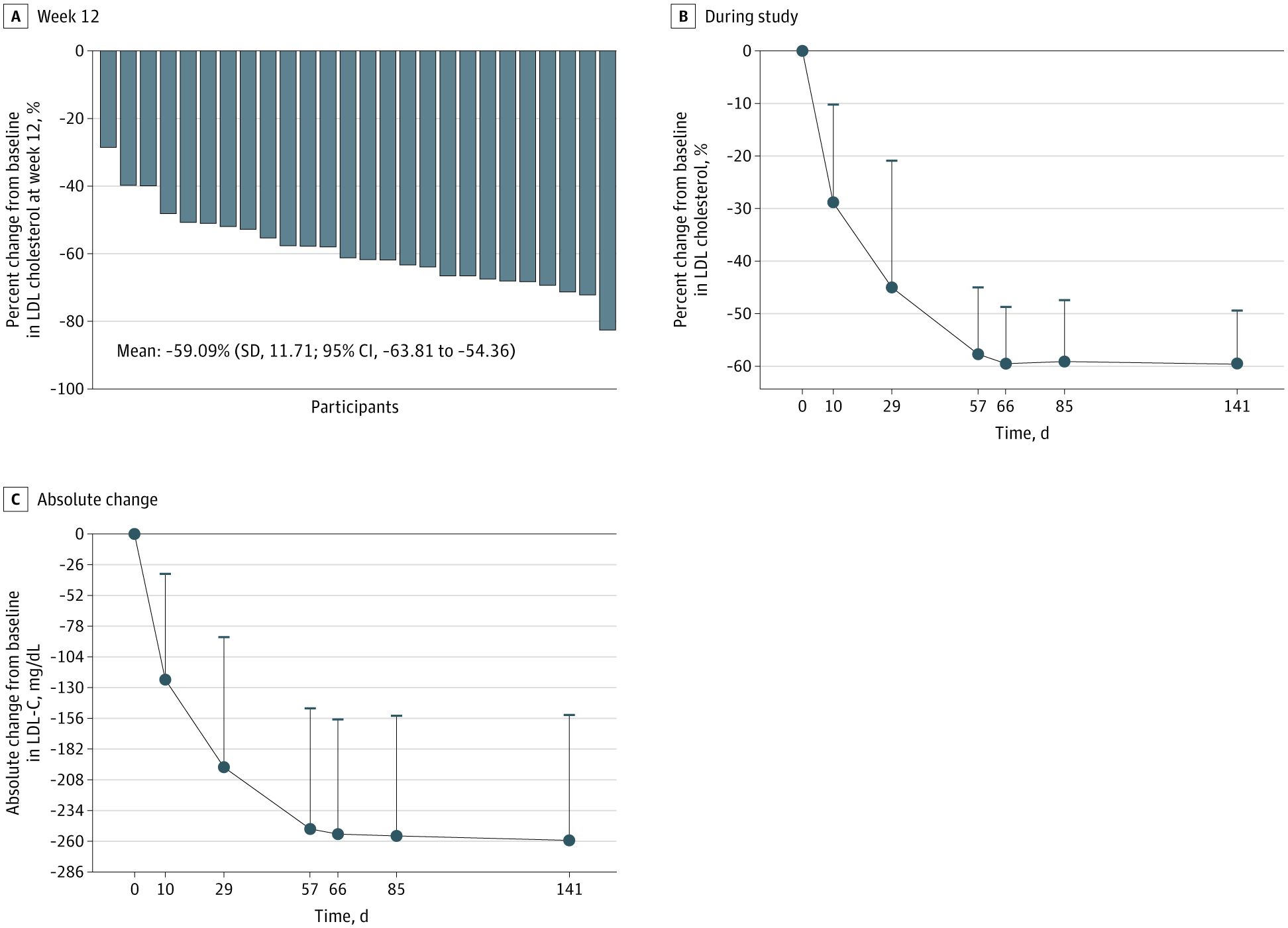
Monthly subcutaneous SHR-1918, a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting ANGPTL3, was associated with reduced LDL-C in adults with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia on stable lipid-lowering therapy.
Question Does SHR-1918, a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting angiopoietinlike 3 (ANGPTL3), lower the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level in adults with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) taking stable lipid-lowering therapy?
Findings In this phase 2 nonrandomized clinical trial of 26 patients, SHR-1918 at 600 mg every 4 weeks was associated with a substantial reduction in LDL-C level exceeding half in adults with HoFH taking stable lipid-lowering therapy and was also associated with lower levels of other lipids, with evidence of a manageable safety profile.
Meaning The promising findings observed in this trial support the launch of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 randomized clinical trial to verify the effect and safety of SHR-1918 for HoFH management.