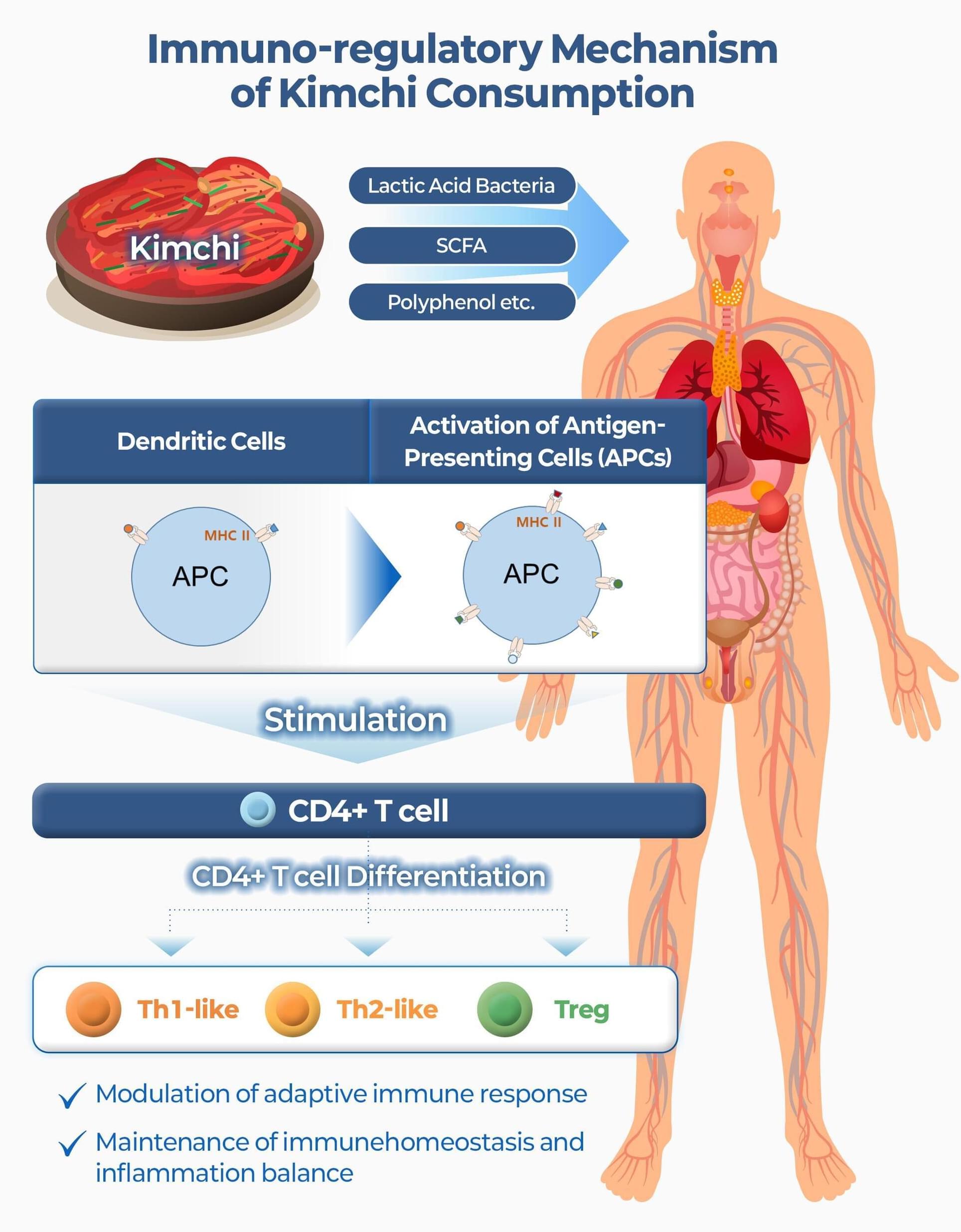
Amid concerns about the simultaneous spread of multiple respiratory diseases, such as colds and influenza, with the change of seasons in current times, a clinical study has scientifically proven that kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food, enhances the function of human immune cells and maintains the balance of the immune system.
The World Institute of Kimchi has reported the results of a single-cell genetic analysis that suggests that kimchi consumption has immunomodulatory effects, which include the suppression of excessive immune responses while simultaneously enhancing defense functions.
The results of the research are published in npj Science of Food.