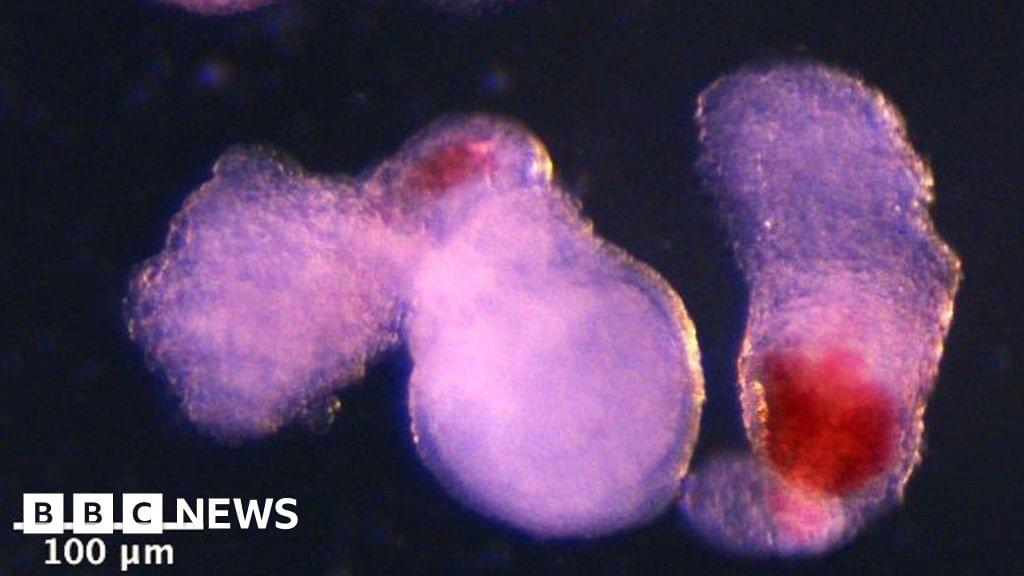
Prof Azim Surani, senior author of the paper, said: “Although it is still in the early stages, the ability to produce human blood cells in the lab marks a significant step towards future regenerative therapies — which use a patient’s own cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues.”
Human blood stem cells, also known as hematopoietic stem cells, are immature cells that can develop into any type of blood cell.
These include red blood cells that carry oxygen and various types of white blood cells crucial to the immune system.