We showed that a void model is about one hundred million times more likely than a void-free model.



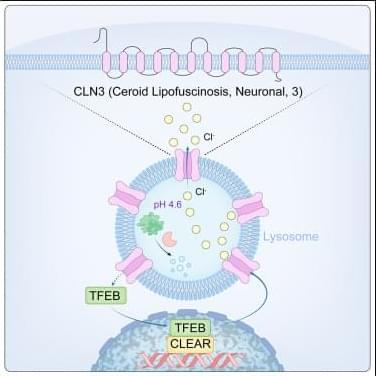
Lysosomes degrade damaged organelles and macromolecules to recycle nutrient components. Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are linked to mutations of genes encoding lysosomal proteins and may lead to age-related disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases. But, how lysosomal dysfunction contributes to neurodegenerative diseases is not clear yet…
The researchers identify CLN3 (ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal 3), linked to Batten disease as a conserved lysosomal protein that regulates lysosomal chloride homeostasis, pH, and protein degradation.
Curcumin analog C1 is a natural compound with anti-inflammatory properties could enhance CLN3 activity and improve lysosomal function by activating TFEB. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/CLN3-n-chloride-efflux-n-lysosomes
Wang et al. identify CLN3 as a conserved lysosomal protein that regulates lysosomal chloride homeostasis, pH, and protein degradation. Transcription factor EB (TFEB) activation enhances CLN3 function, revealing the TFEB-CLN3 signaling axis as a promising therapeutic target for lysosomal storage disorders.
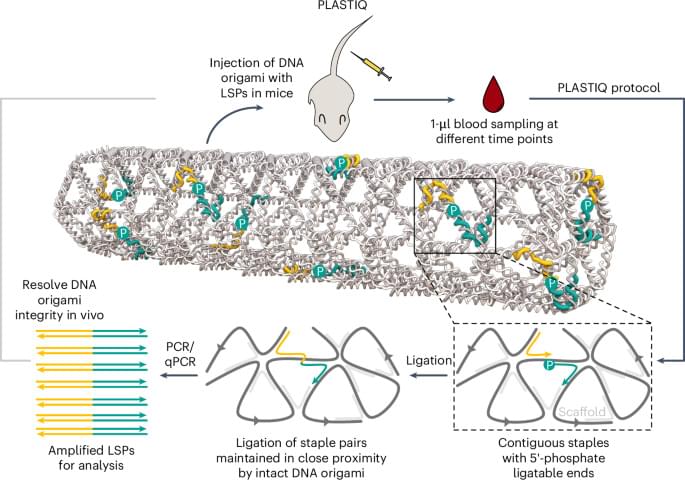
Impressive leap forwards for DNA origami: an elegant staple strand proximity ligation method for tracking DNA origami pharmacokinetics in vivo! This approach even allows analysis of stability of subregions within a DNA origami nanostructure. I think DNA origami has a lot of therapeutic potential, so it is exciting to see this solution to one of its translational barriers. Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-025-02091-z Paper title: “Resolving DNA origami structural integrity and pharmacokinetics in vivo”
Using origami samples in test tubes, we sequentially performed ligation, PCR and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE; Fig. 2a). For both Wrod and Lrod, amplification bands appeared only after ligation (Supplementary Fig. 3) and matched the sizes of single-LSP controls (Fig. 2d, g). When the origami was heat denatured before ligation, no LSP bands were detected (Fig. 2e, h), confirming that proximity ligation requires intact structures. By contrast, we showed that scaffold-targeted qPCR or origamiFISH assays37,38 still detected DNA regardless of the structural state (Fig. 2e, h), emphasizing their inability to distinguish intact origami from degraded origami.
Previous studies have shown that the coating of DNA nanostructures with the oligolysine-PEG polymer can protect them against nucleases and denaturation in low-salt environments, potentially increasing their stability in vivo23. Since PEGylation confers a physical barrier for the interaction of enzymes with DNA helices, we hypothesized that the ligase might also have decreased accessibility to PEGylated origamis. However, our in vitro experiments with PEGylated PEG-Lrod showed comparable ligation and amplification efficiencies to the bare Lrod (Supplementary Fig. 4). Another approach to enhance lattice-based origami stability in low-salt buffers and improved resistance to nucleases is sequence-specific covalent UV crosslinking26. We tested the application of the PLASTIQ protocol to a crosslinked version of the Lrod (UV-Lrod) with the same LSPs as Lrod. We observed a similar amplification pattern when compared to the non-crosslinked Lrod after PAGE electrophoresis of the pooled PCR-amplified LSPs (Extended Data Fig. 1).
Together, these results demonstrate that PLASTIQ reliably detects DNA origami integrity at the single-helix level for both wireframe and lattice designs, and that it is compatible with PEGylated or UV-crosslinked nanostructures.
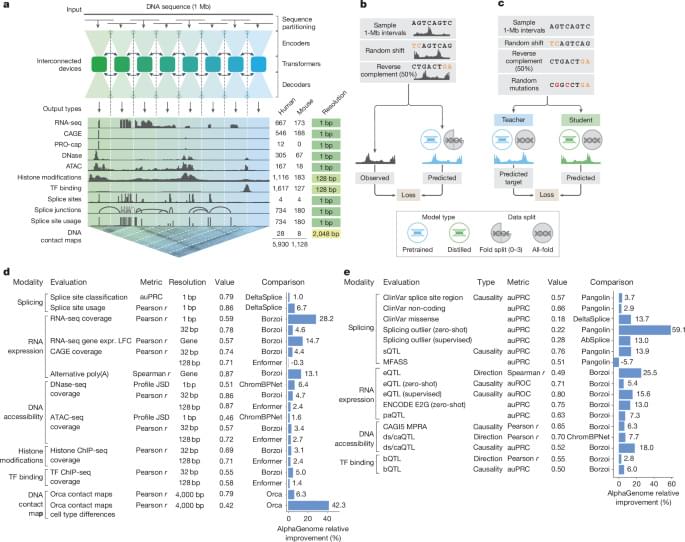
What makes it special is its versatility. Where older models might only predict how a mutation affects gene activity, AlphaGenome forecasts thousands of biological outcomes simultaneously—whether a variant will alter how DNA folds, change how proteins dock onto genes, disrupt the splicing machinery that edits genetic messages, or modify histone “spools” that package DNA. It’s essentially a universal translator for genetic regulatory language.
AlphaGenome is a deep learning model designed to learn the sequence basis of diverse molecular phenotypes from human and mouse DNA (Fig. 1a). It simultaneously predicts 5,930 human or 1,128 mouse genome tracks across 11 modalities covering gene expression (RNA-seq, CAGE and PRO-cap), detailed splicing patterns (splice sites, splice site usage and splice junctions), chromatin state (DNase, ATAC-seq, histone modifications and transcription factor binding) and chromatin contact maps. These span a variety of biological contexts, such as different tissue types, cell types and cell lines (see Supplementary Table 1 for the summary and Supplementary Table 2 for the complete metadata). These predictions are made on the basis of 1-Mb of DNA sequence, a context length designed to encompass a substantial portion of the relevant distal regulatory landscape. For instance, 99% (465 of 471) of validated enhancer–gene pairs fall within 1 Mb (ref. 12).
AlphaGenome uses a U-Net-inspired2,13 backbone architecture (Fig. 1a and Extended Data Fig. 1a) to efficiently process input sequences into two types of sequence representations: one-dimensional embeddings (at 1-bp and 128-bp resolutions), which correspond to representations of the linear genome, and two-dimensional embeddings (2,048-bp resolution), which correspond to representations of spatial interactions between genomic segments. The one-dimensional embeddings serve as the basis for genomic track predictions, whereas the two-dimensional embeddings are the basis for predicting pairwise interactions (contact maps). Within the architecture, convolutional layers model local sequence patterns necessary for fine-grained predictions, whereas transformer blocks model coarser but longer-range dependencies in the sequence, such as enhancer–promoter interactions.
Ray Kurzweil predicts humans and AI will merge by 2045, boosting intelligence a millionfold with nanobots, bringing both hope and challenges for the future.
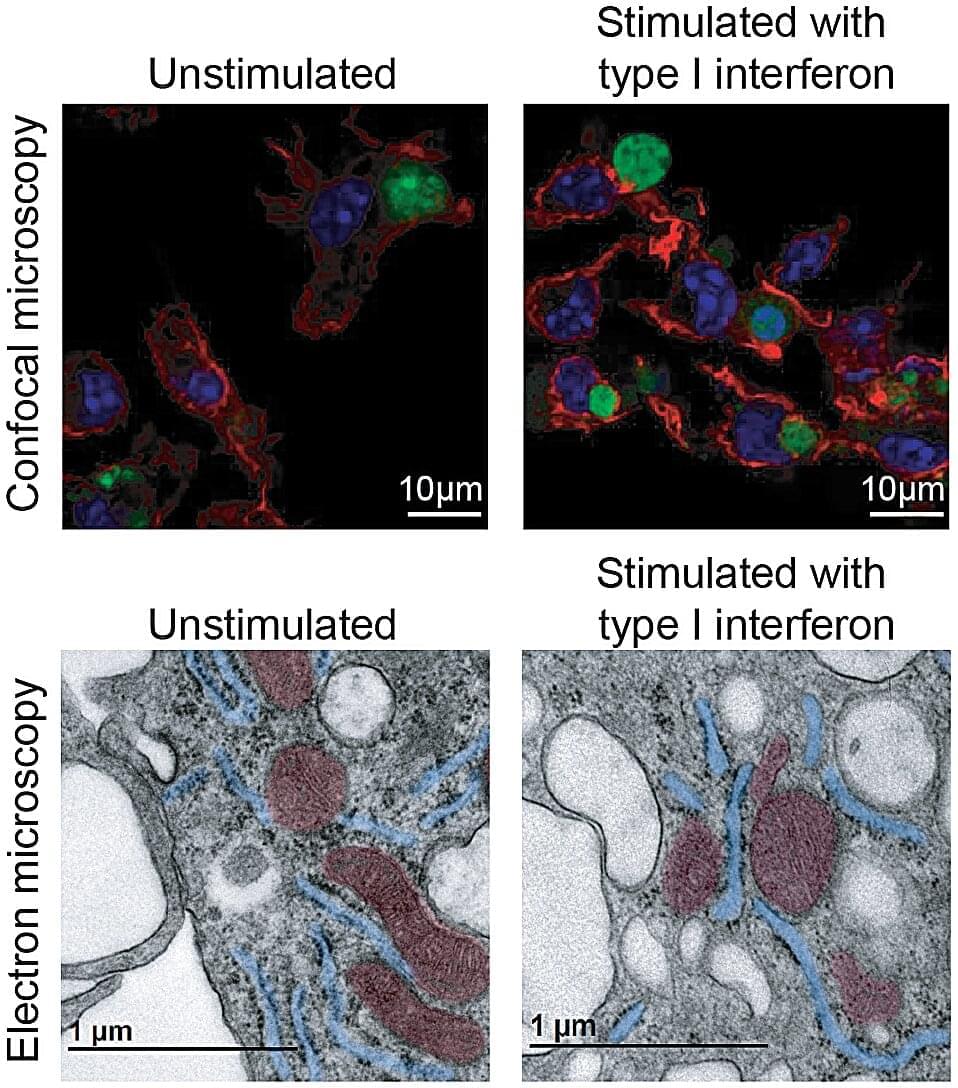
When our body fights an infection, the immune system must quickly activate defenses and trigger a beneficial inflammatory response. But it is just as important to resolve that inflammation and return to homeostasis. Macrophages play a key role in this balance: they are cells specialized in phagocytosing, or engulfing, cells that have died due to viral infection and in repairing infection—or inflammation—related tissue damage.
A study conducted at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC) and published in Immunity reveals the mechanism by which a signal associated with antiviral and inflammatory responses— type I interferon (IFN-I)—tunes macrophage mitochondria to enhance the clearance of tissue damage and prevent uncontrolled inflammation.
IFN-I is a cytokine that can promote either inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses, depending on the disease context. It activates a specific inflammatory program known as interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs).
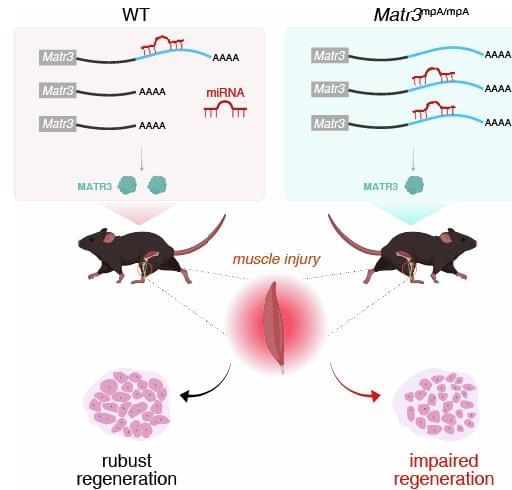
3′UTR shortening in muscle stem cell differentiation.
Global changes in alternative polyadenylation (APA) leads to alterations in 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) length and is accompanied by cell differentiation. However, APA role in muscle stem cell differentiation remain unclear.
The authors show that preferential 3′UTR shortening during stem cell differentiation occurs via CFI-mediated APA regulation.
They also demonstrate that 3′UTR shortening is a general strategy to escape repression by myomiRs.
This study reveals a tendency toward 3′UTR shortening, which alleviates miRNA repression of mRNAs critical for differentiation, ensuring efficient muscle differentiation and regeneration.
The authors used Matr3 expression to demonstrate the APA and miR-1/206 antagonistic role in myogenesis and they show that mutating the proximal Matr3 polyadenylation site in mice impairs muscle regeneration. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/3%E2%80%B2UTR-shortening-alleviates-miRNA-repression

About 1 in 7 users (14.6%) of injectable GLP-1 receptor agonists (RAs) have taken or are taking them at lower doses than those approved by the FDA, and many decided to do so without clinician input, a new survey found.
The most common reasons for GLP-1 RA microdosing are to manage tolerability, save money, and transition from weight loss to weight maintenance, according to the survey by Evidation, a California-based company that gathers healthcare information directly from members via its app.
The situation was far different among respondents who were actively microdosing — only 39.8% of them said they got their medication from their current healthcare clinician. Almost 24% reported getting their GLP-1 RA from a telehealth service. Less common sources included med spas, weight-loss clinics and directly from the manufacturer.
Telemedicine services typically offer lower-cost compounded versions of GLP-1 RAs, making them an attractive option for patients, noted an article in Medscape Medical News.
When asked about their most trusted source of information on microdosing, a larger percentage of GLP-1 RA users answered social media (26.8%) and online research (24.4%) than answered their healthcare clinician (20.3%).