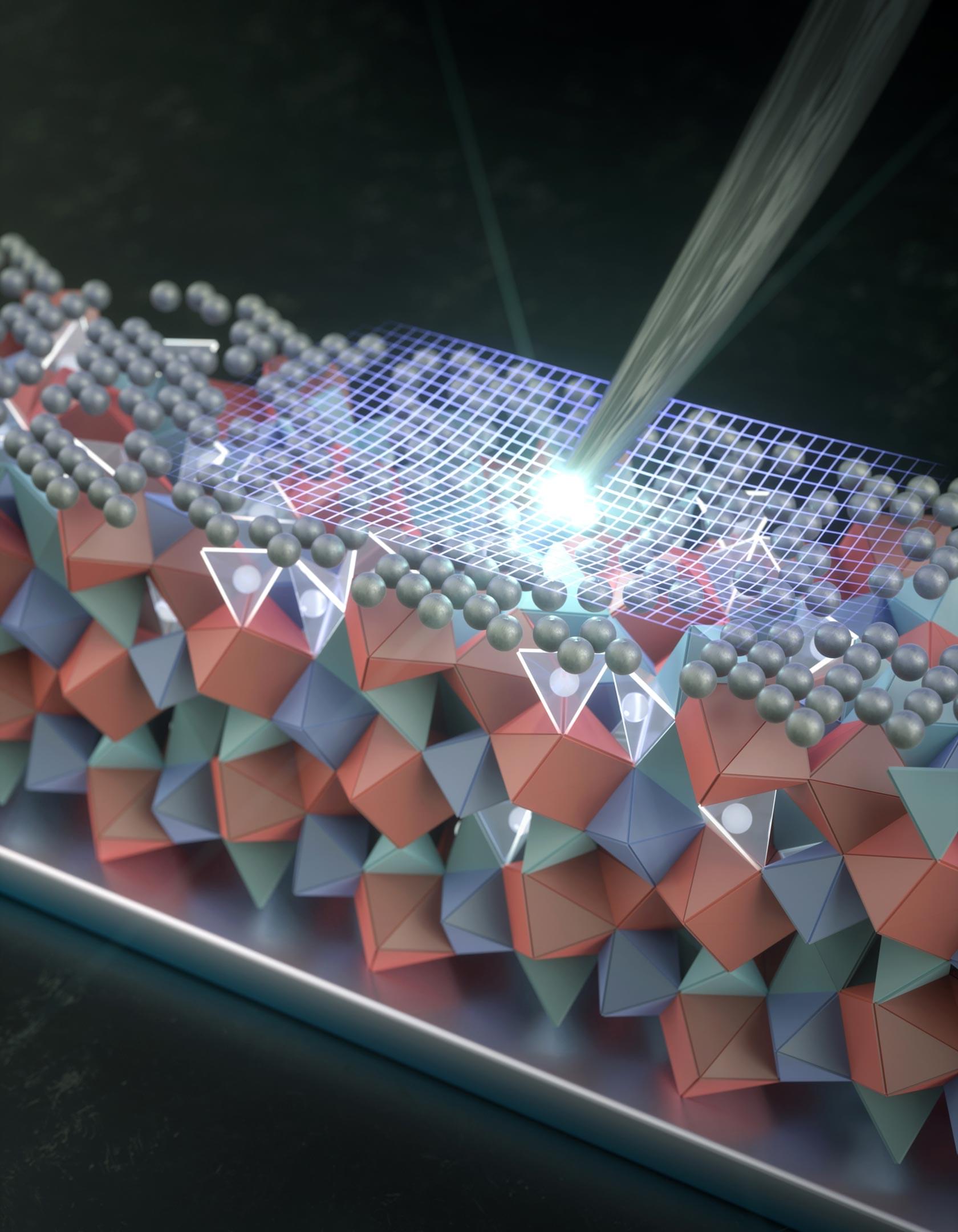
A nanoscale silver coating could be the key to making ultra-powerful solid-state batteries finally work.
Replacing the liquid electrolyte inside today’s batteries with a solid one could unlock a new generation of rechargeable lithium metal batteries. In theory, these batteries would be safer, store far more energy, and recharge much faster than the lithium-ion batteries now in widespread use. Scientists and engineers have been chasing this goal for decades, but progress has been slowed by a persistent flaw. Solid, crystal-based electrolytes tend to develop microscopic cracks that gradually spread during repeated charging and use, eventually causing the battery to fail.
A thin silver layer with a big impact.