A quantum experiment suggests time may not be fixed. Photons appeared to react before being hit, challenging classical physics and opening debates on time’s true nature.




A Canadian startup called Xanadu has built a new quantum computer it says can be easily scaled up to achieve the computational power needed to tackle scientific challenges ranging from drug discovery to more energy-efficient machine learning.
Aurora is a “photonic” quantum computer, which means it crunches numbers using photonic qubits—information encoded in light. In practice, this means combining and recombining laser beams on multiple chips using lenses, fibers, and other optics according to an algorithm. Xanadu’s computer is designed in such a way that the answer to an algorithm it executes corresponds to the final number of photons in each laser beam. This approach differs from one used by Google and IBM, which involves encoding information in properties of superconducting circuits.

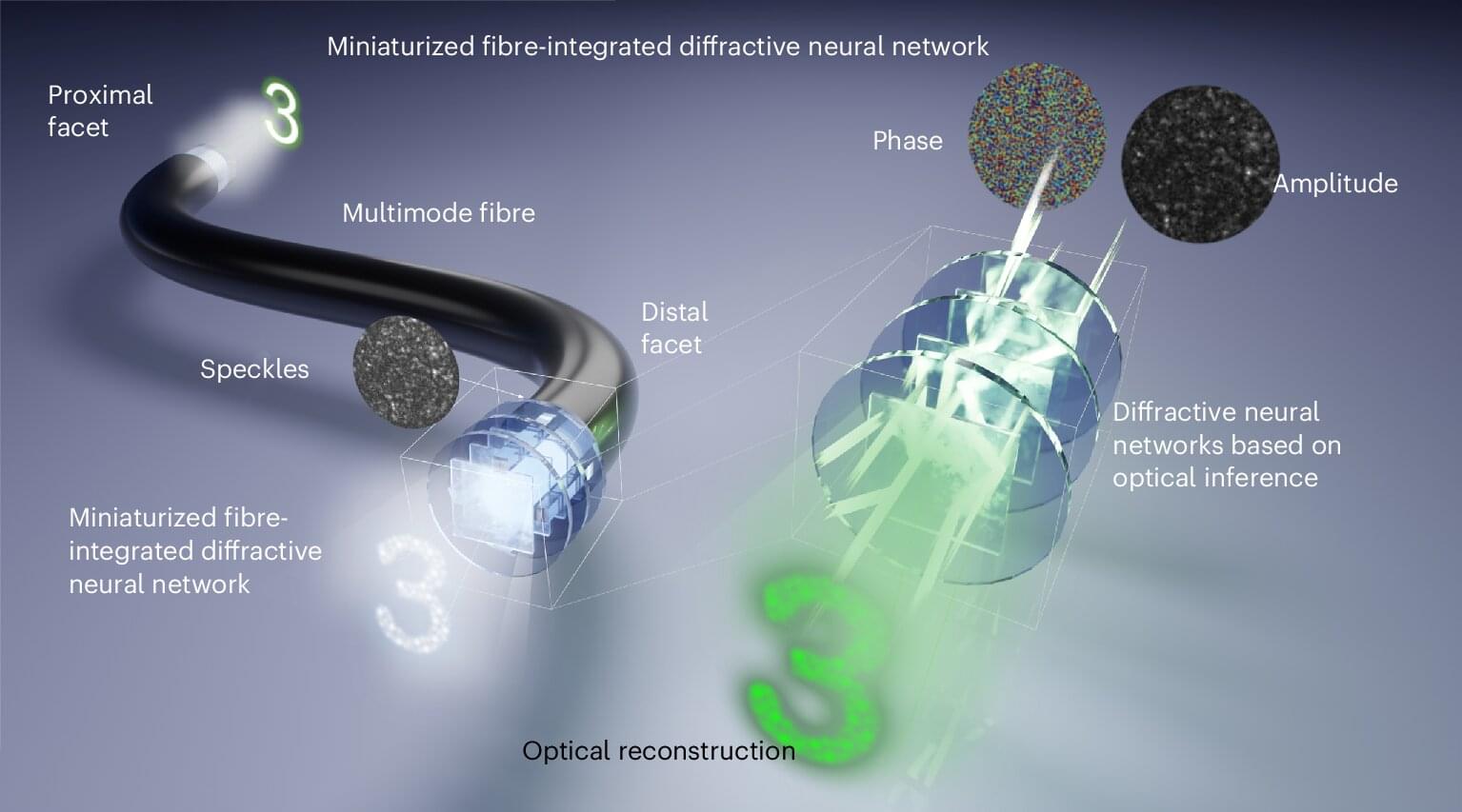
Optical fibers are fundamental components in modern science and technology due to their inherent advantages, providing an efficient and secure medium for applications such as internet communication and big data transmission. Compared with single-mode fibers (SMFs), multimode fibers (MMFs) can support a much larger number of guided modes (~103 to ~104), offering the attractive advantage of high-capacity information and image transportation within the diameter of a hair. This capability has positioned MMFs as a critical tool in fields such as quantum information and micro-endoscopy.
However, MMFs pose a significant challenge: their highly scattering nature introduces severe modal dispersion during transmission, which significantly degrades the quality of transmitted information. Existing technologies, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs) and spatial light modulators (SLMs), have achieved limited success in reconstructing distorted images after MMF transmission. Despite these advancements, the direct optical transmission of undistorted images through MMFs using micron-scale integrated optical components has remained an elusive goal in optical research.
Addressing the longstanding challenges of multi-mode fiber (MMF) transmission, the research team led by Prof. Qiming Zhang and Associate Prof. Haoyi Yu from the School of Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology (SAIST) at the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology (USST) has introduced a groundbreaking solution. The study is published in the journal Nature Photonics.
A new study published in Scientific Reports simulates particle creation in an expanding universe using IBM quantum computers, demonstrating the digital quantum simulation of quantum field theory for curved spacetime (QFTCS).
While attempts to create a complete quantum theory of gravity have been unsuccessful, there is another approach to exploring and explaining cosmological events.
QFTCS maintains spacetime as a classical background described by general relativity, while treating the matter and force fields within it quantum mechanically. This allows physicists to study quantum effects in “curved spacetime” without needing a complete theory of quantum gravity.
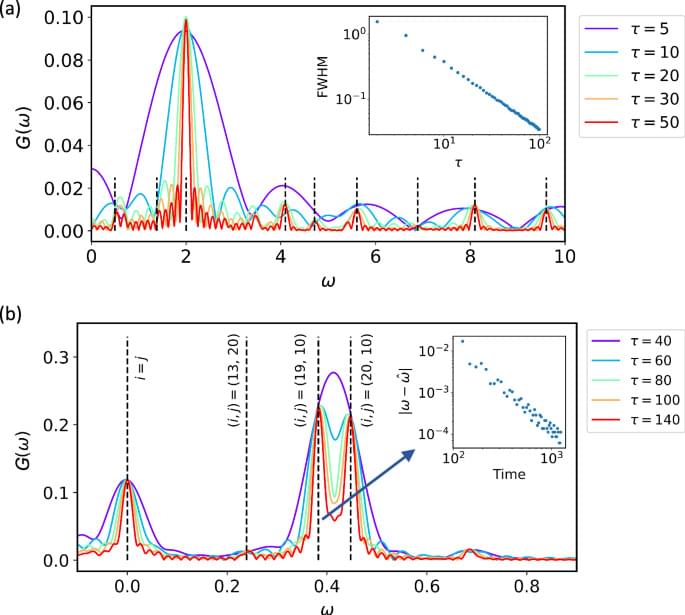
Estimating spectral features of quantum many-body systems has attracted great attention in condensed matter physics and quantum chemistry. To achieve this task, various experimental and theoretical techniques have been developed, such as spectroscopy techniques1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and quantum simulation either by engineering controlled quantum devices8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 or executing quantum algorithms17,18,19,20 such as quantum phase estimation and variational algorithms. However, probing the behaviour of complex quantum many-body systems remains a challenge, which demands substantial resources for both approaches. For instance, a real probe by neutron spectroscopy requires access to large-scale facilities with high-intensity neutron beams, while quantum computation of eigenenergies typically requires controlled operations with a long coherence time17,18. Efficient estimation of spectral properties has become a topic of increasing interest in this noisy intermediate-scale quantum era21.
A potential solution to efficient spectral property estimation is to extract the spectral information from the dynamics of observables, rather than relying on real probes such as scattering spectroscopy, or direct computation of eigenenergies. This approach capitalises on the basics in quantum mechanics that spectral information is naturally carried by the observable’s dynamics10,20,22,23,24,25,26. In a solid system with translation invariance, for instance, the dynamic structure factor, which can be probed in spectroscopy experiments7,26, reaches its local maximum when both the energy and momentum selection rules are satisfied. Therefore, the energy dispersion can be inferred by tracking the peak of intensities in the energy excitation spectrum.

Imagine a world where the act of observation itself holds the key to solving our most complex problems, a world where the very fabric of reality becomes a canvas for computation. This is the tantalizing promise of Observational Computation (OC), a radical new paradigm poised to redefine the very nature of computation and our understanding of the universe itself.
Forget silicon chips and algorithms etched in code; OC harnesses the enigmatic dance of quantum mechanics and the observer effect, where the observer and the observed are inextricably intertwined. Instead of relying on traditional processing power, OC seeks to translate computational problems into carefully crafted observer-environment systems. Picture a quantum stage where potential solutions exist in a hazy superposition, like ghostly apparitions waiting for the spotlight of observation to solidify them into reality.
By meticulously designing these “observational experiments,” we can manipulate quantum systems, nudging them towards desired outcomes. This elegant approach offers tantalizing advantages over our current computational methods. Imagine harnessing the inherent parallelism of quantum superposition for exponentially faster processing, or tapping into the natural energy flows of the universe for unprecedented energy efficiency.

Researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the Slovak Academy of Sciences have unveiled new insights into the interplay between quantum theory and thermodynamics. The team demonstrated that while quantum theory does not inherently forbid violations of the second law of thermodynamics, quantum processes may be implemented without actually breaching the law.
This discovery, published in npj Quantum Information, highlights a harmonious coexistence between the two fields, despite their logical independence. Their findings open up new avenues for understanding the thermodynamic boundaries of quantum technologies, such as quantum computing and nanoscale engines.
This breakthrough contributes to the long-standing exploration of the second law of thermodynamics, a principle often regarded as one of the most profound and enigmatic in physics.