A new study shows that faulty mitochondria may be a root cause of dementia symptoms. Stimulating these cellular “powerhouses” in mice restored memory, offering a potential new approach to treating neurodegenerative diseases.


Penn researchers have revealed that red blood cells, not just platelets, play an active role in clot contraction. For years, scientists believed that red blood cells simply tagged along during clot formation without doing much. A new study from the University of Pennsylvania now shows they play an
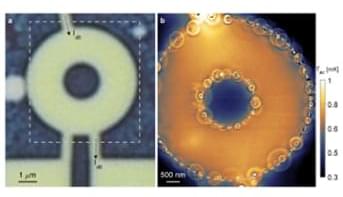
This tool provides scanning cryogenic thermal sensing that is 4 orders of magnitude more sensitive than previous devices allowing the detection of a sub 1 μK temperature difference. Furthermore, it is non-contact and non-invasive and allows thermal imaging of very low intensity, nanoscale energy dissipation down to the fundamental Landauer limit of 40 femtowatts for continuous readout of a single qubit at one gigahertz at 4.2 kelvin.

The skin serves as an important barrier protecting the body from physical, chemical and pathogenic hazards as well as regulating the bi-directional transport of water, ions and nutrients. In order to improve the knowledge on skin structure and function as well as on skin diseases, animal experiments are often employed, but anatomical as well as physiological interspecies differences may result in poor translatability of animal-based data to the clinical situation. In vitro models, such as human reconstructed epidermis or full skin equivalents, are valuable alternatives to animal experiments. Enormous advances have been achieved in establishing skin models of increasing complexity in the past. In this review, human skin structures are described as well as the fast evolving technologies developed to reconstruct the complexity of human skin structures in vitro.


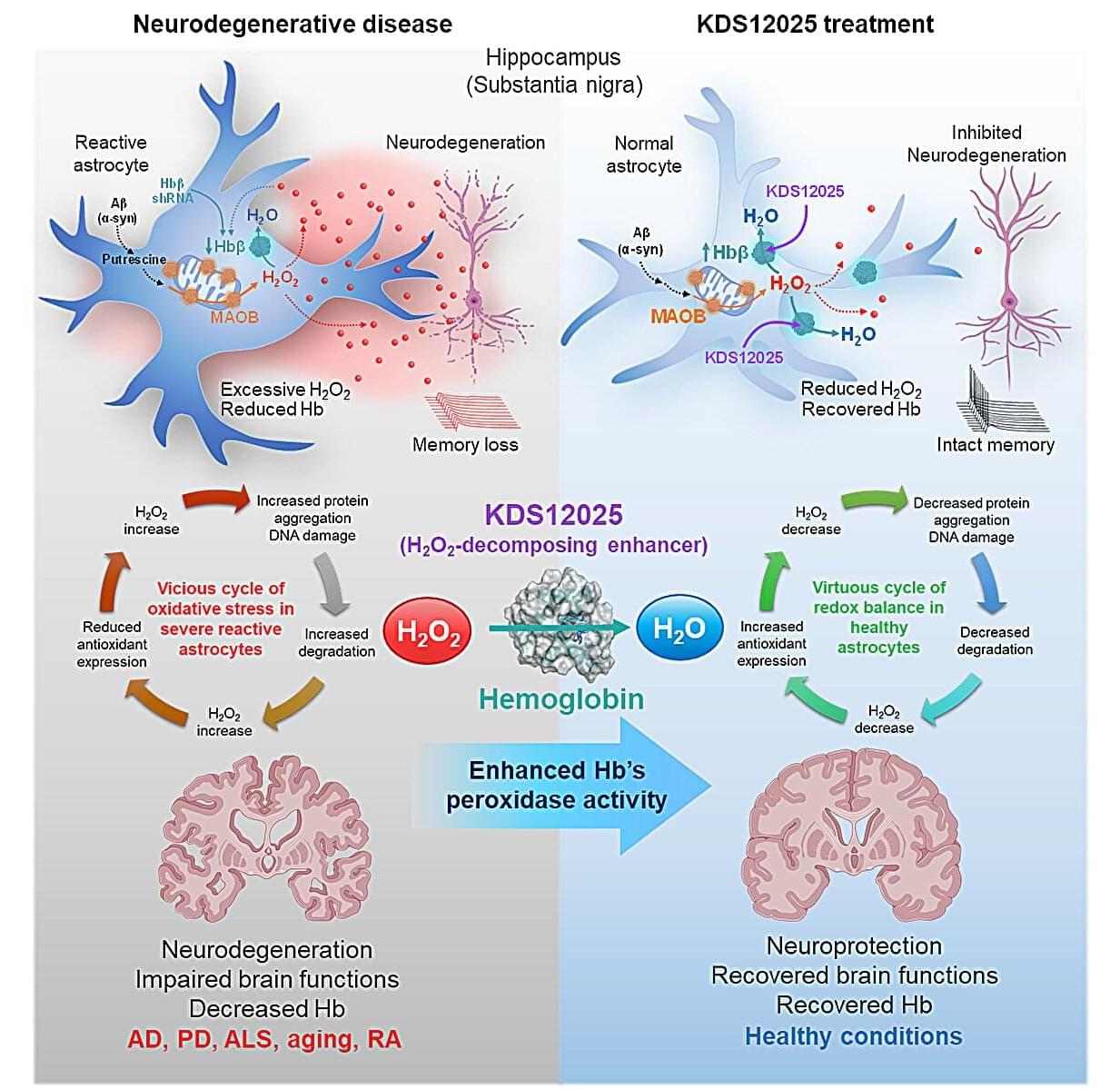
Hemoglobin, long celebrated for ferrying oxygen in red blood cells, has now been revealed to play an overlooked—and potentially game-changing—antioxidant role in the brain.
In neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and aging, brain cells endure relentless damage from the aberrant (or excessive) reactive oxygen species (ROS). For decades, scientists have tried to neutralize ROS with antioxidant drugs, but most failed: they couldn’t penetrate the brain effectively, were unstable, or indiscriminately damaged healthy cells.
This new study, led by Director C. Justin Lee of the Center for Cognition and Sociality within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in Daejeon, South Korea, set out to identify the brain’s own defenses against a particularly harmful form of ROS—hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The study has been published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.
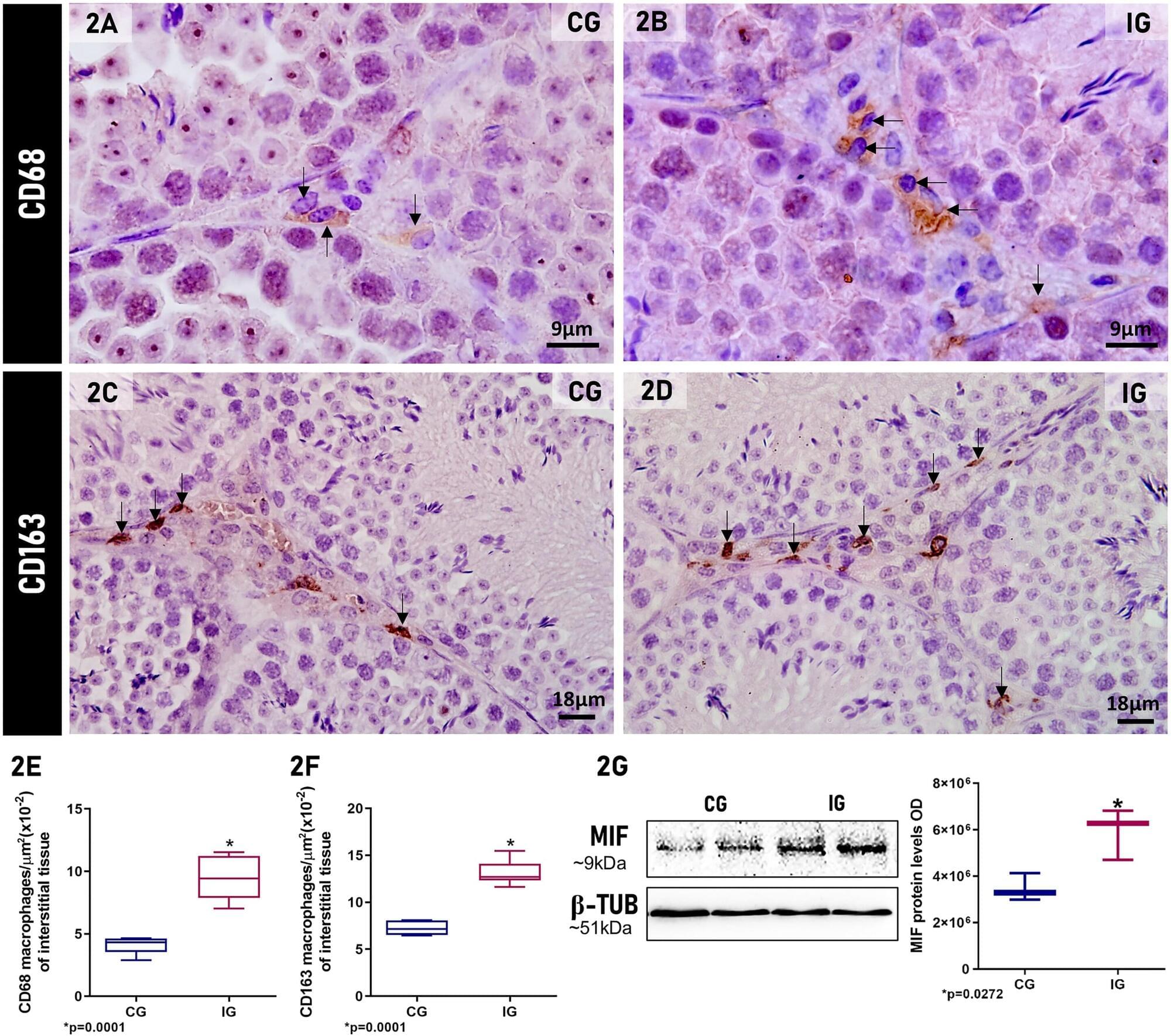
The COVID-19 virus hijacks the machinery of testicular cells that produce the hormone testosterone in order to replicate. It also appropriates the metabolic pathways of these cells and cholesterol, a precursor of testosterone, thereby altering lipid metabolism for its formation.
This has been verified in a study conducted in Brazil by researchers from the Araraquara School of Dentistry at São Paulo State University (FOAr-UNESP), in partnership with the Ribeirão Preto School of Medicine at the University of São Paulo (FMRP-USP), in the testicles of transgenic mice. The research is published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
The study revealed the presence of SARS-CoV-2 particles in lipid inclusions and organelles responsible for testosterone production in Leydig cells for the first time. In addition, the researchers described the mechanism by which the virus interferes with the functioning of these testicular cells. The discovery helps explain why male patients with severe COVID-19 have lower levels of testosterone, and possibly cholesterol.