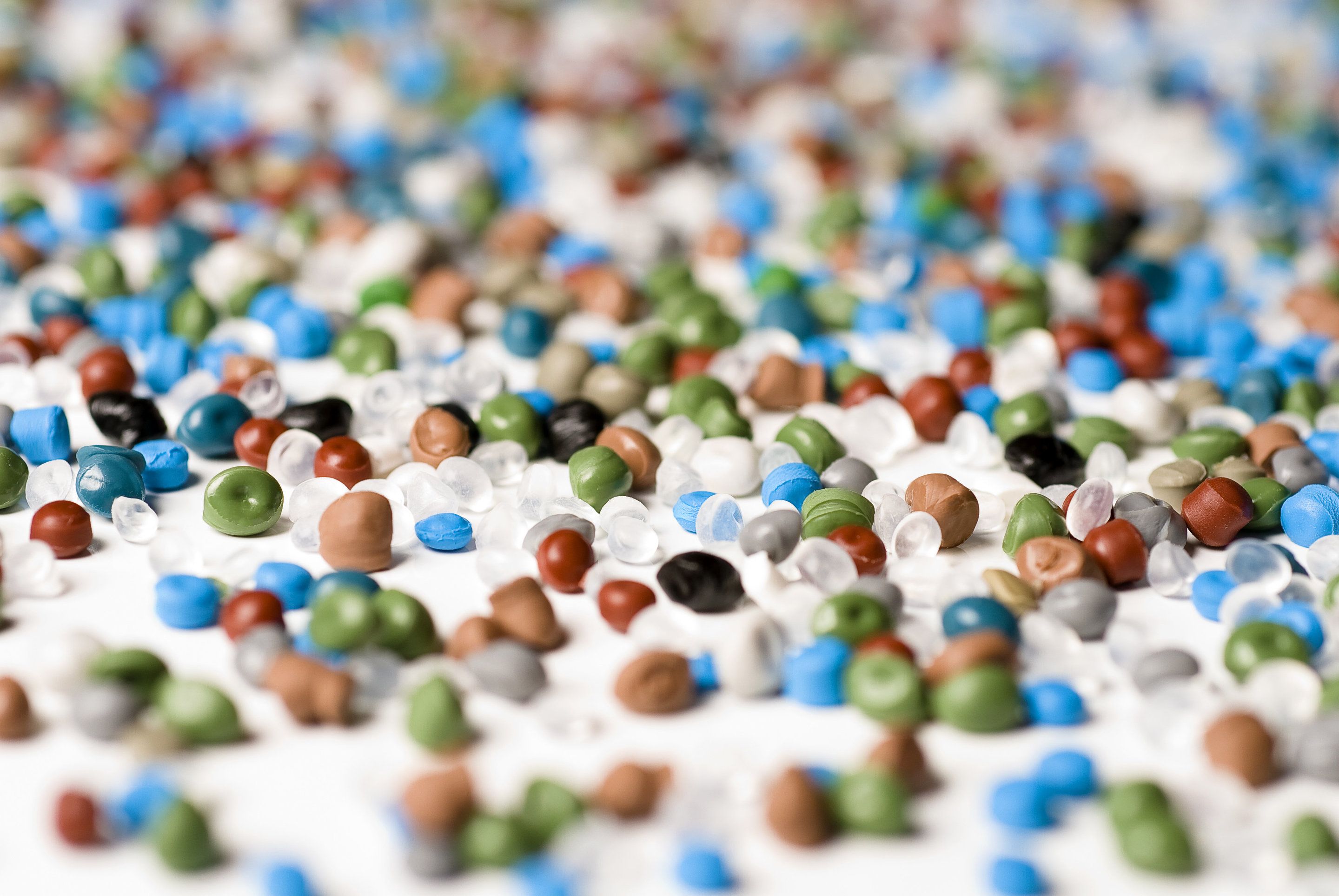
Nurdles. The name sounds inoffensive, cuddly even… However, nurdles are anything but. “Nurdle” is the colloquial name for “pre-production plastic pellets” (which is in itself rather a mouthful); these are the raw material of the plastic industry – the building blocks for plastic bottles, plastic bags, drinking straws, car components, computer keyboards – in fact almost anything you can think of that’s made of plastic.
However, nurdles are also covering our beaches. I found that out for myself when Fauna & Flora International (FFI) first started researching this issue in 2009. Having read about them I went looking on my local beach, and was shocked to find so many nurdles in the strandline and trapped in washed-up seaweed. I had never noticed them before, but they had clearly been accumulating for some time.
While pictures of the tide of larger plastics in the ocean are front page news, the issue of nurdle pollution has received much less attention. Recent storms, however, have resulted in higher levels of nurdles being reported from a range of sites around UK coasts, highlighting the numbers of nurdles that are in our waterways, seas and sediments – a level of pollution which we can only see when they are flushed out and onto the beach. The Great Nurdle Hunt (an initiative of our partner Fidra) has mapped nurdle finds from around the UK and Europe, which has identified a number of nurdle hotspots in key industrial estuaries. However, this problem isn’t unique to Europe; nurdles are reported worldwide, but only hit the headlines when there are significant local spills from containers lost at sea, as recently occurred in South Africa. However, such one-off events aren’t the only source of nurdle pollution.