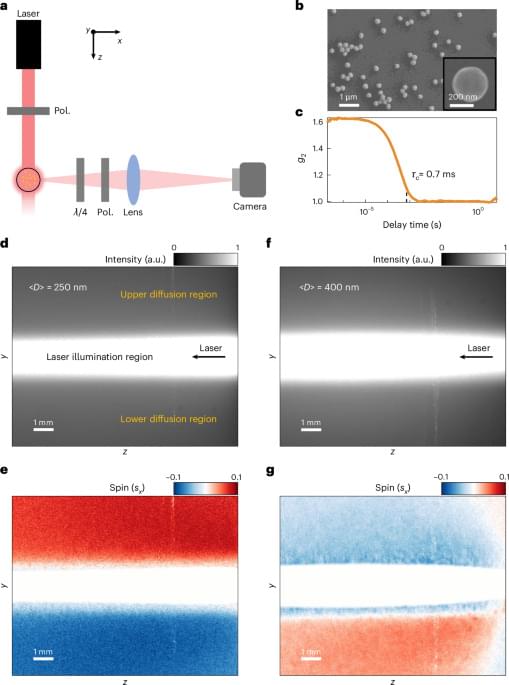
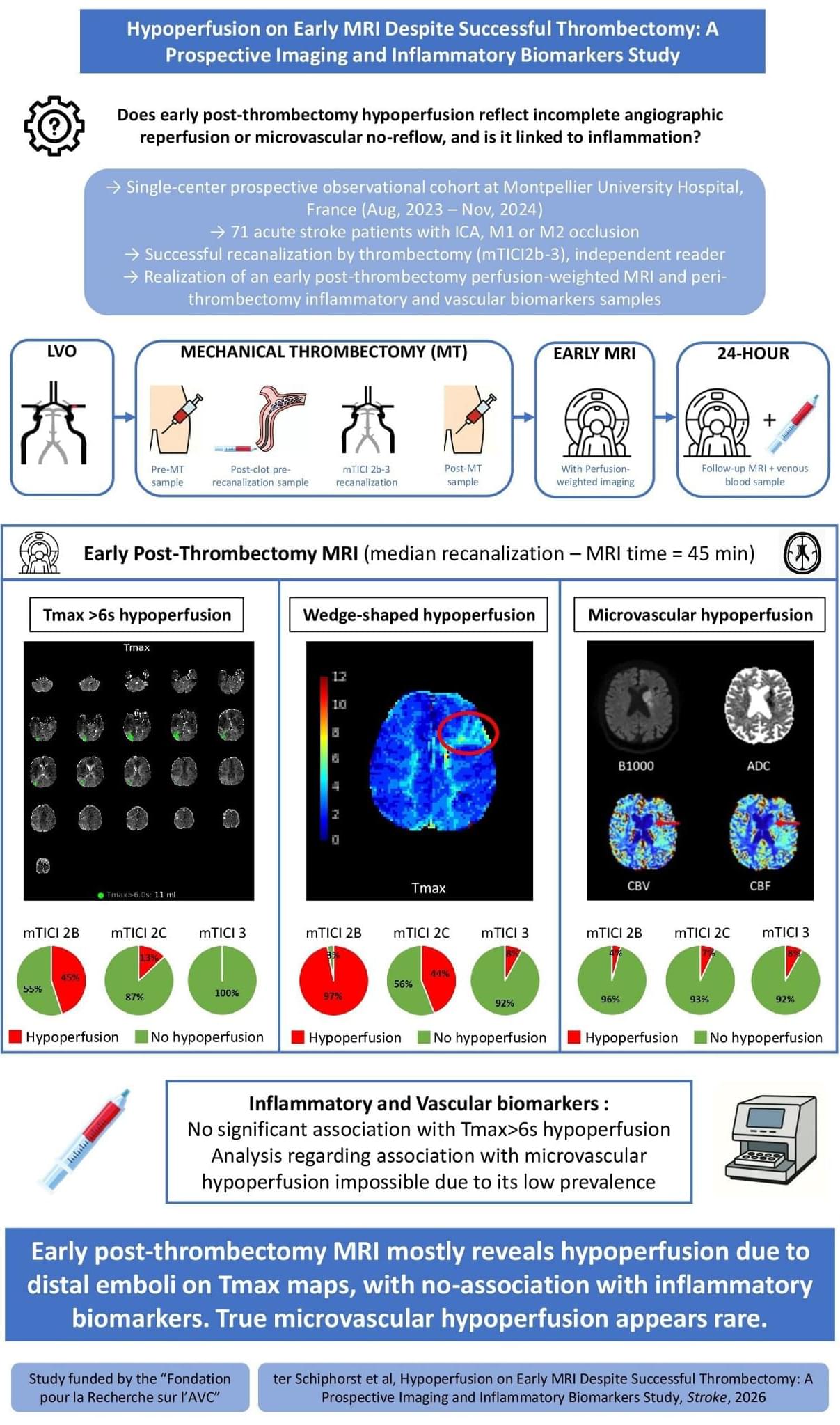
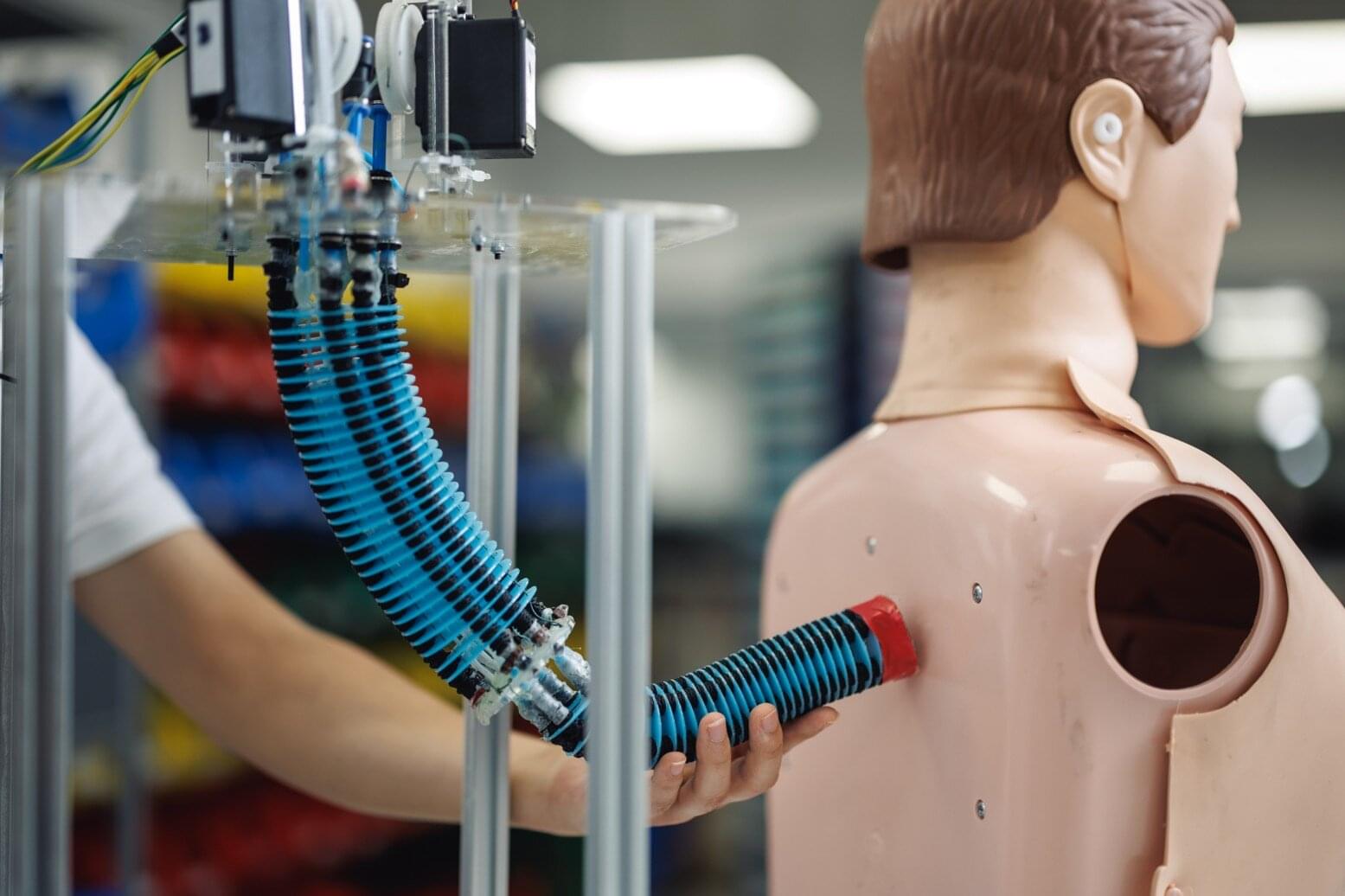
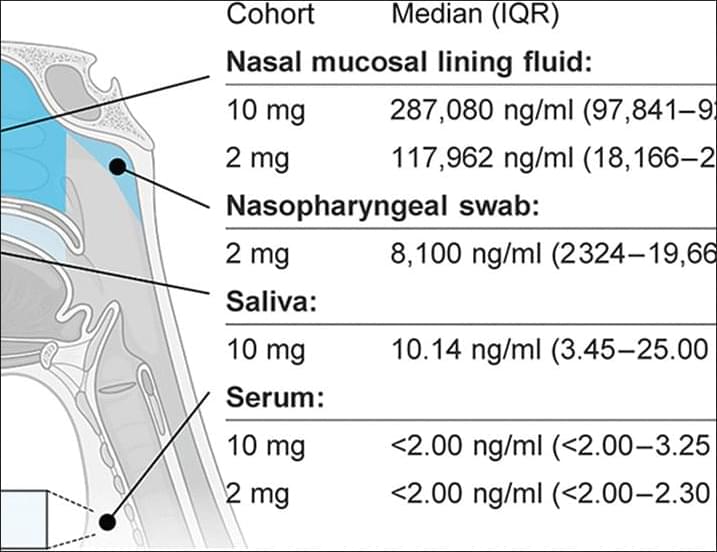
To become an Interplanetary Species we need to colonize another planet, and Mars will be our first target. To establish a base there, and a future settlement, we need to get their first, so we will also examine the Aldrin Cycler, a type of spacecraft that may make traveling to other worlds far easier.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
National Space Society Roadmap:
https://space.nss.org/nss-roadmap-to–… this channel to get access to perks: / @isaacarthursfia Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon:
/ isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord version:
/ mars-base-narration-only Credits: Becoming an Interplanetary Species: Mars Base Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur Episode 261; October 22, 2020 Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur Written by: Isaac Arthur Editors: Jerry Guern Keith Blockus Matthew Acker Cover Art: Jakub Grygier https://www.artstation.com/jakub_grygier Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik https://www.artstation.com/zeuxis_of_… Sam McNamara Sergio Botero https://www.artstation.com/sboterod?f… Tristan 3D Music Sergey Cheremisninov, “Sirius” https://www.s-cheremisinov.com Reign Pagaran, “Distant Voyager” Aerium, “Fifth Star of Aldebaran”
/ @officialaerium Denny Schneidemesser, “Across the Universe” & “Luminous Rays”
/ denny-schneidemesser.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @isaacarthursfia.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord version: / mars-base-narration-only.
Credits:
Becoming an Interplanetary Species: Mars Base.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 261; October 22, 2020
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Written by:
Isaac Arthur.
Editors: