Studies show that centenarians, people who live to 100, accumulate health conditions more slowly and have a lower disease burden compared to shorter-lived individuals.


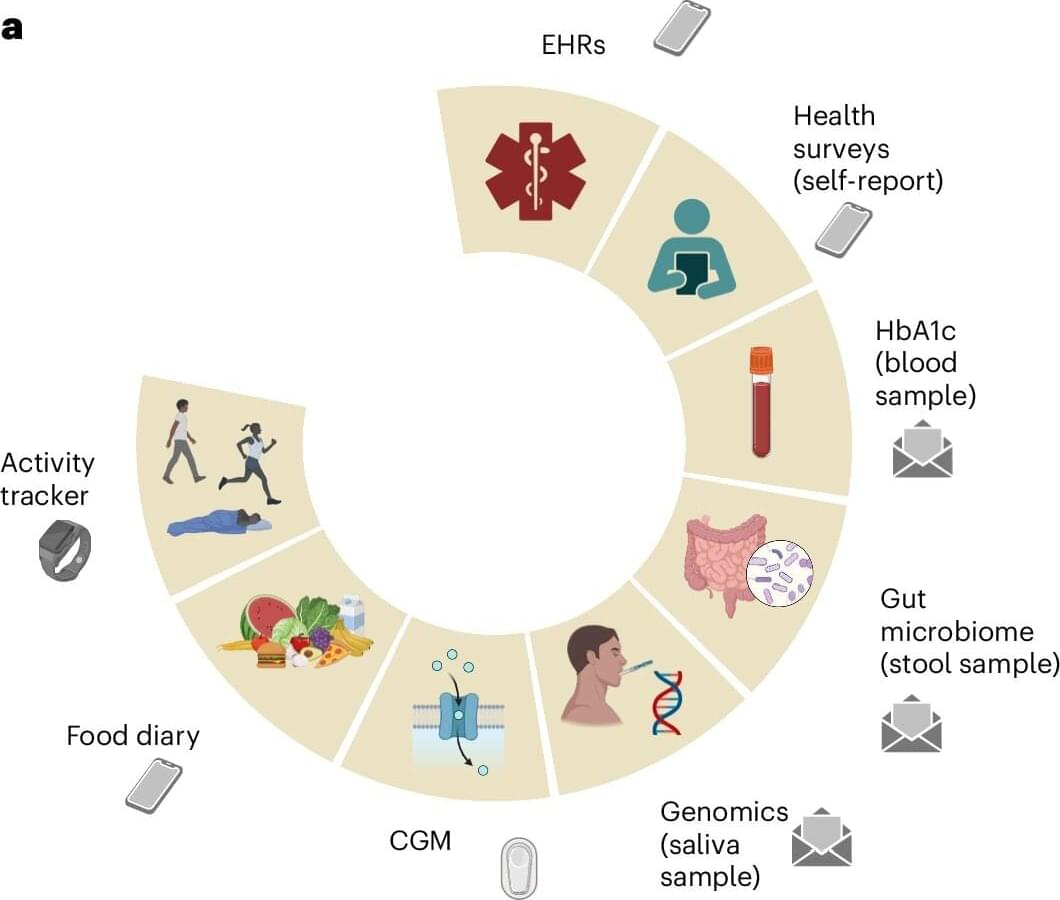
Spread the love 19 11 To diagnose either type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes, clinicians typically rely on a lab value known as HbA1c. This test captures a person’s average blood glucose levels over the previous few months. But HbA1c cannot predict who is at highest risk of progressing from healthy to prediabetic, or from prediabetic to full-blown diabetes.
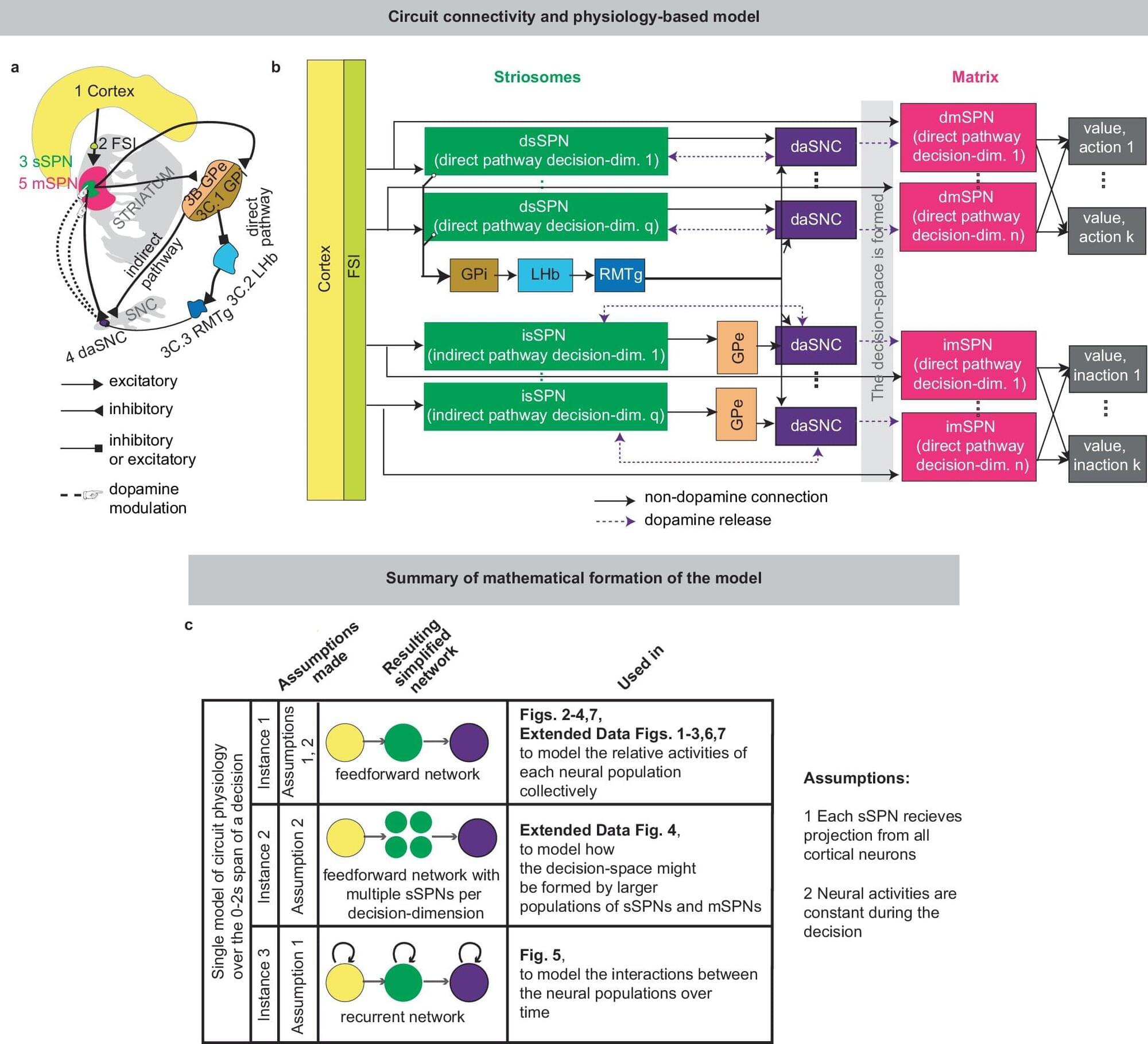
Scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, working in collaboration with a team from the University of Texas at El Paso, have developed a novel computational framework for understanding how a region of the brain known as the striatum is involved in the everyday decisions we make and, importantly, how it might factor into impaired decision-making by individuals with psychiatric disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder and substance use disorder.
In a study published in Nature Communications, the team reported that modulating activity within the striosomal compartment—a neurochemically discrete area of the striatum—might be an important therapeutic strategy for promoting healthier decision-making in people with psychiatric disorders.
“Though it has been established that the striatum is clearly important for cost-benefit decision-making, the precise role of the striosomal compartment has remained elusive,” says Ki Goosens, Ph.D., Associate Professor of Pharmacological Sciences and Psychiatry, at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and co-lead author of the study.
A virus from humble black-eyed peas is showing extraordinary promise in the fight against cancer. Unlike other plant viruses, the cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) can awaken the human immune system and transform it into a cancer-fighting powerhouse, without infecting human cells. By comparing it to a similar, but ineffective, virus, researchers uncovered that CPMV uniquely triggers potent interferons and immune responses, making it a low-cost, plant-grown immunotherapy on the fast track toward clinical trials.
A collaboration between the University of Sydney and Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine has found that a common blood-thinner works as an antidote to cobra venom. The discovery has the potential to save thousands of lives a year.

A paper coauthored by geneticist George Church has been retracted following an internal review at a university where several coauthors are based.
The article appeared in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in 2022. The work supports an anti-aging gene therapy developed by BioViva, a company for which Church serves as an adviser. The paper’s authors claim cytomegalovirus (CMV) can be a gene therapy vector for a treatment for “aging-associated decline” that can be inhaled or injected monthly.
The work has been cited 41 times, two of which are citations from corrections to the article, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science.
AI-powered brain implant restores speech in paralysis patient after 18 years.
UC Berkeley and UCSF use AI-driven brain-computer interface to restore near real-time speech in paralysis patient.


Georgetown Lombardi, Washington’s only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center, serves as the research engine for MedStar Health, Georgetown University’s clinical partner. Georgetown Lombardi is also an NCI-recognized research consortium with John Theurer Cancer Center of Hackensack Meridian Health in Bergen County, New Jersey.
They have a blog with alot of useful cancer information you can share. There is info about them circulating about cancer vaccines and clinical trials. Check em out:
(You can repost their posts or contact them to recieve information from them directly. Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center 3,800 Reservoir Rd. NW Washington D.C. 20,057 Phone: 202−444−2223)