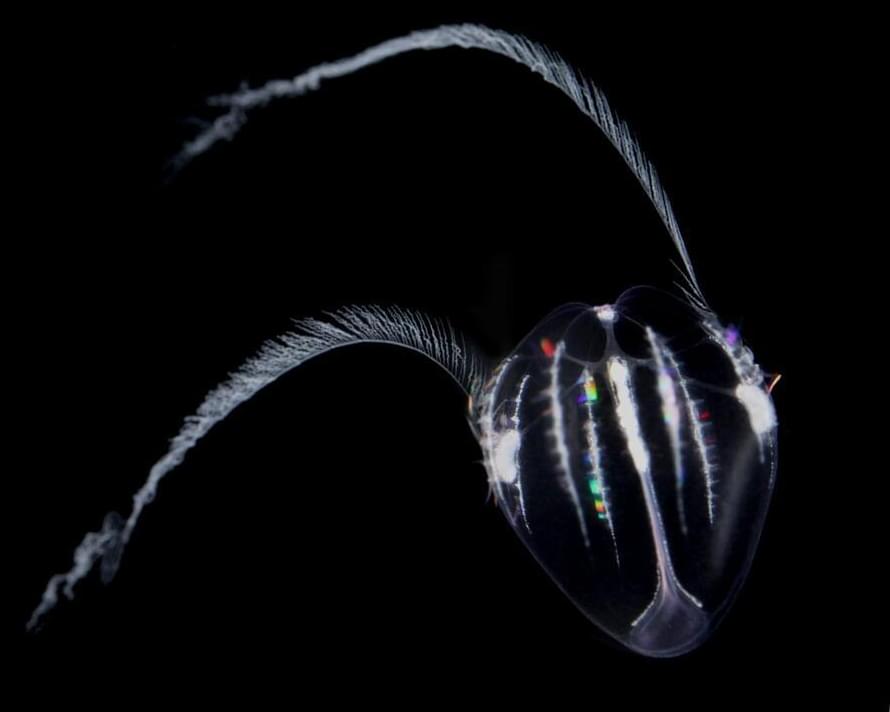
A recent article in PNAS unveils a remarkable discovery: the ability for reverse development in a ctenophore, commonly known as a comb jelly. These findings indicate that life cycle flexibility in animals may be more widespread than previously believed.
Animal life cycles typically follow a familiar pattern, declined in countless variations: they are born, grow, reproduce, and die, giving way to the next generation. Only a few species are able to deviate from this general principle, the best-known example being the ‘immortal jellyfish’ Turritopsis dohrnii, which can revert from an adult medusa back to a polyp. This elusive group of animals with flexible life cycles now includes the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi.
“The work challenges our understanding of early animal development and body plans, opening new avenues for the study of life cycle plasticity and rejuvenation. The fact that we have found a new species that uses this peculiar “time-travel machine” raises fascinating questions about how spread this capacity is across the animal tree of life,” said Joan J. Soto-Angel, a postdoctoral fellow in the Manet Team at the Department of Natural History at the University of Bergen.