Extrusive and cohesive cohesin cooperate to repair double-strand breaks in DNA.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
Jiazhi Hu Authors Info & Affiliations
Science.
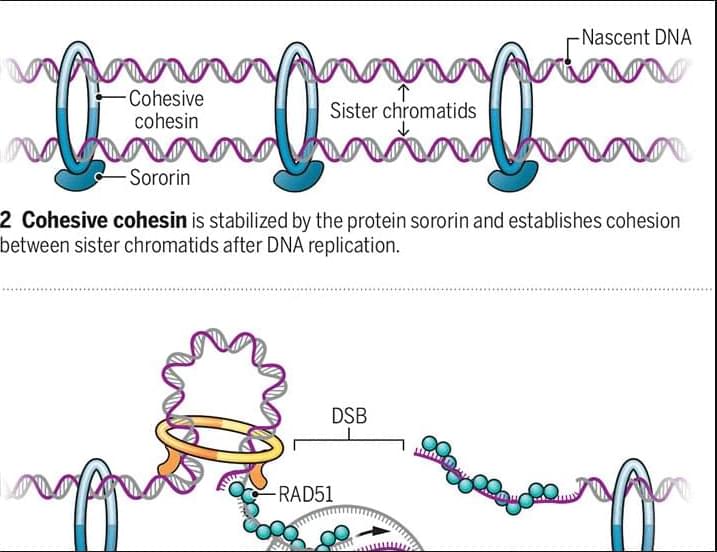
Extrusive and cohesive cohesin cooperate to repair double-strand breaks in DNA.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
Jiazhi Hu Authors Info & Affiliations
Science.
At the heart of every camera is a sensor, whether that sensor is a collection of light-detecting pixels or a strip of 35-millimeter film. But what happens when you want to take a picture of something so small that the sensor itself has to shrink down to sizes that cause the sensor’s performance to crater?
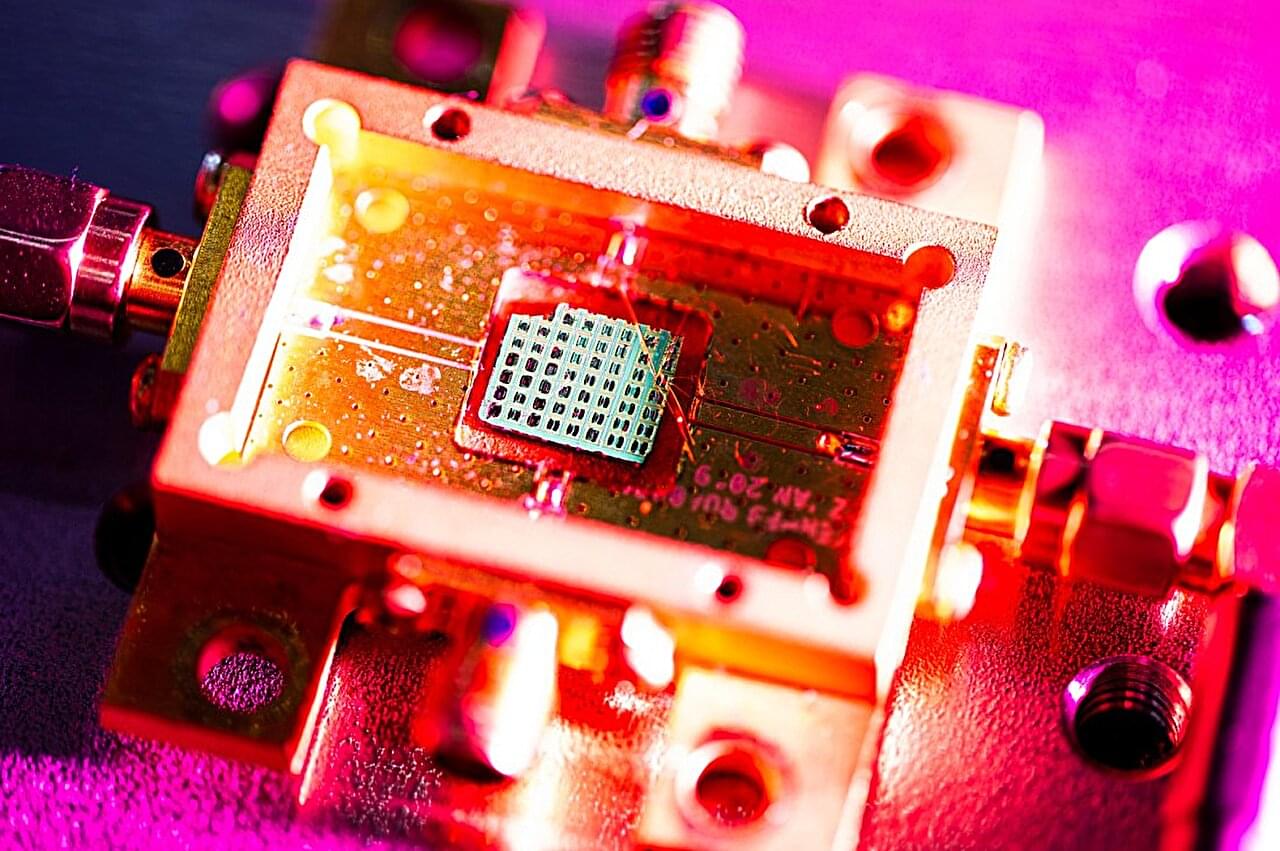
Now, Northeastern University researchers have made a breakthrough discovery in sensing technologies that allows them to detect objects as small as individual proteins or single cancer cells, without the additional need to scale down the sensor. Their breakthrough uses guided acoustic waves and specialized states of matter to achieve great precision within very small parameters.
The device, which is about the size of a belt buckle, opens up possibilities for sensing at both the nano and quantum scales, with repercussions for everything from quantum computing to precision medicine.

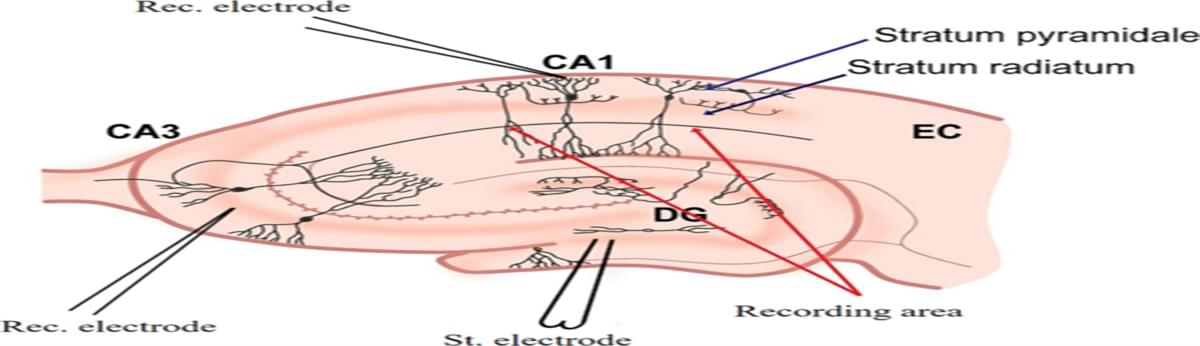
Isting gap in neuromorphic engineering by mimicking biological neuron dynamics and realizing effective clinical applications to promote functional recovery and quality of life enhancement in patients with brain injury. The novel neuromorphic engineering approaches leverage the dynamic behavior of brain neurons, incorporating electronic circuits that emulate neuronal dynamics. A basic configuration involves a neural model designed to mimic the dynamics of a living neuron, with the potential to replace damaged brain tissue when implanted, thus restoring signal propagation. An enhanced configuration integrates a closed-loop system, wherein the feedback signal from biological neurons synchronizes the artificial neuron with its living counterpart, allowing continuous self-adjustment of system parameters and promoting a neuro-autogenerative regime.
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://youtube.com/watch?v=1C2tPFCGL1U
Please support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:
- BetterHelp: https://betterhelp.com/lex to get 10% off.
- Grammarly: https://grammarly.com/lex to get 20% off premium.
- Magic Spoon: https://magicspoon.com/lex and use code LEX to get $5 off.
- Blinkist: https://blinkist.com/lex and use code LEX to get 25% off premium.
- Eight Sleep: https://www.eightsleep.com/lex and use code LEX to get special savings.
GUEST BIO:
Chris Mason is a professor of genomics, physiology, and biophysics at Cornell, doing research on the long-term effects of space on the human body. He is the author of The Next 500 Years: Engineering Life to Reach New Worlds.
PODCAST INFO:
Podcast website: https://lexfridman.com/podcast.
Apple Podcasts: https://apple.co/2lwqZIr.
Spotify: https://spoti.fi/2nEwCF8
RSS: https://lexfridman.com/feed/podcast/
Full episodes playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLrAXtmErZgOdP_8GztsuKi9nrraNbKKp4
Clips playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLrAXtmErZgOeciFP3CBCIEElOJeitOr41
SOCIAL:
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/lexfridman.
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/lexfridman.
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/lexfridman.
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/lexfridman.
- Medium: https://medium.com/@lexfridman.
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/lexfridman.
- Support on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/lexfridman

Cedars-Sinai researchers created “young” immune cells from human stem cells that reversed cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s symptoms in mice. The treated animals showed better memory and healthier brain structures. The cells seemed to protect the brain indirectly, possibly through anti-aging signals in the blood. The findings suggest a new, personalized path to slowing brain aging.
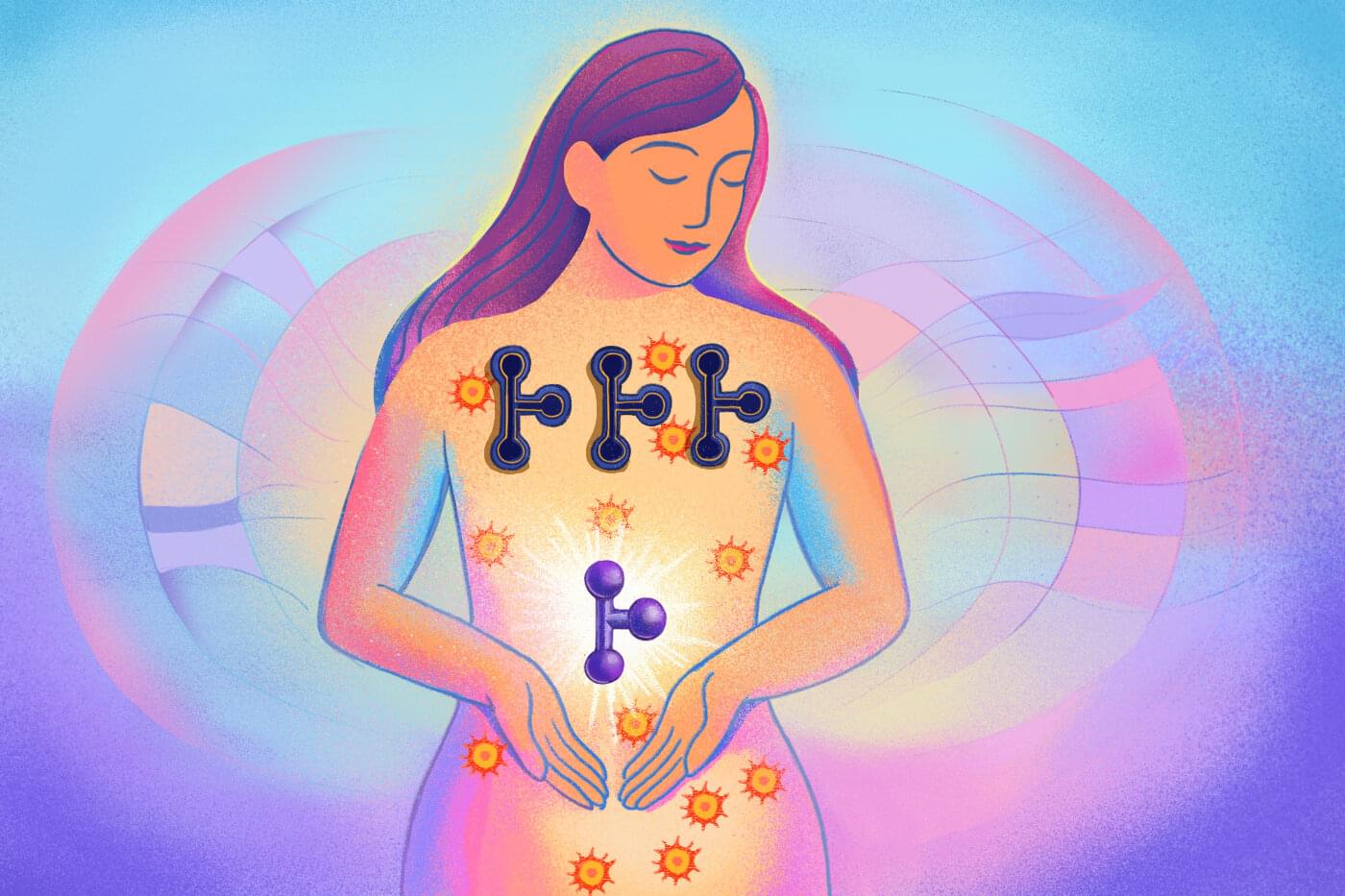

Northeastern University researchers have made a breakthrough drug discovery, developing the first synthetic endogenous cannabinoid compound, with repercussions for new therapeutics from pain and inflammation to cancer.
Spyros P. Nikas, an associate research professor in Northeastern’s Center for Drug Discovery, says that the discovery hinges on the distinction between two different kinds of cannabinoid chemicals, endogenous and exogenous. Exogenous cannabinoids are those produced outside the human body, like THC or CBD, both derived from the cannabis plant and present in marijuana.
Our own bodies, however, are also producing cannabinoids all the time. Called endogenous cannabinoids —or just “endocannabinoids”—these chemicals “modulate a wide range of physiological and pathophysiological responses,” Nikas says, processes that include mood, inflammation and even neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The research is published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
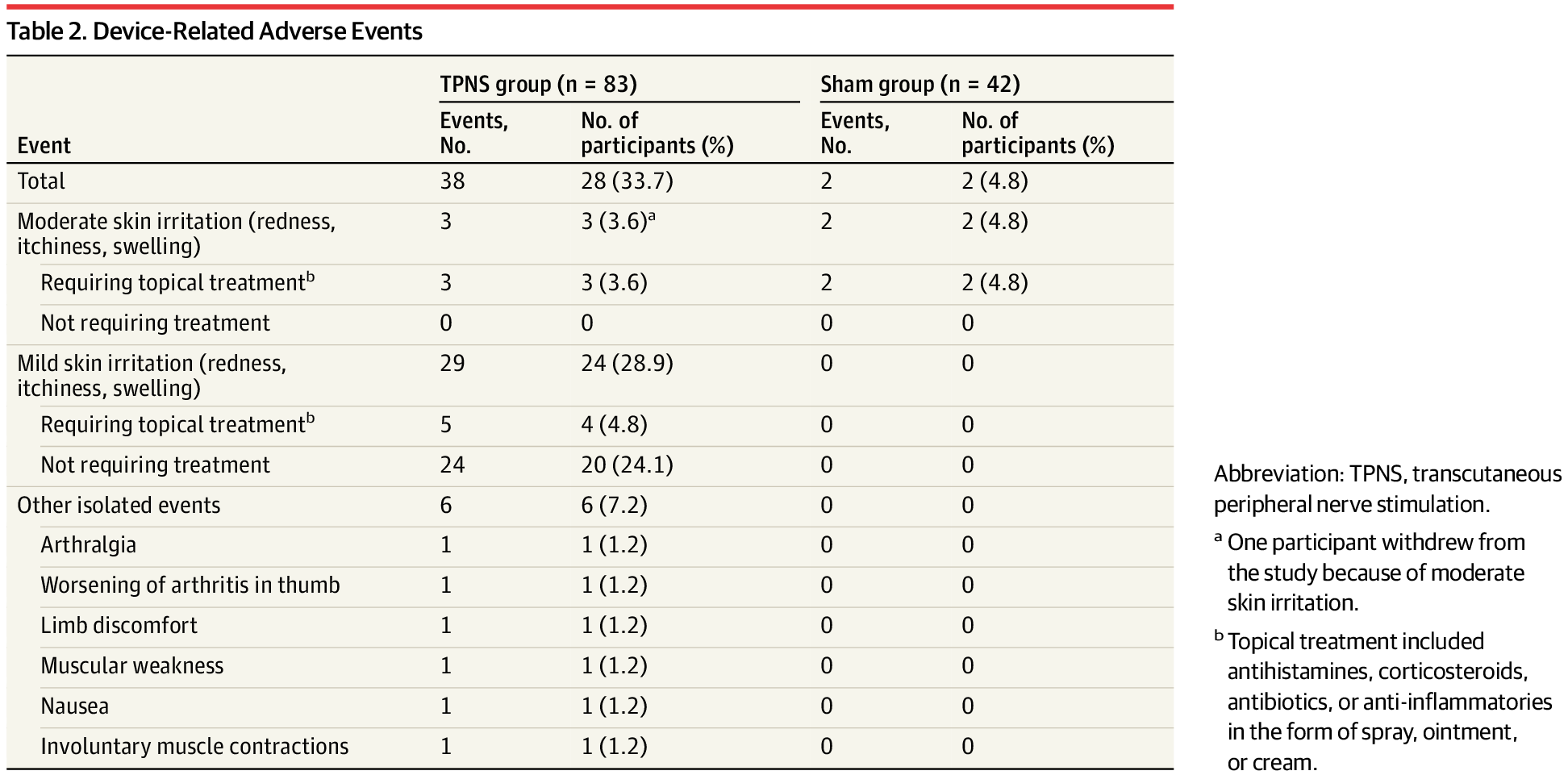
Essential tremor (ET), the most common upper limb tremor, can impair daily activities. In a multicenter RCT, an artificial intelligence–driven transcutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation (TPNS) device reduced mADL scores by 6.9 points at 90 days, compared with a 2.7-point reduction in the sham group.
Question Is an artificial intelligence (AI)–driven TPNS device superior to a sham device in reducing essential tremor?
Findings In this randomized clinical trial that included 125 adults with essential tremor, use of the TPNS device reduced the modified Activities of Daily Living score of the Essential Tremor Rating Assessment Scale by a clinically meaningful 6.9 points at 90 days, significantly more than the 2.7-point reduction seen in the sham-treated group.
Meaning The TPNS device improved activities related to upper limb tremor at 90 days and could be an effective noninvasive treatment for essential tremor.

Question What are the main predictors for high health care costs among patients with head and neck cancer?
Findings In this population-based cohort study, advanced cancer stage and receiving multiple treatment modalities were the strongest predictors of high health care costs. Female sex, older age, and lower socioeconomic status were associated with an increased likelihood for high health care costs, although with a weaker effect size.
Meaning Future research should focus on evaluating screening strategies and early diagnosis to assess their potential effects on cost reduction and improved outcomes for patients with head and neck cancer.