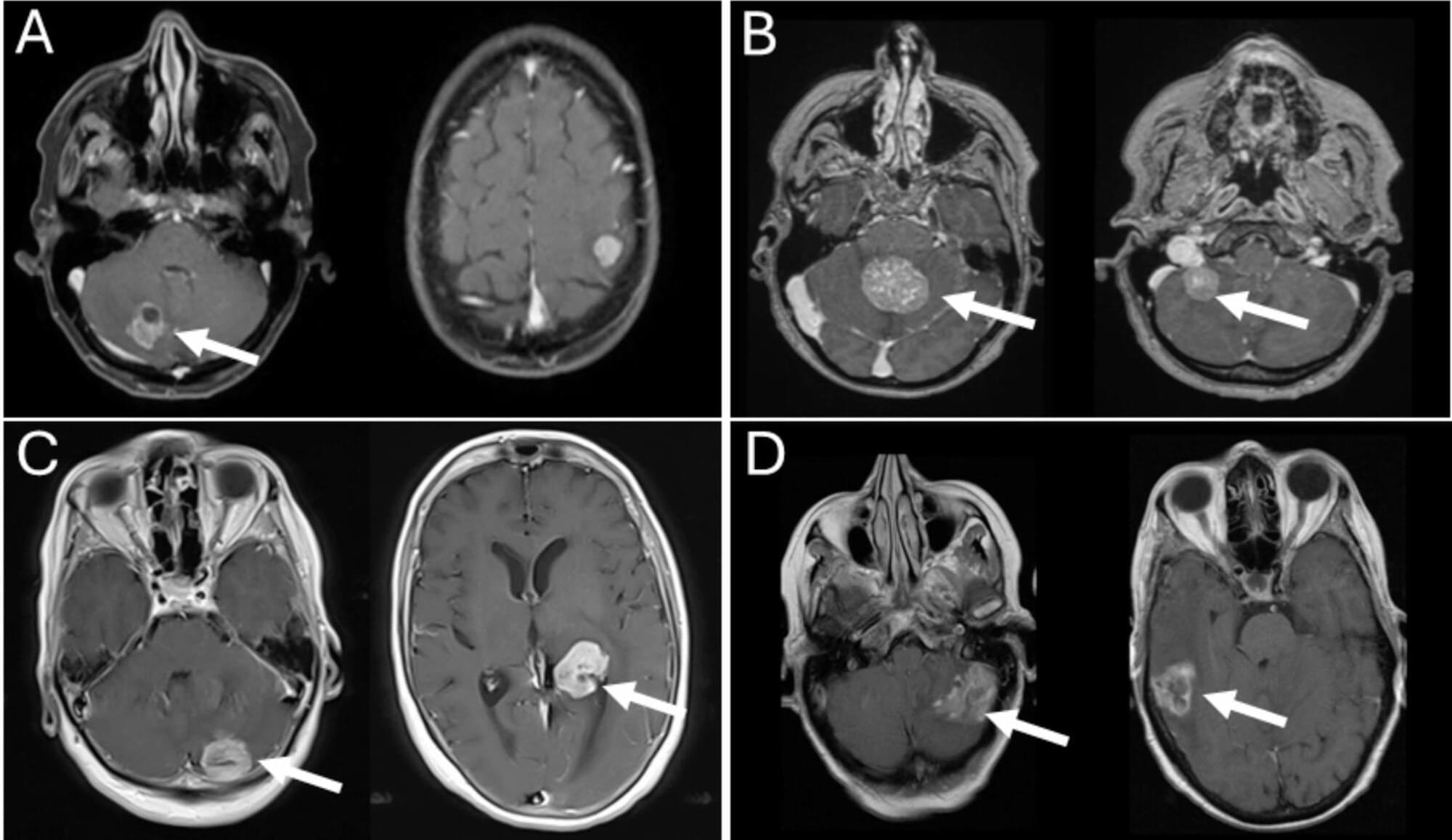
Purpose Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most common primary tumor entities that develop brain metastases (BM) during disease progression. Multiple BM are associated with poorer prognosis, but various surgical, radiotherapeutic and systemic treatment approaches improve survival. We aimed to identify prognostic factors and evaluate the overall survival following BM surgery in patients with multiple BCBM. Methods All metachronous metastasized female patients with resected BCBM at our institution between 2008 and 2019 were included. Data on clinical, radiologic, and histopathologic parameters were recorded and analyzed using univariate and multivariate regression models. Results Among the 93 patients included in the final analysis, 30 individuals presented with multiple BM. Compared to patients with single BM, those with multiple BM were more likely to have infratentorial BM (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.35, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.03–10.83, p = 0.044), HER2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2)-positive BC (aOR 3.93, 95% CI 1.23–12.53, p = 0.021) and hepatic metastases (aOR 5.86, 95% CI 1.34–25.61, p = 0.019). There was no significant difference in postoperative survival between individuals with multiple (median: 12.5 months) and single BM (17.0 months, p = 0.186). In the multivariate Cox regression analysis, adjuvant radiotherapy (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 5.93, 95% CI 1.06–33.26, p = 0.043) and trastuzumab treatment (aHR 4.95, 95% CI 1.72–14.25, p = 0.003) were associated with longer postoperative survival multiple BCBM patients. Conclusion BC patients with multiple BM show remarkable postoperative survival, particularly if combined with adjuvant radiotherapy. Our data justify the surgery of multiple BCBM in patients with appropriate clinical condition and feasible location of BM.