2Dietrich School of Arts & Sciences, University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.
3Division of Genetics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
As we age, the immune system gradually declines in function, leaving the body more vulnerable to disease. Scientists have discovered a new way to rejuvenate a key component of immune function, potentially boosting health in later years.
A team from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard focused on the thymus, a small organ in front of the heart that’s crucial for the development of T cells. These immune cells act as guards, identifying and fighting threats such as cancer and infections.
From early adulthood, the thymus shrinks and slows, limiting T cell production. In mouse models, the researchers were able to repurpose part of the liver as a thymus substitute, sending the molecular signals that stimulate T-cell production.
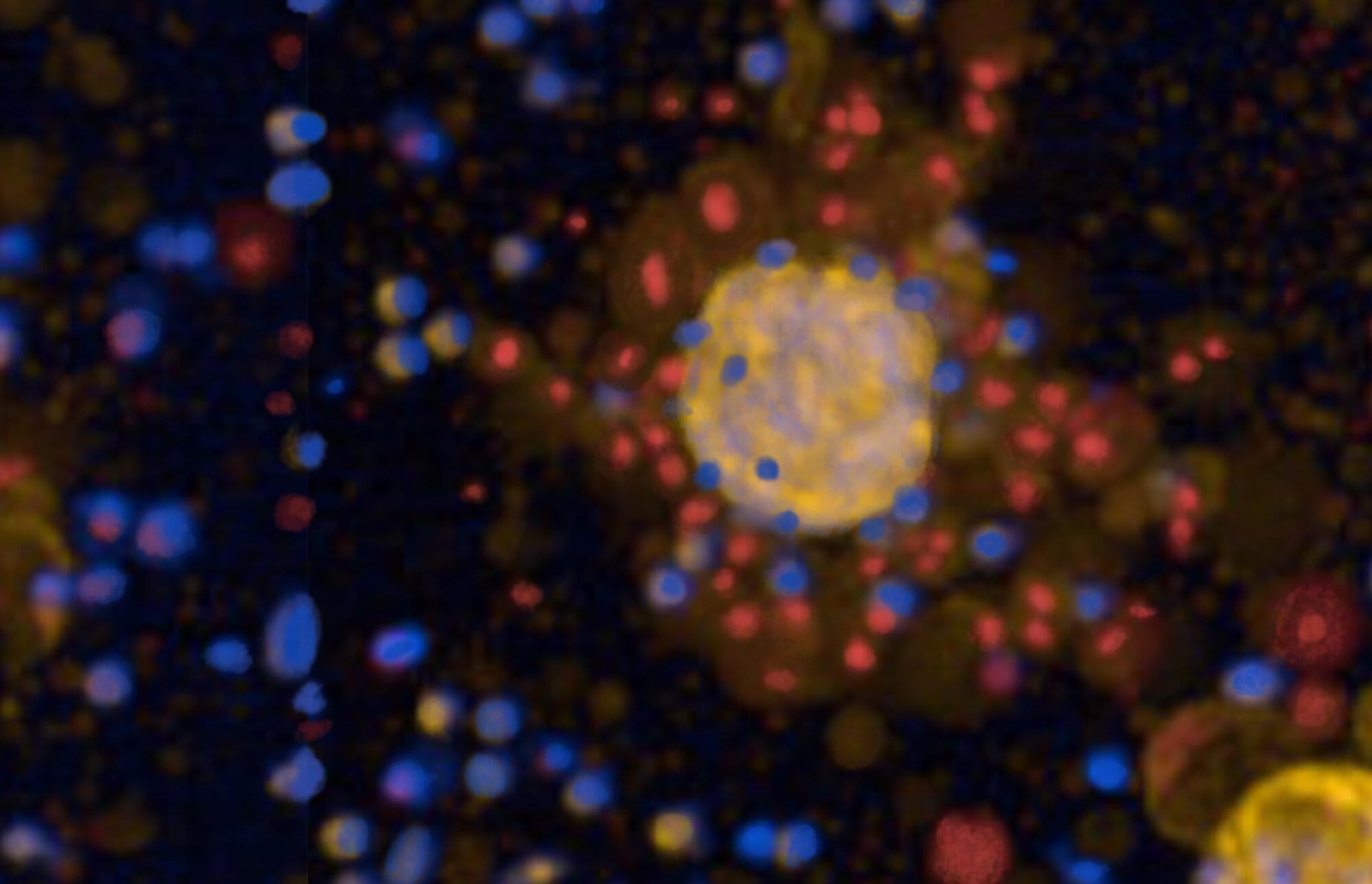
Lung cancer varies widely from patient to patient, and that diversity makes it hard to find effective treatments. Researchers at the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH) have developed a method to evaluate multiple therapeutic approaches on patient-derived “tumoroids”—miniature tumors grown from tissue removed during surgery at Charité
By testing drug responses across these tumoroids, the team showed that therapeutic success depends on a complex interplay of tumor characteristics rather than a single factor. Their results suggest that tumoroid-based testing could help physicians tailor treatments to individual patients and improve clinical decision-making.
The BIH researchers have published their findings in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
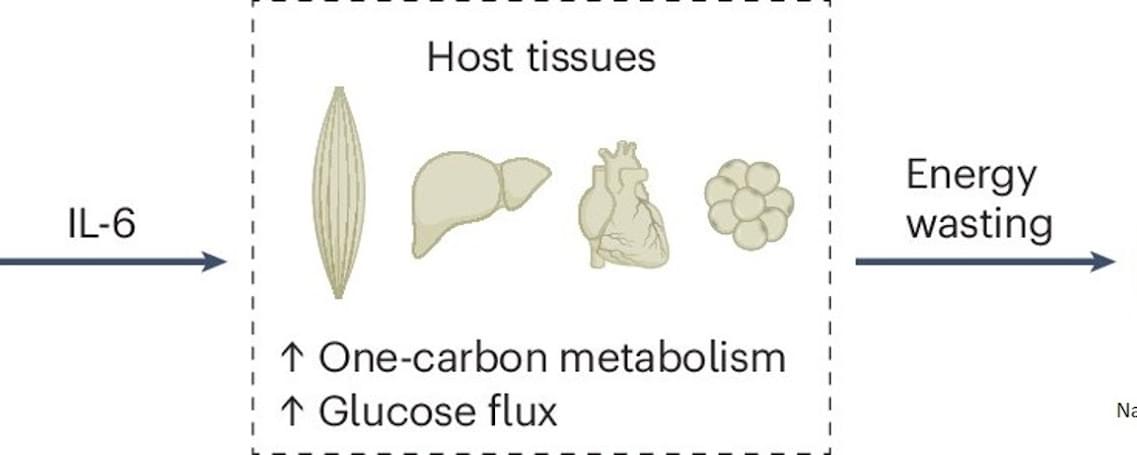
Combined metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis in eight different organs of tumor-bearing mice with and without cachexia allowed researchers to create metabolic signatures typical of cancer-associated weight loss. High-throughput analyses identified a cachexia-specific metabolic and genetic signature that provides insight into the progression of these metabolic changes.
The researchers found that all organs showed increased activation of the so-called “one carbon cycle”, a biochemical process essential for the synthesis of nucleotides, amino acids, and cell regeneration. Products of this cycle, such as sarcosine or dimethylglycine, could potentially serve as biomarkers for cachexia in the future.
The study also revealed that hyperactivation of the one carbon cycle in muscle is associated with increased glucose metabolism (glucose hypermetabolism) and muscle atrophy. Early experiments suggest that inhibiting this process could prevent muscle loss. Comparative analyses across eight different mouse tumor models (lung, colon, and pancreatic cancer) confirmed that the one carbon signature represents a universal cachexia signature, independent of cancer type.
Currently, there is no approved drug for cancer cachexia in Germany. New approaches are being explored to address cancer-related appetite loss. This study provides the first evidence of how metabolism itself could potentially be normalized. Early experiments in cell cultures show that interventions targeting the one carbon cycle can have positive effects. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission.
Cachexia is a metabolic disorder that causes uncontrolled weight loss and muscle wasting in chronic diseases and cancer. A new study shows that cachexia affects more than just muscles. Numerous organs respond in a coordinated manner, ultimately contributing to muscle loss. Analysis of metabolome and transcriptome data, along with glucose tracing in tumor-bearing mouse models, identified a novel mechanism that plays a key role in cancer-associated weight loss.
A loss of 10% of body weight within six months – what may sound desirable in some contexts – often causes uncertainty and frustration in cancer patients with cachexia, as they are unable to maintain or gain body weight despite wanting to. Cachexia (from the Greek kakós, “bad,” and héxis, “condition”) affects 50–80% of all cancer patients, reduces quality of life, diminishes the effectiveness of cancer therapies, and increases mortality.
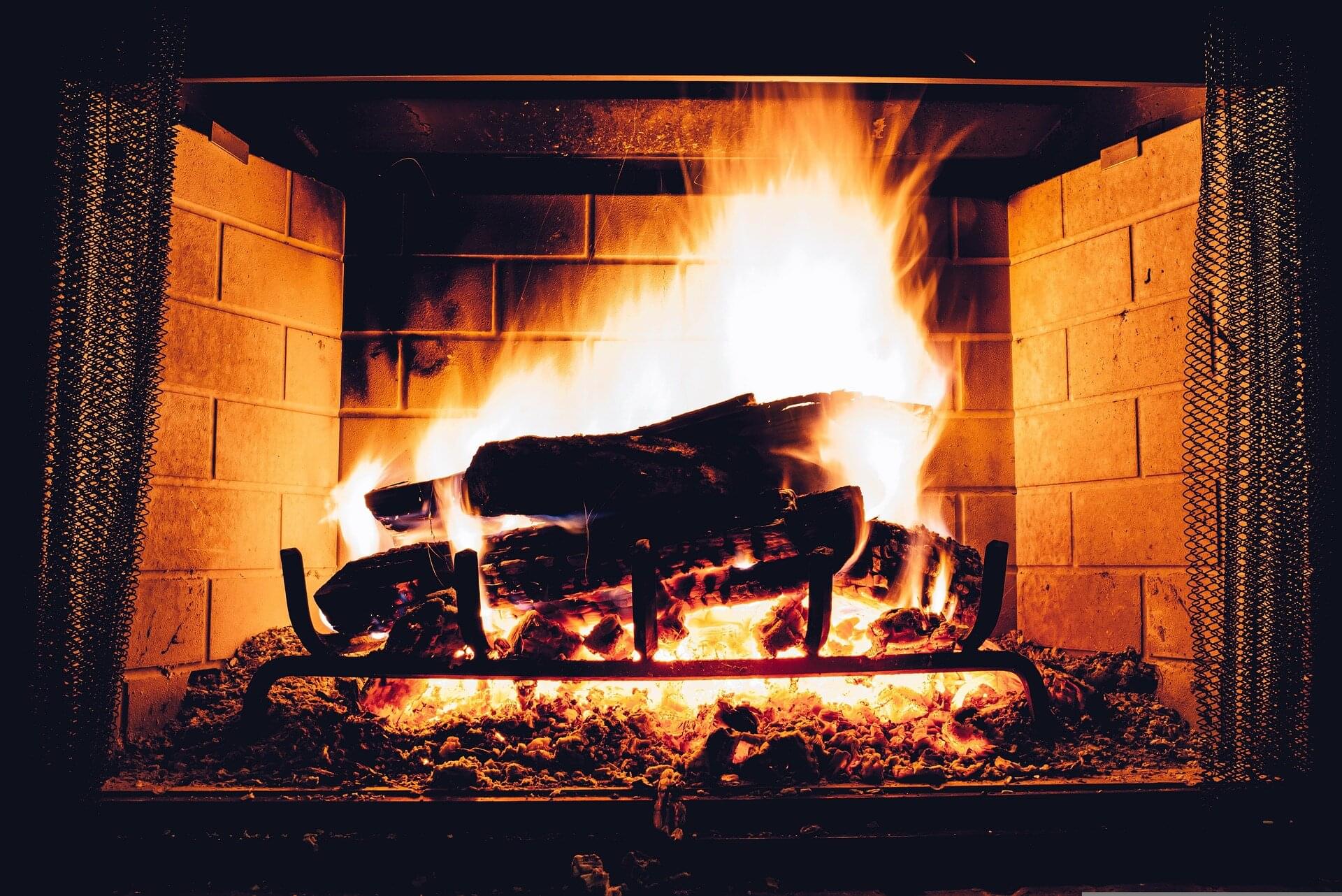

Throwing another log into a crackling fireplace on a cold winter’s night might seem like a cozy, harmless tradition. But Northwestern University scientists have found residential wood burning is a major—yet often overlooked—contributor to winter air pollution across the United States.
Although only 2% of U.S. homes rely on wood as their primary heating source, residential wood burning accounts for more than one-fifth of Americans’ wintertime exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5), the new study found.
These tiny airborne particles can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream, where they are linked to increased risks of heart disease, lung disease and even premature death. Among their findings, the scientists calculated that pollution from residential wood burning is associated with about 8,600 premature deaths per year.

Stronger brains strengthen resilience, productivity, and shared prosperity. It is time to invest accordingly.
The brain is the body’s most complex and vital organ, regulating everything from basic life functions to complex decision-making. It is also the foundation of how people live, work, and connect, making it central to individual well-being, high-performing organizations, and resilient economies. Despite rapid technological advances, nothing yet replicates the brain’s capacity to contribute to society.
AI will reshape work, and competitiveness will hinge on combining human and machine strengths. Countries and companies must evolve their strategies to enable collaboration and harness the complementary strengths of human intelligence and technology, or risk slower growth and being left behind in the next era of the global economy. And while the stakes are high if we fail to invest in the health of our brains and the skills that make us uniquely human, the potential gains—individually, socially, and economically—are even greater if we choose to do so.
In this report, brain health is defined as a state of optimal brain functioning, supported by the promotion of healthy brain development and the prevention or treatment of mental, neurological, and substance use disorders in people of all ages. But health alone is not enough. Brain skills—the foundational cognitive, interpersonal, self-leadership, and technological literacy abilities that enable people to adapt, relate, and contribute meaningfully—are equally critical to societal progress. Together, these form what is called brain capital.
Underinvestment in the brain has a substantial cost. The global disease burden of brain health conditions is rising, driven by an aging population, increased stressors, and elevated uncertainty about the future. When societies overlook the brain’s central role in health and productivity, the impact is felt in disrupted lives, lost potential, and a heavy toll on families and caregivers. Scaling cost-effective interventions to prevent, treat, and help people recover from brain health conditions could avert 267 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) globally by 2050, generating up to $6.2 trillion in cumulative GDP gains.1 Investing early can create even greater returns—quality early-childhood programs have demonstrated annual returns of 7 to 13 percent and delivered benefit-to-cost ratios of up to nine to one in low-and middle-income countries.
In this report by the McKinsey Health Institute, in collaboration with the World Economic Forum, the authors make the case for investing in the brain, introduce five levers for action, and offer a road map for next steps. While specific actions may vary by stakeholder, region, or sector, there is a need for a shared aspiration and framework for change. This report aims to fill that gap.
“ (
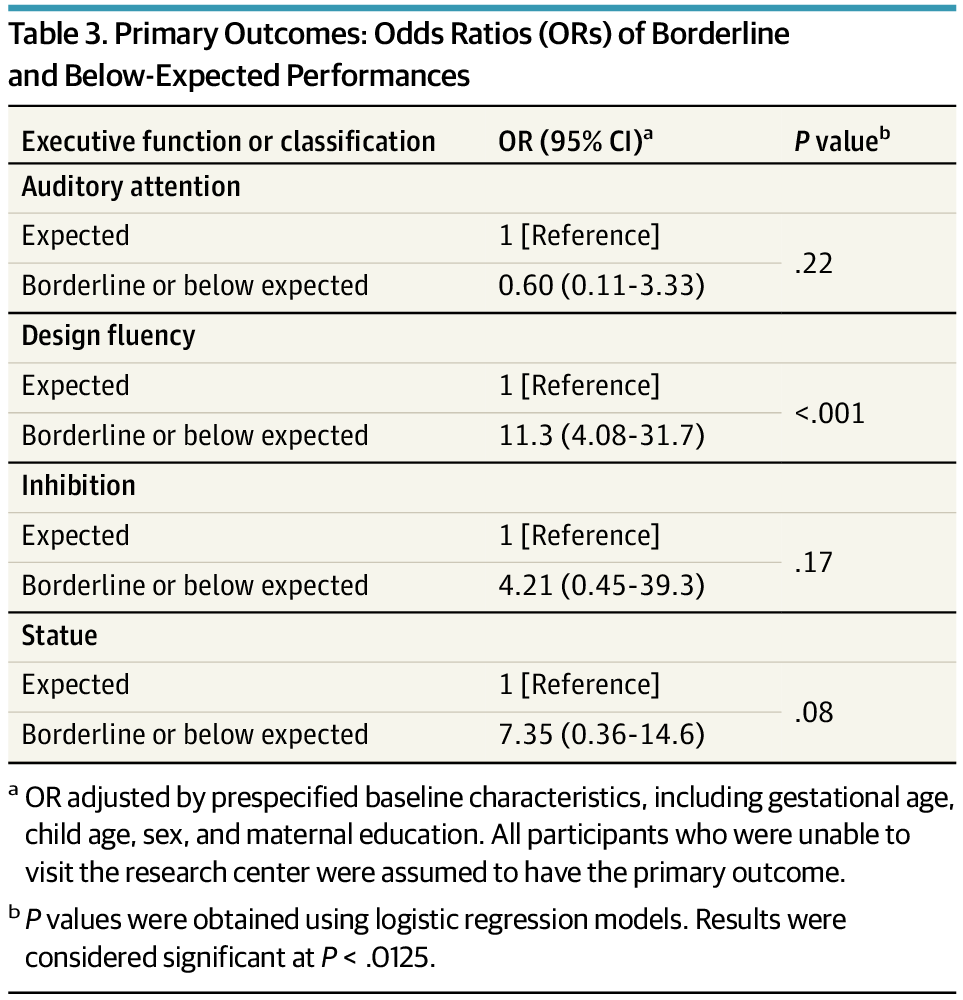
Enhanced developmental intervention (EDI), initiated in the neonatal intensive care unit and continued at home for 2 years, improved executive function at school age among very preterm children compared with usual care.
All executive domains assessed showed better performance with EDI, especially for design fluency. These findings support sustained neurodevelopmental benefit for Preterm children, with implications for long-term outcomes.
Question What are the long-term effects of an enhanced early intervention on the executive functions of children born preterm?
Findings In this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial among 80 very low-birth-weight preterm children, it was observed that parent-led early intervention improved executive function.
Meaning Early intervention may strengthen cognitive skills, such as attention, self-regulation, and problem-solving, which could improve academic, emotional, and social outcomes, highlighting the importance of early intervention for long-term developmental success.
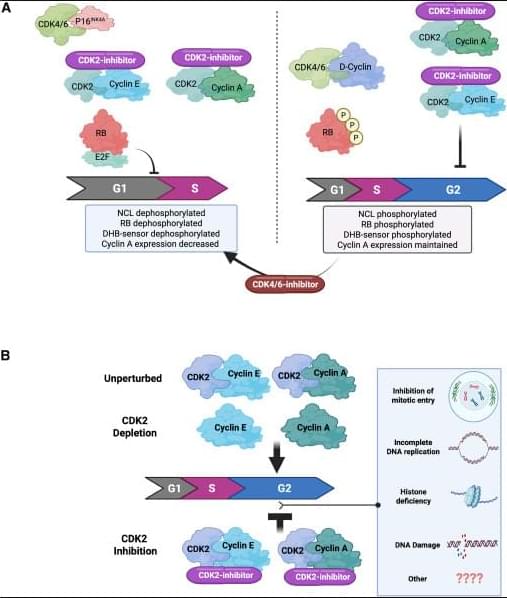
How CDK2 inhibitors halt cancer cell division👇
✅G1 arrest in p16INK4A-high, cyclin E–high tumors (A, left). In tumors with high p16INK4A and cyclin E, catalytic CDK2 inhibitors block phosphorylation of key CDK2 substrates, including RB and nucleolin, and reduce signals from CDK activity sensors. This suppresses E2F transcriptional activity, leading to reduced cyclin A expression and failure to enter S phase. The net result is a G1 cell-cycle arrest, driven by effective shutdown of the RB–E2F axis.
✅4N accumulation when p16INK4A is absent (A, right). In tumors lacking p16INK4A, CDK2 catalytic inhibition alone does not efficiently block RB phosphorylation or early G1 molecular events. Instead, cells continue through S phase and accumulate with 4N DNA content, indicating arrest later in the cycle (post-replication). In this context, adding a CDK4/6 inhibitor can mimic the p16INK4A state, restore RB dephosphorylation, repress E2F, and shift cells toward a G1 arrest, highlighting the importance of dual CDK control of RB.
✅Catalytic inhibition vs genetic depletion of CDK2 (B). Genetic loss of CDK2 is often tolerated because cells can compensate using cyclin A–CDK1 to complete G2/M. In contrast, catalytic CDK2 inhibitors trap CDK2 in inactive complexes with cyclins, which may interfere with normal handoff to CDK1 and other cell-cycle processes. This leads to accumulation of cells with 4N DNA content, reflecting a block after DNA replication.
✅Why the outcomes differ. These findings suggest that CDK2 has roles beyond simple kinase activity—its inactive, cyclin-bound state under catalytic inhibition may disrupt network dynamics differently than complete protein loss. The precise mechanisms of the 4N arrest are still being investigated and may involve defects in S/G2 transitions, replication stress responses, or mitotic entry control.
✅Therapeutic implication. Tumor response to CDK2 inhibitors depends strongly on p16INK4A status, cyclin E levels, and RB pathway integrity. This supports combination strategies (CDK2 + CDK4/6 inhibition) in selected cancers and emphasizes the need for biomarker-guided patient stratification.

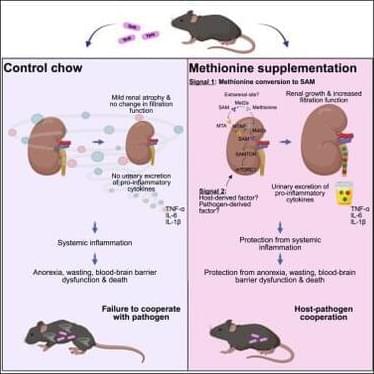
Nutritional strategy to prevent immune-mediated damage.
Excessive immune response with the inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production may lead to tissue damage.
With Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection in mic, the researchers found that dietary methionine enhances kidney filtration and promotes urinary excretion of inflammatory cytokines during infection and protects against anorexia, wasting, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and lethality.
Mechanistically, methionine and its metabolite S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) activate renal mTORC1 signaling, promoting renal growth and enhanced glomerular filtration function.
By improving cytokine clearance, this pathway mitigates immune-mediated damage and reveals a nutritional strategy to promote cooperative defenses. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/Dietary-methionine
Troha et al. found that dietary methionine enhances kidney filtration and promotes urinary excretion of inflammatory cytokines during infection. By improving cytokine clearance, this pathway mitigates immune-mediated damage and reveals a nutritional strategy to promote cooperative defenses.