Two intellectual property lawyers on why questions of AI inventorship and profit remain wide open



Many of the latest large language models (LLMs) are designed to remember details from past conversations or store user profiles, enabling these models to personalize responses. But researchers from MIT and Penn State University found that, over long conversations, such personalization features often increase the likelihood an LLM will become overly agreeable or begin mirroring the individual’s point of view.
This phenomenon, known as sycophancy, can prevent a model from telling a user they are wrong, eroding the accuracy of the LLM’s responses. In addition, LLMs that mirror someone’s political beliefs or worldview can foster misinformation and distort a user’s perception of reality.
Unlike many past sycophancy studies that evaluate prompts in a lab setting without context, the MIT researchers collected two weeks of conversation data from humans who interacted with a real LLM during their daily lives. They studied two settings: agreeableness in personal advice and mirroring of user beliefs in political explanations.

#cybersecurity #ai #quantum
Artificial intelligence and quantum computing are no longer hypothetical; they are actively altering cybersecurity, extending attack surfaces, escalating dangers, and eroding existing defenses. We are in a new ear of emerging technologies that are directly impacting cybersecurity requirements.
As a seasoned observer and participant in the cybersecurity domain—through my work, teaching, and contributions to Homeland Security Today, my book “Inside Cyber: How AI, 5G, IoT, and Quantum Computing Will Transform Privacy and Our Security”, — I have consistently underscored that technological advancement is outpacing our institutions, policies, and workforce preparedness.
Current frameworks, intended for a pre-digital convergence era, are increasingly unsuitable. In order to deal with these dual-use technologies that act as force multipliers for both defenders and enemies, we must immediately adjust our strategy as time is of the essence.


To tackle this challenge, the MATRIX AI Consortium for Human Well-Being at UT San Antonio plans to launch a new initiative that establishes a national hub for “neuromorphic” computing available for public use.
Neuromorphic computing is a revolutionary approach that mimics the human brain’s structure to process information with a fraction of the energy used by traditional computers. Unlike standard processors that crunch data in a fixed sequence, neuromorphic chips operate like biological neurons. They are event-based, meaning that they activate only when there is something new to process, saving energy between events.
The initiative, called THOR: The Neuromorphic Commons, is funded by the National Science Foundation. THOR will make the promising technology available for researchers nationwide to explore and conduct experiments, serving as the largest-ever full-stack neuromorphic platforms to be open to the public.
Remember to stay protected online guys, with Proton VPN: https://go.getproton.me/SH2D8. Use that link to receive a whopping 70% off your purchase.
In 2023, the narrative was simple: Google was the dinosaur, and ChatGPT was the meteor. The media declared \.

Industrial yeasts are a powerhouse of protein production, used to manufacture vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, and other useful compounds. In a new study, MIT chemical engineers have harnessed artificial intelligence to optimize the development of new protein manufacturing processes, which could reduce the overall costs of developing and manufacturing these drugs.
Using a large language model (LLM), the MIT team analyzed the genetic code of the industrial yeast Komagataella phaffii — specifically, the codons that it uses. There are multiple possible codons, or three-letter DNA sequences, that can be used to encode a particular amino acid, and the patterns of codon usage are different for every organism.
The new MIT model learned those patterns for K. phaffii and then used them to predict which codons would work best for manufacturing a given protein. This allowed the researchers to boost the efficiency of the yeast’s production of six different proteins, including human growth hormone and a monoclonal antibody used to treat cancer.
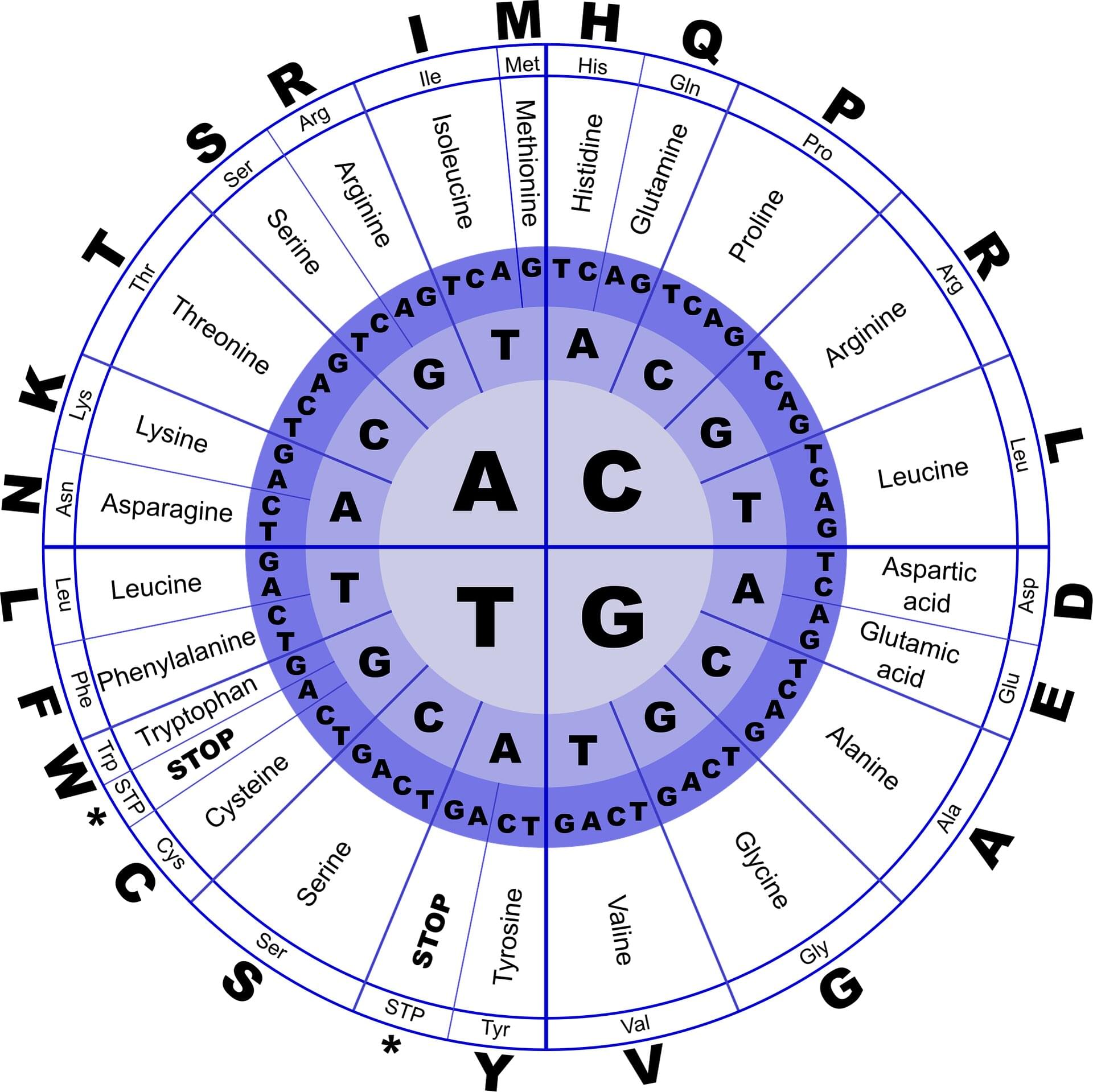
Industrial yeasts are a powerhouse of protein production, used to manufacture vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, and other useful compounds. In a new study, MIT chemical engineers have harnessed artificial intelligence to optimize the development of new protein manufacturing processes, which could reduce the overall costs of developing and manufacturing these drugs.
Using a large language model (LLM), the MIT team analyzed the genetic code of the industrial yeast Komagataella phaffii—specifically, the codons that it uses. There are multiple possible codons, or three-letter DNA sequences, that can be used to encode a particular amino acid, and the patterns of codon usage are different for every organism.
The new MIT model learned those patterns for K. phaffii and then used them to predict which codons would work best for manufacturing a given protein. This allowed the researchers to boost the efficiency of the yeast’s production of six different proteins, including human growth hormone and a monoclonal antibody used to treat cancer.
The rapid advancement of technologies, particularly AI, is driving the world towards an economic singularity where the marginal cost of essentials approaches zero, leading to a deflationary future and a potential transformation of traditional systems and societies ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Education Transformation.
🎓 Q: How will AI reduce education time while improving effectiveness?
A: AI will customize education to each child’s learning style, reducing daily learning time to 1 hour per day while delivering 5 times more effective learning compared to traditional methods, with costs falling to zero within 3–5 years and breaking the university industry that currently creates massive student debt.
Healthcare Revolution.