A new study shows that tiny gold particles could circumvent damaged photoreceptors in patients with macular degeneration and help restore vision.


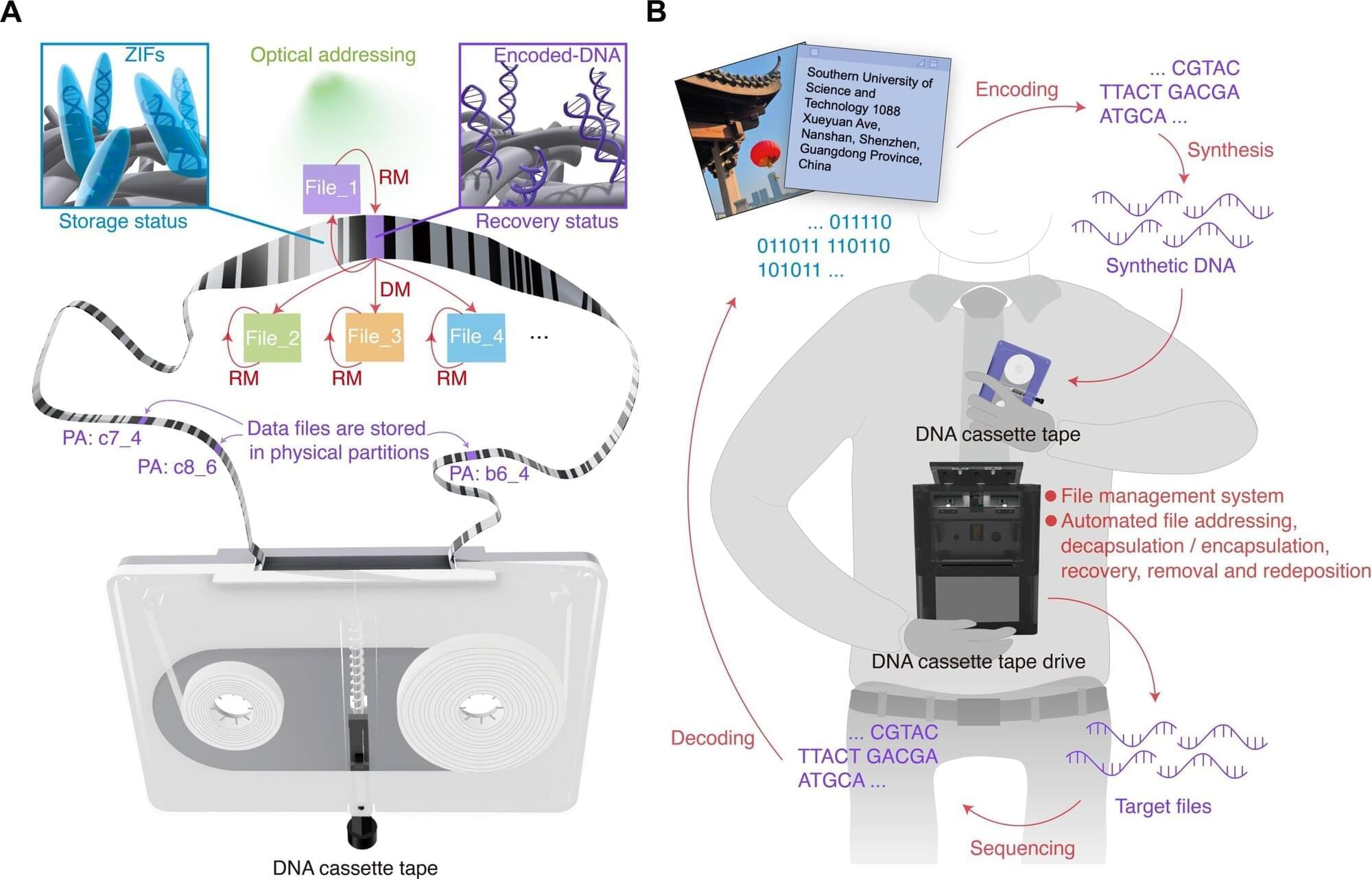
Our increasingly digitized world has a data storage problem. Hard drives and other storage media are reaching their limits, and we are creating data faster than we can store it. Fortunately, we don’t have to look too far for a solution, because nature already has a powerful storage medium with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). It is this genetic material that Xingyu Jiang at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China and colleagues are using to create DNA storage cassettes.

A more precise and personalized form of electric brain stimulation may be a more effective and faster treatment for people with moderate to major depression compared to other similar treatments, according to a UCLA Health study.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, examined the effectiveness of a noninvasive brain stimulation treatment known as high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) in treating depression. Transcranial direct current stimulation uses electrodes placed on a patient’s scalp to deliver noninvasive, safe levels of electrical currents to targeted areas of the brain.
For depression, the treatment is used to target brain networks that regulate emotional processing and self-referential thoughts. TDCS has not been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a treatment for depression, and clinical research into various forms of tDCS is ongoing.
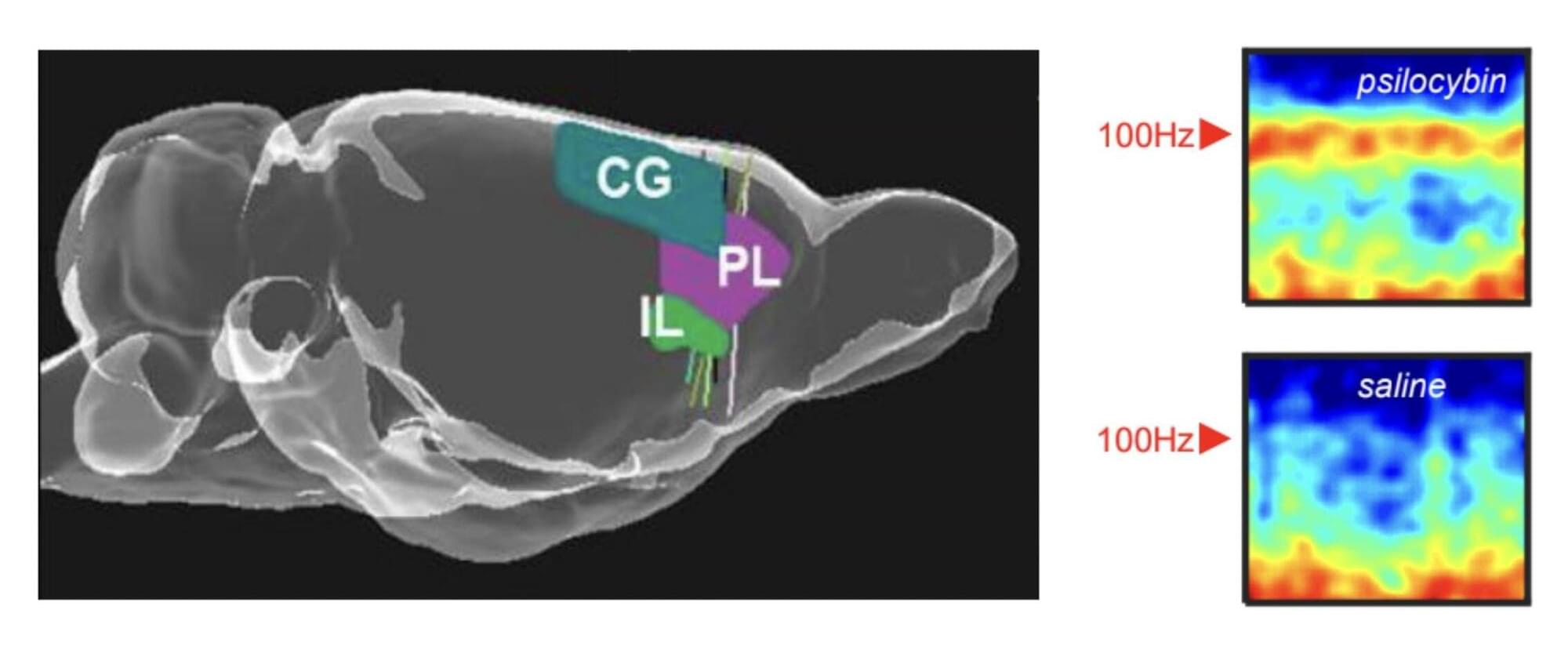
Psychedelics, a class of psychoactive drugs that typically induce peculiar mental states and hallucinations, are still prohibited for recreational use in most countries worldwide. In recent years, some neuroscientists and medical researchers have been exploring the potential therapeutic effects of these drugs, focusing on the treatment of depression, anxiety and various substance use disorders.
Researchers at the University of Bristol, Compass Pathways plc and other institutes recently carried out a new study involving rats, exploring the effects of the psychedelic compound on the activity of neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex, a brain region that supports decision-making, attention and the regulation of emotions. Their paper, published in Molecular Psychiatry, outlines some of the neural patterns associated with the intake of this compound, which had not yet been observed in human experiments.
“Psychedelic drugs like psilocybin have profound effects on our brains and minds,” Matt Jones, Professor of Neuroscience at the University of Bristol and senior author of the paper, told Medical Xpress. “These effects are fascinating and—as a long history of psychedelic use and recent clinical trials attest—potentially beneficial. This study was driven by two interrelated questions. Firstly, how does a relatively simple, small molecule alter brain activity to completely change our mental model of the world? Secondly, can those effects be harnessed to help treat mental illness?”

We take our understanding of where we are for granted, until we lose it. When we get lost in nature or a new city, our eyes and brains kick into gear, seeking familiar objects that tell us where we are.
How our brains distinguish objects from background when finding direction, however, was largely a mystery. A new study provides valuable insight into this process, with possible implications for disorientation-causing conditions such as Alzheimer’s. The work is published in the journal Science.
The scientists, based at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University and the University Medical Center Göttingen, ran an experiment with mice using ultrasound imaging to measure and record brain activity. The mice were shown visual stimuli, either an object or a scrambled image showing no distinct object.

Researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, have developed new organic compounds that act as highly sensitive oxygen sensors. These sensors can accurately detect even the slightest amounts of oxygen in the environment—information that is crucial in situations where oxygen concentration can determine the success of a process or even a person’s life.
The sensors can be applied in medicine; for example, in diagnosing tumor hypoxia, a condition in which there is almost no oxygen around a tumor; in the food industry, to check whether packaging has lost its seal; and in biotechnology, to precisely monitor cell cultivation processes.
Moreover, their performance can be observed with the naked eye, while their record-high sensitivity ensures rapid and reliable detection. The study is published in the journal Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.

A newly discovered set of mathematical equations describes how to turn any sequence of random events into a clock, scientists at King’s College London reveal. The paper is published in the journal Physical Review X.
The researchers suggest that these formulas could help to understand how cells in our bodies measure time and to detect the effects of quantum mechanics in the wider world.
Studying these timekeeping processes could have far-reaching implications, helping us to understand proteins with rhythmic movements which malfunction in motor neuron disease or chemical receptors that cells use to detect harmful toxins.

Rice University biosciences professor Matthew Bennett has received a $1.99 million grant from the National Science Foundation to lead research on engineered bacterial consortia that could form the basis of biological computing systems. The four-year project will also involve co-principal investigators Kirstin Matthews, Caroline Ajo-Franklin and Anastasios Kyrillidis from Rice along with Krešimir Josić from the University of Houston. The research team aims to develop platforms that integrate microbial sensing and communication with electronic networks, paving the way for computing systems constructed from living cells instead of traditional silicon-based hardware.
The project highlights the growing potential of synthetic biology, where microbes are examined not just as living organisms but as processors of information. If successful, Bennett’s research could accelerate medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring and the development of next-generation computing applications.
“Microbes are remarkable information processors, and we want to understand how to connect them into networks that behave intelligently,” Bennett said. “By integrating biology with electronics, we hope to create a new class of computing platforms that can adapt, learn and respond to their environments.”
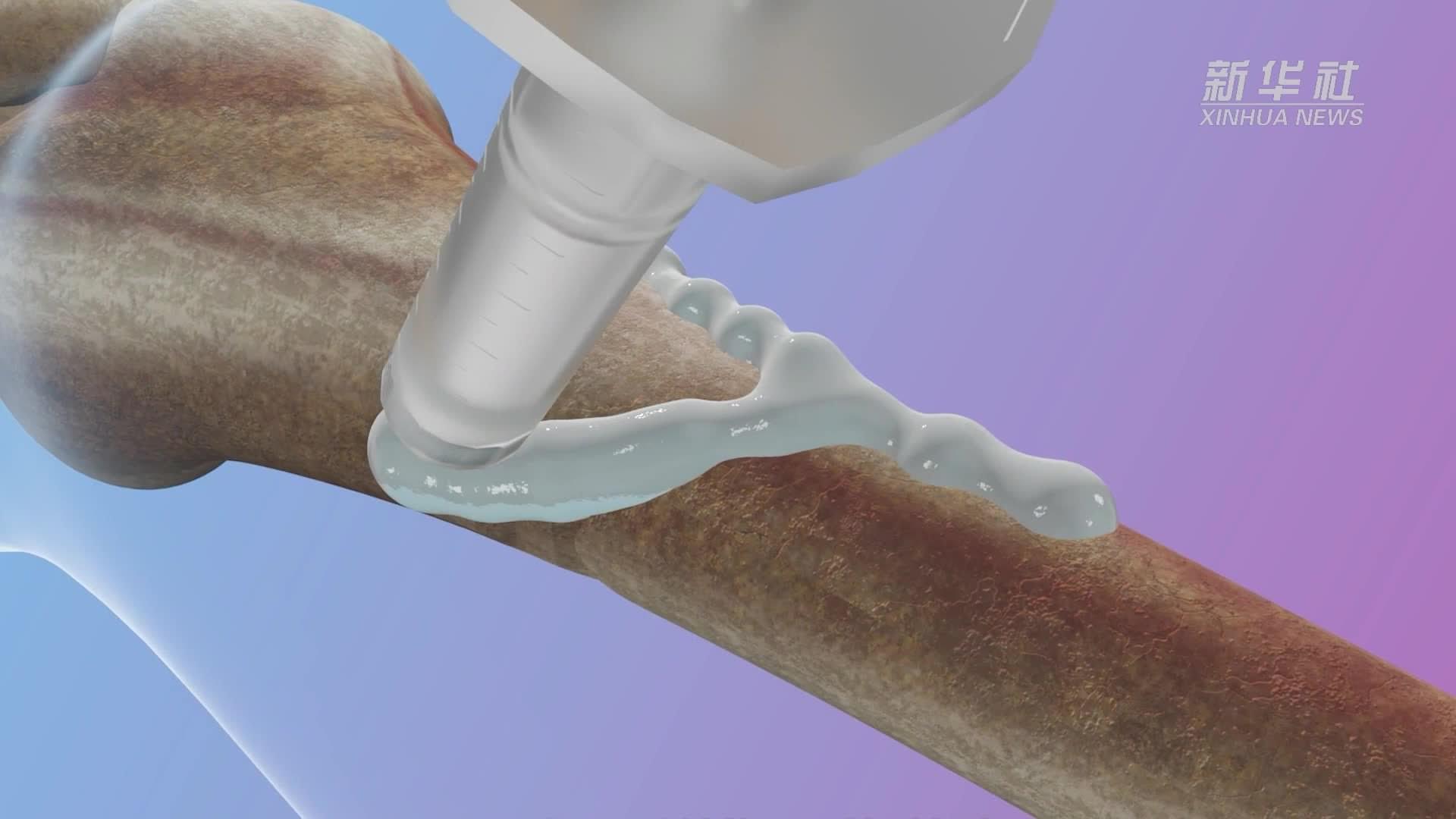
Material capable of securely bonding fractured bone fragments within 2–3 minutes in a blood-rich environment.
Chinese researchers on Tuesday unveiled their self-developed world’s first “bone glue” material capable of securely bonding fractured bone fragments within 2–3 minutes in a blood-rich environment.
Inspired by oysters, this new biomaterial, with a maximum adhesion strength of over… pic.twitter.com/7ozvRrQBP0— China Science (@ChinaScience) September 10, 2025
ในช่วงไม่กี่ปีที่ผ่านมา จีนได้แสดงศักยภาพด้านวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์อย่างต่อเนื่อง หนึ่งในผลงานที่ได้รับความสนใจระดับโลกคือการพัฒนาวัสดุชีวภาพชนิดใหม่ที่เรียกว่ากาวกระดูก (Bine Glue) ที่สามารถเชื่อมกระดูกที่หักให้ติดกันได้ภายในระยะเวลาเพียง 3 นาที