Scientists at the University of Oxford have harnessed the ability of quantum teleportation for the first time, hoping to scale the idea with supercomputers.



Hundreds of quantum computing firms around the world are racing to commercialise these once-exotic devices, but the jury is still out on who is going to pull ahead and produce a machine that actually does something useful.

Imagine a world where your thoughts aren’t confined to the boundaries of your skull, where your consciousness is intimately connected to the universe around you, and where the neurons in your brain communicate instantly across vast distances.
This isn’t science fiction — it’s the intriguing possibility suggested by applying the principle of quantum entanglement to the realm of consciousness.
Quantum entanglement, often described as the “spooky action at a distance,” is a phenomenon that baffled even Einstein. In essence, it describes a scenario where two particles become so deeply linked that they share the same fate, regardless of the distance separating them. Measuring the state of one instantly reveals the state of its partner, even if they are light-years apart.
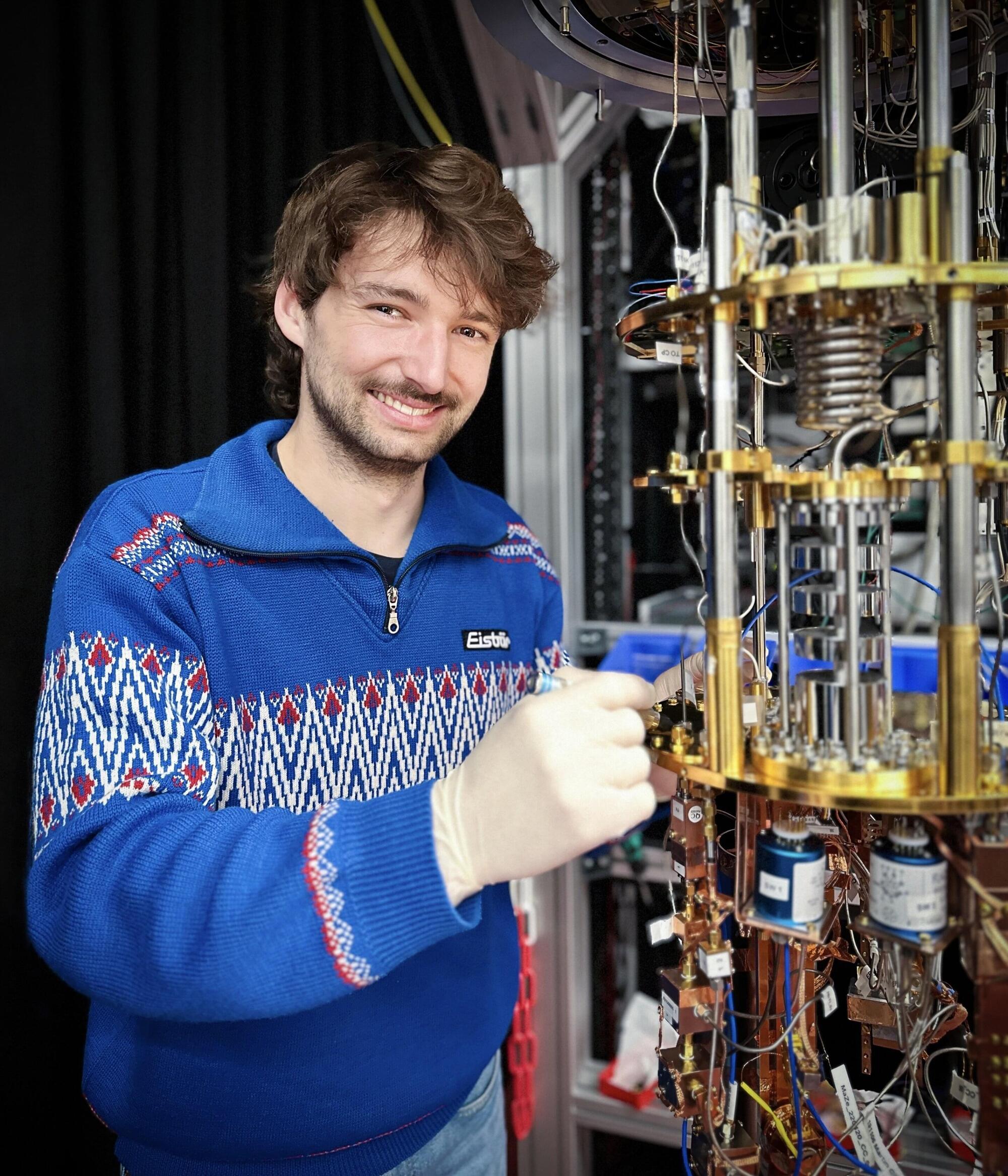
Qubits—the fundamental units of quantum information—drive entire tech sectors. Among them, superconducting qubits could be instrumental in building a large-scale quantum computer, but they rely on electrical signals and are difficult to scale.
In a breakthrough, a team of physicists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) has achieved a fully optical readout of superconducting qubits, pushing the technology beyond its current limitations. Their findings are published in Nature Physics.
Following a year-long rally, quantum computing stocks were brought to a standstill barely a few days into the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. The reason for this sudden setback was Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang’s keynote at the CES 2025 tech trade show, where he predicted that “very useful quantum computers” were still two decades down the road.

This hybrid system allows precise manipulation of quantum states while naturally modeling real-world physics, enabling breakthroughs in fields like magnetism, superconductors, and even astrophysics.
Breakthrough in Quantum Simulation
Physicists working in Google’s laboratory have developed a new type of digital-analog quantum simulator, capable of studying complex physical processes with unprecedented precision and adaptability. Two researchers from PSI’s Center for Scientific Computing, Theory, and Data played a crucial role in this breakthrough.
A theoretical particle that travels faster than light, the tachyon has long intrigued physicists and fueled decades of speculation. Initially conceived as a possible solution to quantum and relativity paradoxes, tachyons remain purely hypothetical. Despite the lack of experimental evidence, they continue to serve as a thought-provoking concept in modern physics.
A recent study by an international team of researchers has reignited interest in tachyons, suggesting they might be possible within the framework of Einstein’s special theory of relativity. This bold claim challenges conventional understandings of causality and time, raising fundamental questions about the structure of reality. If confirmed, it could lead to a radical shift in how scientists perceive the limits of physical laws.
Physicist Gerald Feinberg introduced the idea of tachyons in 1962, proposing that such particles could always travel faster than light without ever slowing down to subluminal speeds. His argument was based on the concept of imaginary mass, a theoretical construct involving the square root of a negative number. This allowed for the mathematical possibility of faster-than-light motion without explicitly violating relativity.
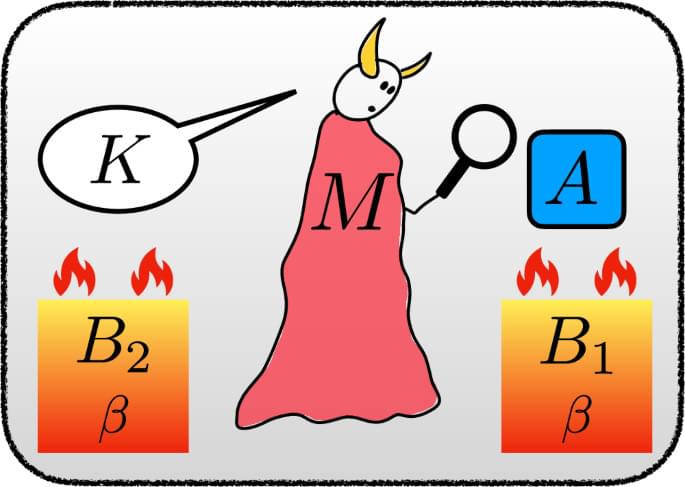
npj Quantum Inf ormation — Universal validity of the second law of information thermodynamics is indeed universal: it must hold for any quantum feedback control and erasure protocol, regardless of the measurement process involved, as long as the protocol is overall compatible with thermodynamics. Our comprehensive analysis not only encompasses new scenarios but also retrieves previous ones, doing so with fewer assumptions. This simplification contributes to a clearer understanding of the theory.
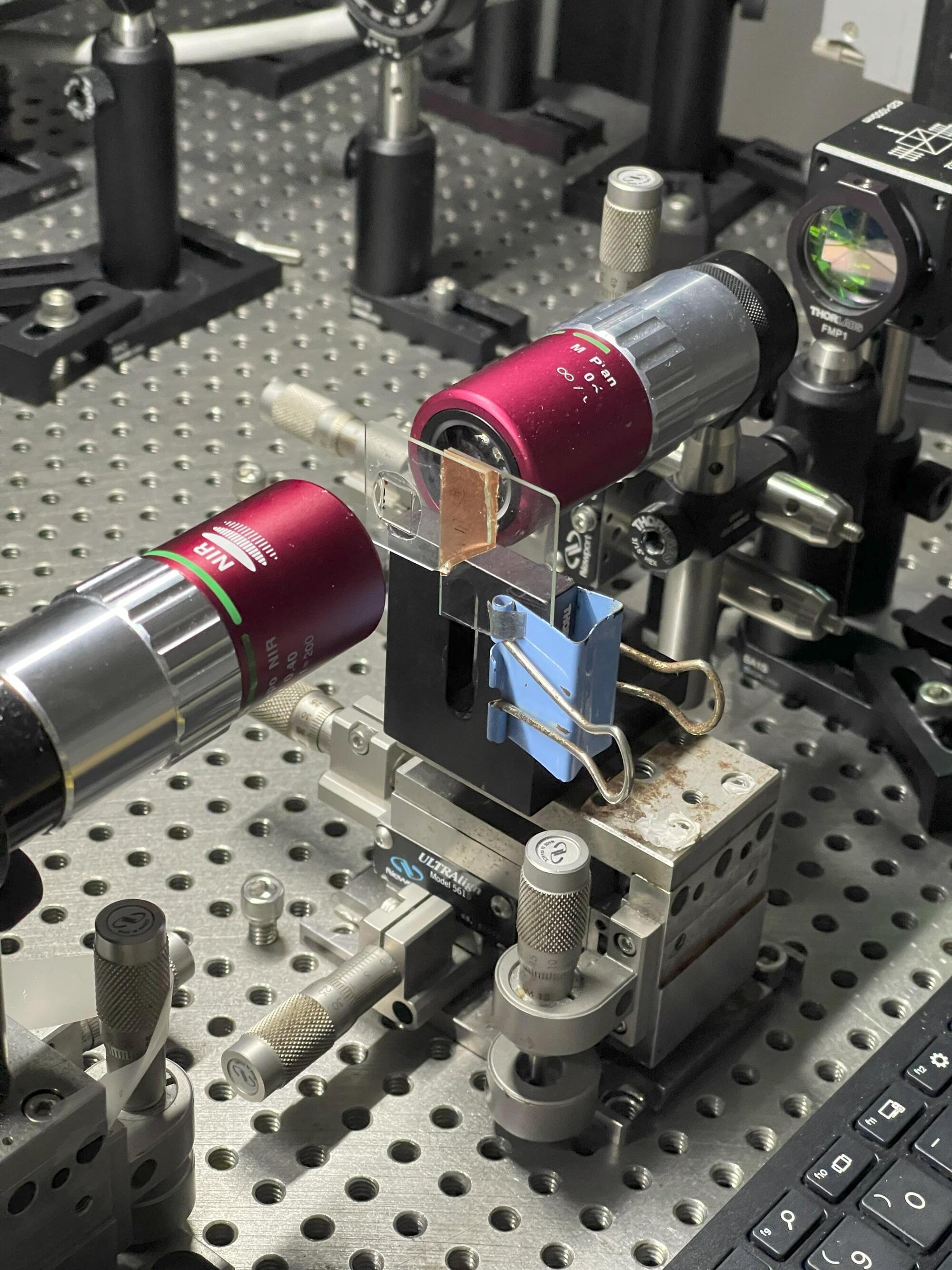
In the realm of quantum information distribution, sending a signal from point A to point B is like a baseball pitcher relaying a secret pitch call to the catcher. The pitcher has to disguise the signal from the opposing team and coaches, base runners, and even onlookers in the stands so no one else cracks the code.
The catcher can’t just stay in one spot or rely on the same finger pattern every time, because savvy opponents are constantly working to decipher any predictable sequence. If the signs are intercepted or misread, the batter gains an advantage, and the entire inning can unravel for the pitcher.
But what if there was a way for pitchers to bolster their signals by adding extra layers of “dimensionality” to each call, effectively increasing the chances of delivering it correctly to the catcher no matter how many eyes are watching? What if by incorporating more nuanced gestures—a subtle shift in glove position, a specific tap on the mound—the pitcher could craftily conceal their intentions?
Exotic superconducting states could exist in a wider range of materials than previously thought, according to a theoretical study by two RIKEN researchers published in Physical Review B.
Superconductors conduct electricity without any resistance when cooled below a critical temperature that is specific to the superconducting material. They are broadly classified into two types: conventional superconductors whose superconducting mechanism is well understood, and unconventional superconductors whose mechanism has yet to be fully determined.
Superconductors have intrigued scientists since their first experimental demonstration at the beginning of the 20th century. This is not just because they have numerous applications, including great promise for quantum computing, but also because superconductors host a rich range of fundamental physics that has allowed physicists to gain a deeper understanding of material science.