This cave may have been home to some of the last Neanderthals on Earth.


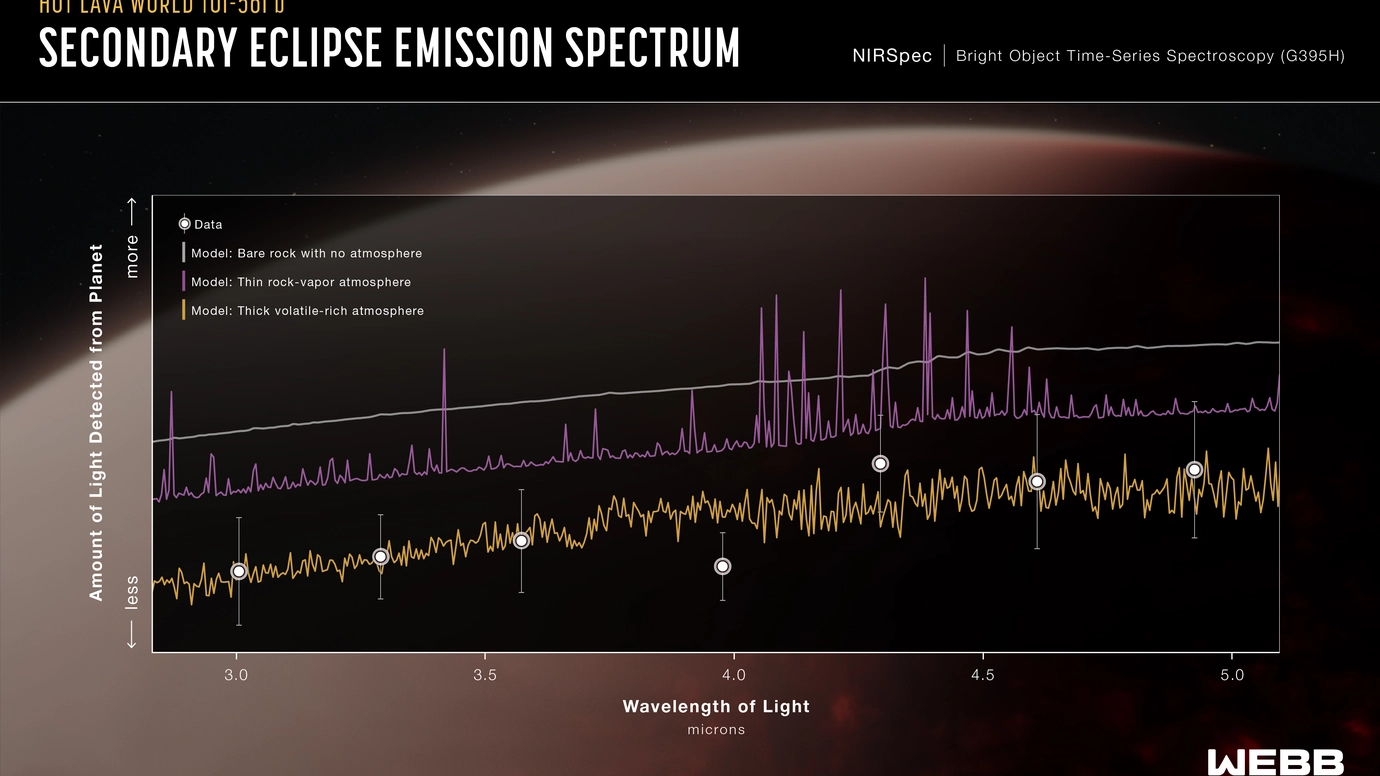
A Carnegie-led team of astronomers detected the strongest evidence yet of an atmosphere around a rocky planet beyond our solar system. Their work, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, used NASA’s JWST to reveal an alien atmosphere in an unexpected place—an ancient, ultra-hot super-Earth that likely hosts a magma ocean.
TOI-561 b is a rocky world that’s about twice Earth’s mass but bears little resemblance to our home planet due to its proximity to its host star. Although the star is slightly less massive and cooler than our sun, the planet orbits at one fortieth the distance of Mercury in our own solar system. On TOI-561 b, a year lasts just 10.56 hours, and one side of the planet is in perpetual daylight.
“Based on what we know about other systems, astronomers would have predicted that a planet like this is too small and hot to retain its own atmosphere for long after formation,” explained Carnegie Science Postdoctoral Fellow Nicole Wallack, the paper’s second author. “But our observations suggest it is surrounded by a relatively thick blanket of gas, upending conventional wisdom about ultra-short-period planets.”


The TOI Tech Desk is a dedicated team of journalists committed to delivering the latest and most relevant news from the world of technology to readers of The Times of India. TOI Tech Desk’s news coverage spans a wide spectrum across gadget launches, gadget reviews, trends, in-depth analysis, exclusive reports and breaking stories that impact technology and the digital universe. Be it how-tos or the latest happenings in AI, cybersecurity, personal gadgets, platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, Facebook and more; TOI Tech Desk brings the news with accuracy and authenticity.

The road to a more sustainable planet may be partially paved with manganese. According to a new study by researchers at Yale and the University of Missouri, chemical catalysts containing manganese—an abundant, inexpensive metallic element—proved highly effective in converting carbon dioxide into formate, a compound viewed as a potential key contributor of hydrogen for the next generation of fuel cells.
The new study appears in the journal Chem. The lead authors are Yale postdoctoral researcher Justin Wedal and Missouri graduate research assistant Kyler Virtue; the senior authors are professors Nilay Hazari of Yale and Wesley Bernskoetter of Missouri.


Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless chemical compound comprised of nitrogen and hydrogen that is widely used in agriculture and in industrial settings. Among other things, it is used to produce fertilizers, as well as cleaning products and explosives.
Currently, ammonia is primarily produced via the so-called Haber-Bosch process, an industrial technique that entails prompting a reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen at very high temperatures and pressure. Despite its widespread use, this process is known to be highly energy-intensive and is estimated to be responsible for approximately 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Researchers at Stanford University School of Engineering, Boston College and other institutes have identified new promising catalysts (i.e., materials that speed up chemical reactions) that could enable the sunlight-driven synthesis of ammonia at room temperature and under normal atmospheric pressure.

Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter like PM2.5 components in polluted air can not only cause respiratory diseases, but also increase the risk of depression in older people, especially in those living with preexisting heart, metabolic and neurological conditions.
Depression has caused more loss of healthy life worldwide than any other mental health condition. This disorder has snatched away people’s will to perform the basics of daily activities. An analysis of global health data in 2021 showed that all the years people lived with disability or reduced quality of life because of depression added up to about 56.3 million years.
A recent population-based cohort study collected data from nearly 23.7 million U.S. Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older between 2000 and 2018 to examine specific components of PM2.5 exposure, both individually and in combination, and its associations with the risk of developing depression. Among those tracked, more than 5.5 million developed depression during the follow-up period. These findings are published in JAMA Network Open.