A new analysis suggests modern satellite networks could suffer catastrophic collisions within days of losing control during a major solar storm. The phrase “House of Cards” is often associated today with a Netflix political drama, but its original meaning refers to a structure that is inherently
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Scientists Discover a New Quantum State of Matter Once Considered Impossible
A quantum state of matter has appeared in a material where physicists thought it would be impossible, forcing a rethink on the conditions that govern the behaviors of electrons in certain materials.
The discovery, made by an international team of researchers, could inform advances in quantum computing, improve electronic efficiencies, and deliver enhanced sensing and imaging technologies.
The state, described as a topological semimetal phase, was theoretically predicted to appear at low temperatures in a material composed of cerium, ruthenium, and tin (CeRu4Sn6), before experiments verified its existence.
Air Pollution Linked to Higher ALS Risk And Faster Decline
The scientist Stephen Hawking lived with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), the most common type of motor neurone disease, for 55 years. He was one of the longest-surviving people with the condition.
However, most people with motor neurone disease are not as lucky. It often progresses quickly, and many pass away within two to five years of diagnosis.
There is still no cure. Genetics account for only about 10% of cases, and the rest of the causes are still largely a mystery.
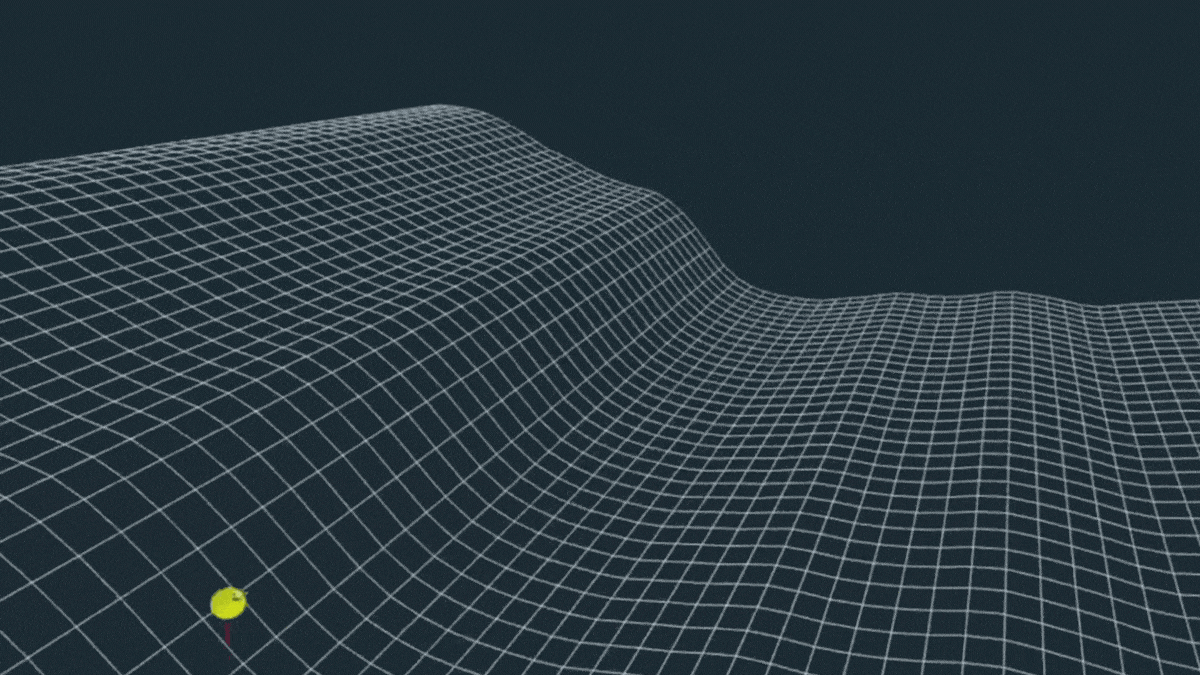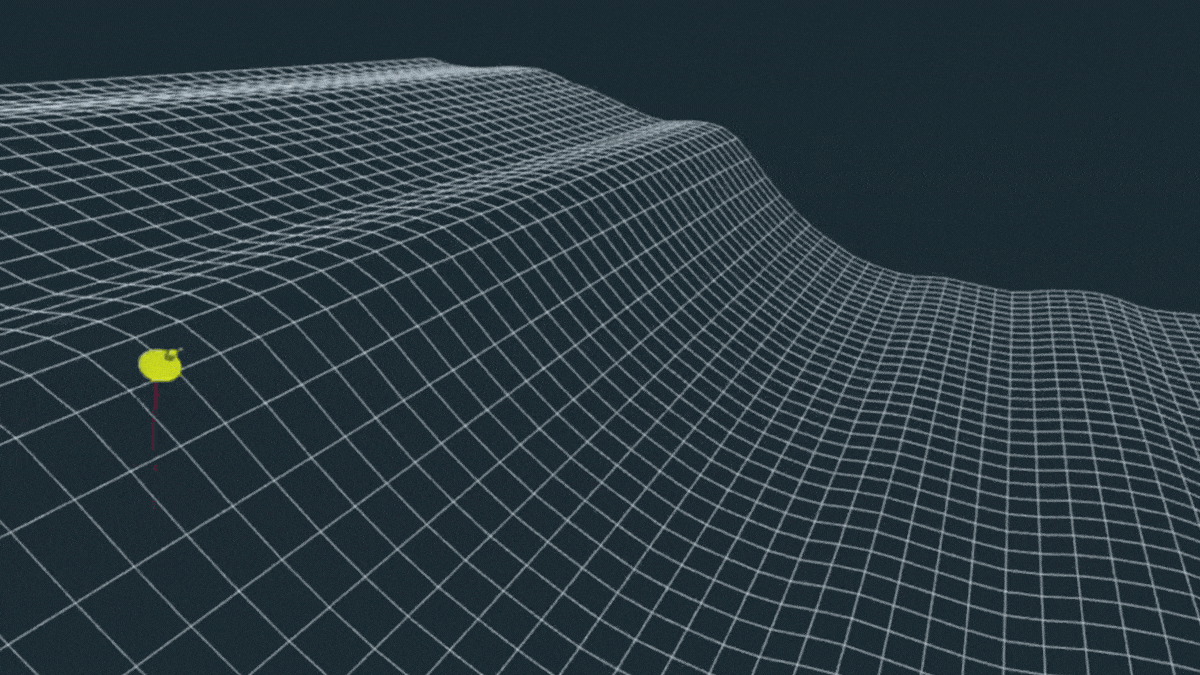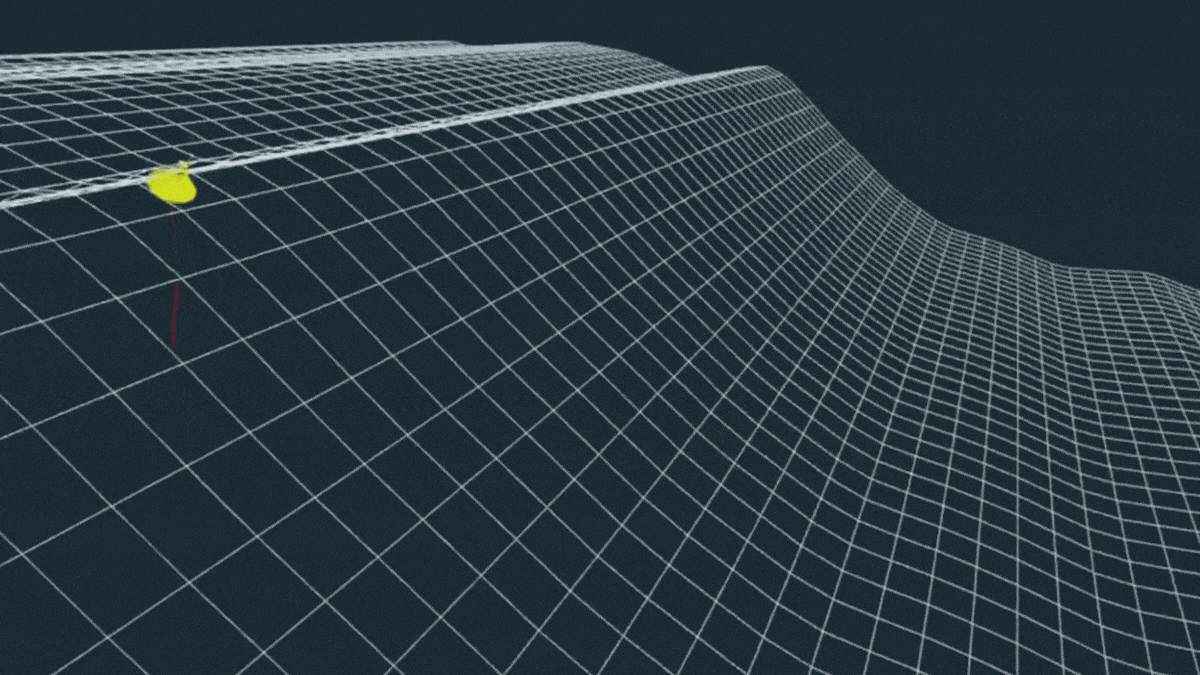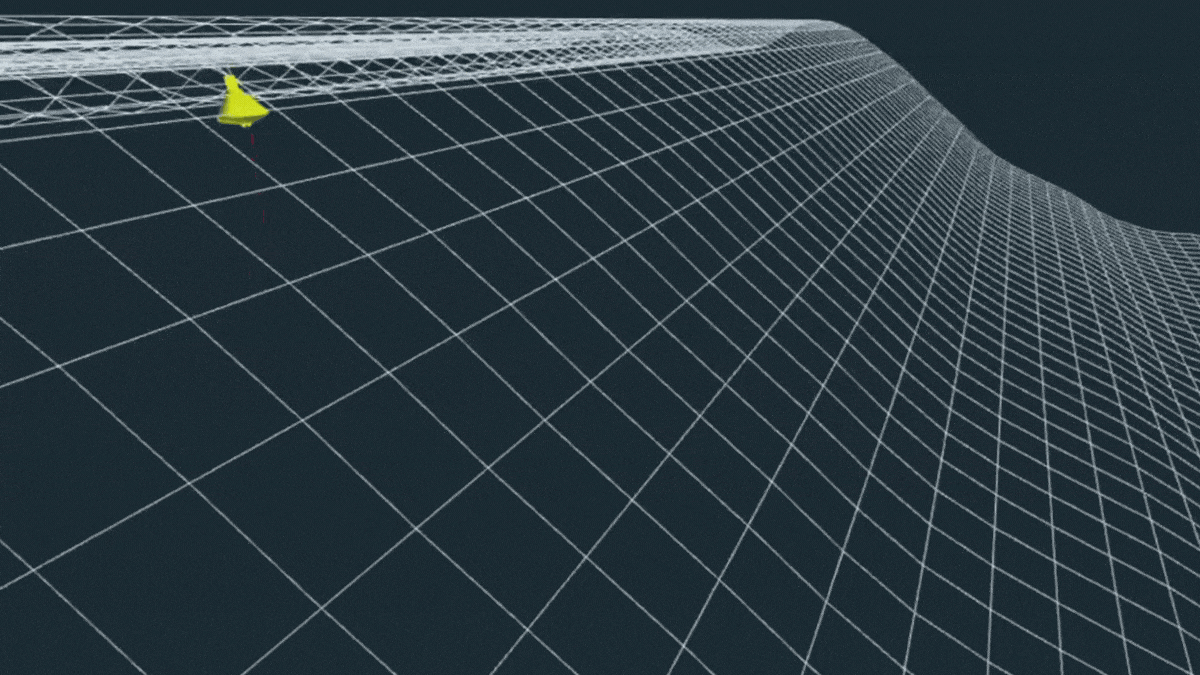
Gigantic Wave in The Pacific Was The Most Extreme ‘Rogue Wave’ on Record
In November 2020, a freak wave appeared, lifting a lone buoy off the coast of British Columbia 17.6 meters (58 feet) high.
A few years later, the four-story wall of water was confirmed to be the most extreme rogue wave ever recorded.
Such an extraordinary event is thought to happen only once every 1,300 years. And if the buoy hadn’t been taken for a ride, we might never have known it had occurred.

