Aug 5, 2024
MIT Claims New Artificial Neuron 1 Million Times Faster Than the Real Thing
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: robotics/AI
Think and you’ll miss it: researchers at MIT claim to have successfully created analog synapses that are one million times faster than those in our human brains.
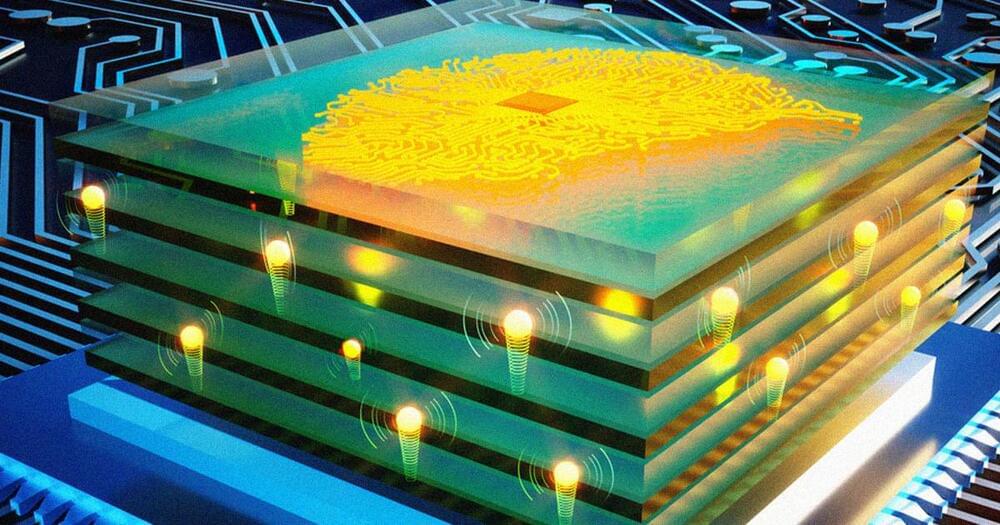
Just as digital processors need transistors, analog ones need programmable resistors. Once put into the right configuration, these resistors can be used to create a network of analog synapses and neurons, according to a press release.
These analog synapses aren’t just ultra-fast, they’re remarkably efficient, too. And that’s pretty important, because as digital neural networks grow more advanced and powerful, they require more and more energy, increasing their carbon footprint considerably.