Nov 26, 2024
Cyanobacterial circadian clock uses an AM radio-like mechanism to control cellular processes
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biological, media & arts, physics
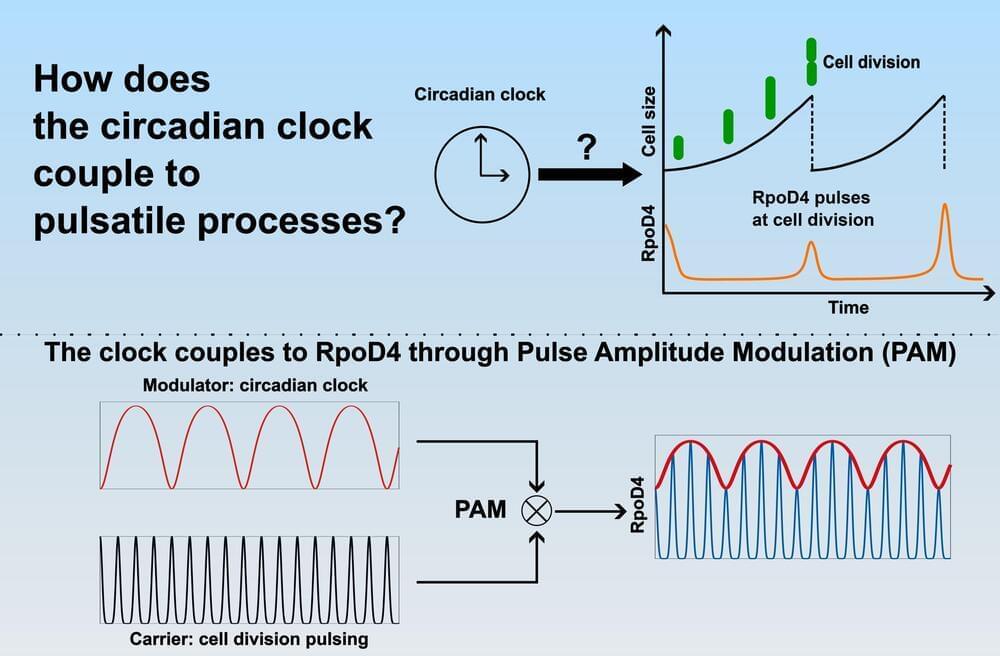
Cyanobacteria, an ancient lineage of bacteria that perform photosynthesis, have been found to regulate their genes using the same physics principle used in AM radio transmission.
New research published in Current Biology has found that cyanobacteria use variations in the amplitude (strength) of a pulse to convey information in single cells. The finding sheds light on how biological rhythms work together to regulate cellular processes.
In AM (amplitude modulation) radio, a wave with constant strength and frequency—called a carrier wave—is generated from the oscillation of an electric current. The audio signal, which contains the information (such as music or speech) to transmit, is superimposed onto the carrier wave. This is done by varying the amplitude of the carrier wave in accordance with the frequency of the audio signal.