Sci. Adv. 12, eady5905 (2026). DOI:10.1126/sciadv.ady5905
Select the format you want to export the citation of this publication.
By Rachel Tompa
Research led by Stanford Medicine points to the first non-invasive imaging method to visualize senescent cells, which are alive but dormant and play a key role in many diseases.

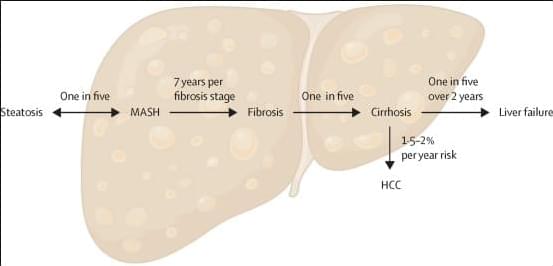
Globally, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is now the most common chronic liver disease, affecting up to one in three people in the general population, with an estimated increase in prevalence of more than 50% in the last three decades. The rise in prevalence of MASLD will result in substantial increases in the number patients with decompensated cirrhosis and those developing liver cancer by 2030. Despite the complex pathobiology of MASLD, two major breakthroughs in phase 3 clinical trials now herald an era of licensed therapies for MASLD.
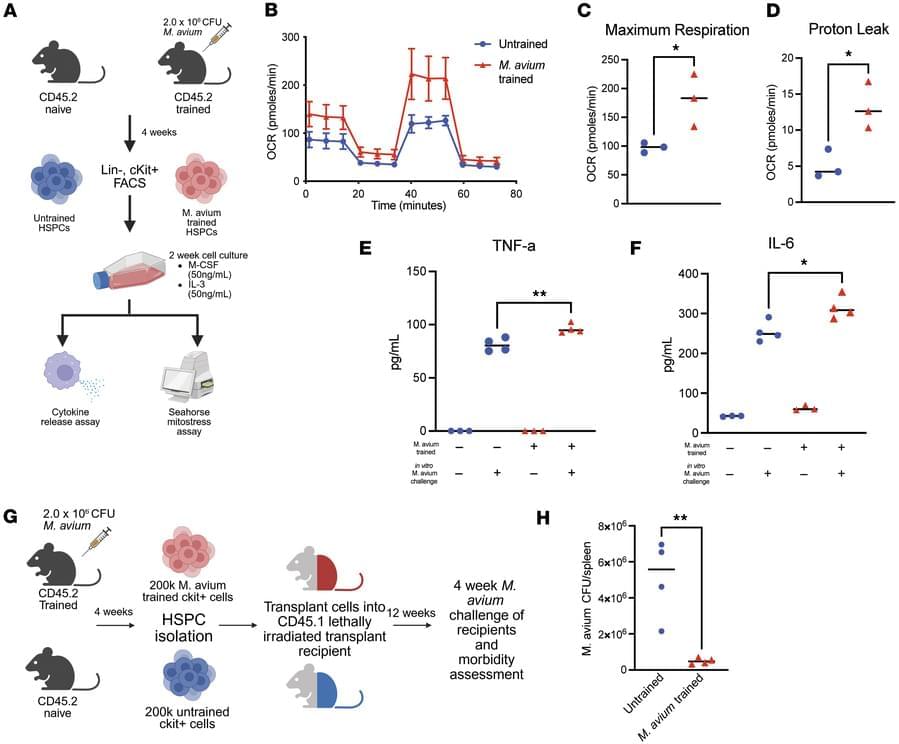
Katherine Y. King & team now identify epigenetic changes in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in a mycobacterial infection model that are retained in downstream macrophages, providing mechanistic mediators of innate immune memory and explaining persistence of central trained immunity.
1Graduate Program in Cancer and Cell Biology.
2Department of Pediatrics, Division of Infectious Disease, Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine.
3Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine Center.
4Department of Molecular and Human Genetics.

From the article:
Nipah virus outbreaks have been associated with a high death rate in the past, with fatality levels reported between 40 and 75 per cent depending on the outbreak and the viral strain involved.
The virus has been documented in Bangladesh, India, Malaysia, the Philippines and Singapore, with Bangladesh recording the highest number of 341 cases and 241 deaths, according to the International Society for Infectious Disease.
Airports across parts of Asia have begun tightening health surveillance and travel screening after an outbreak of Nipah virus in an Indian state.
Thailand, Nepal and Taiwan are among the countries and territories that have stepped up precautionary measures after five Nipah virus cases were confirmed in India’s West Bengal.
Nipah is a zoonotic disease that mainly spreads to humans from infected pigs and bats, but can also be passed on through close person-to-person contact.

Free Access: Protein Glycosylation: An Emerging Regulator of Allergic Diseases. Pan Li, Xianghong Wang, Ming Zeng, Zheng Liu.
Read the article here: doi.org/10.1111/all.
With over 140 references, this review article provides an overview of the role of glycosylation in type 2 inflammation, associated allergic diseases, and therapeutic implications. It includes a discussion on the glycosylation of key proteins involved in Th2 inflammation, including cytokines and their receptors, IgE, FcεRI, IgG, mucins, STAT6, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4).

Unraveling the mysteries of how biological organisms function begins with understanding the molecular interactions within and across large cell populations. A revolutionary new tool, developed at the University of Michigan, acts as a sort of tape recorder produced and maintained by the cell itself, enabling scientists to rewind back in time and view interactions on a large scale and over long periods of time.
Developed in the lab of Changyang Linghu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Cell and Developmental Biology and Biomedical Engineering and Principal Investigator in Michigan Neuroscience Institute, the so-called CytoTape is a flexible, thread-like intracellular protein fiber, designed with the help of AI to act as a tape recorder for large-scale measurement of cellular activities.
The research appears in the journal Nature.
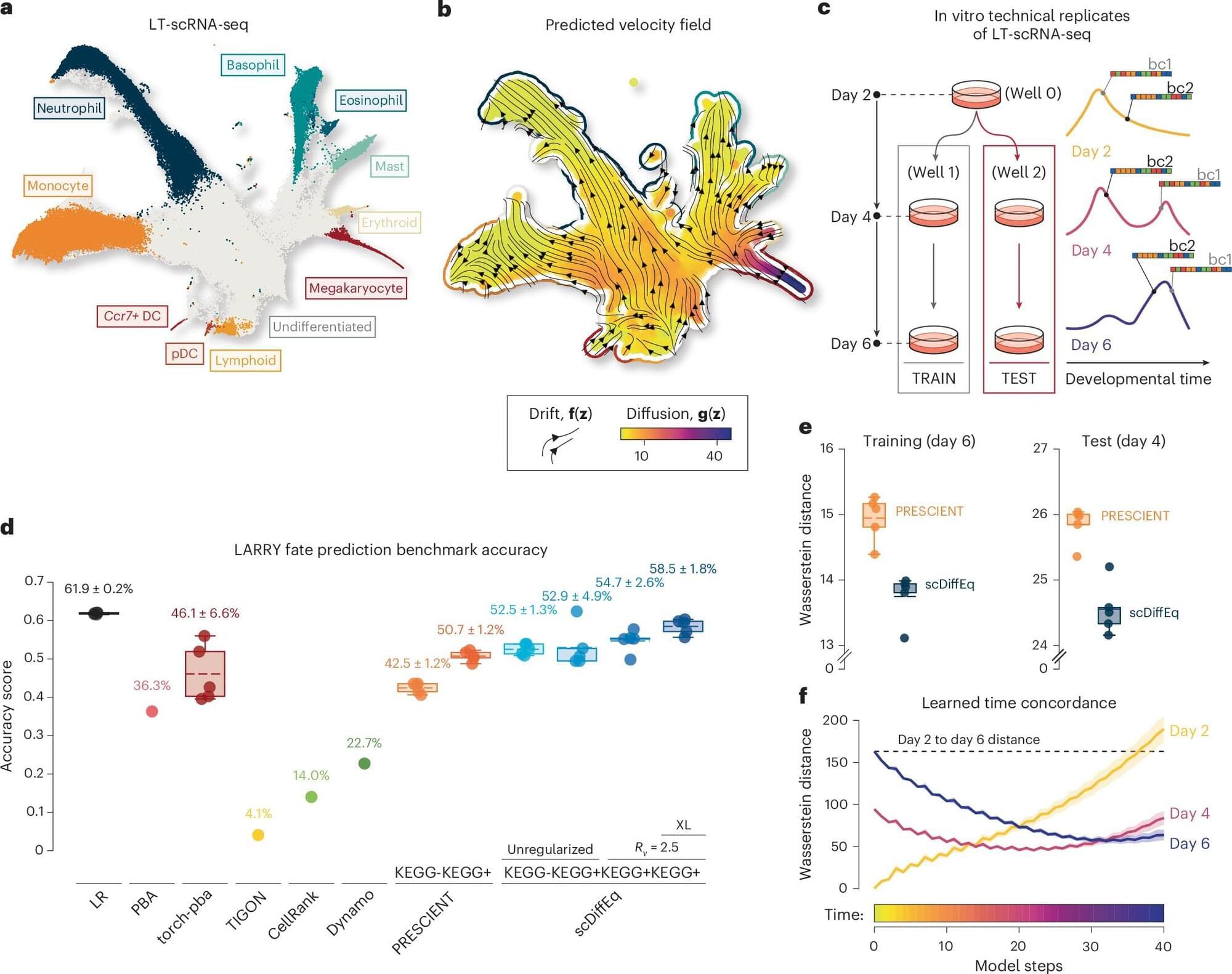
The development of humans and other animals unfolds gradually over time, with cells taking on specific roles and functions via a process called cell fate determination. The fate of individual cells, or in other words, what type of cells they will become, is influenced both by predictable biological signals and random physiological fluctuations.
Over the past decades, medical researchers and neuroscientists have been able to study these processes in greater depth, using a technique known as single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). This is an experimental tool that can be used to measure the gene activity of individual cells.
To better understand how cells develop over time, researchers also rely on mathematical models. One of these models, dubbed the drift-diffusion equation, describes the evolution of systems as the combination of predictable changes (i.e., drift) and randomness (i.e., diffusion).