Japan’s Fugaku supercomputer has gained an edge following the installation of the Reimei quantum computer.
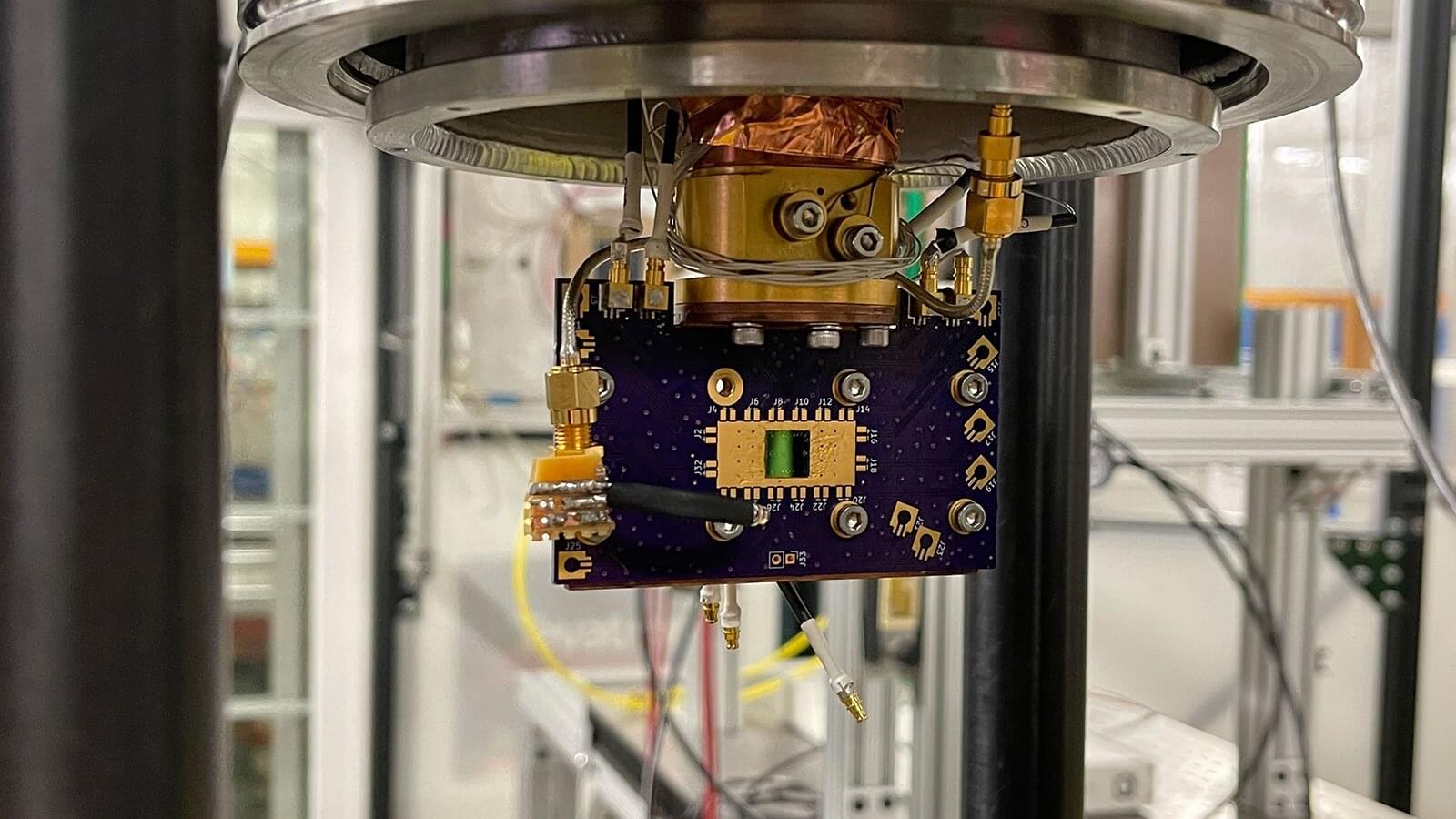



Particle detectors play a crucial role in our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of the universe. They allow scientists to study the behavior and properties of the particles produced in high-energy collisions. Such particles are boosted to near the speed of light in large accelerators and then smashed into targets or other particles where they are then analyzed with detectors. Traditional detectors, however, lack the needed sensitivity and precision for certain types of research.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have made a significant breakthrough in the field of high-energy particle detection in recent experiments conducted at the Test Beam Facility at DOE’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab).
They have found a new use for the superconducting nanowire photon detectors (SNSPDs) already employed for detecting photons, the fundamental particles of light. These incredibly sensitive and precise detectors work by absorbing individual photons. The absorption generates small electrical changes in the superconducting nanowires at very low temperatures, allowing for the detection and measurement of photons. Specialized devices able to detect individual photons are crucial for quantum cryptography (the science of keeping information secret and secure), advanced optical sensing (precision measurement using light) and quantum computing.
A new paper in Nature Physics shows that by cramming lots of rare-earth ions into a crystal, some will form pairs that act as highly coherent qubits, thus debunking the idea that solid-state qubits need to be super dilute in an ultra-clean material to achieve long lifetimes.
According to the study’s authors, one of the major barriers to practical quantum computing has been how to make qubits that retain their quantum information long enough to be useful.
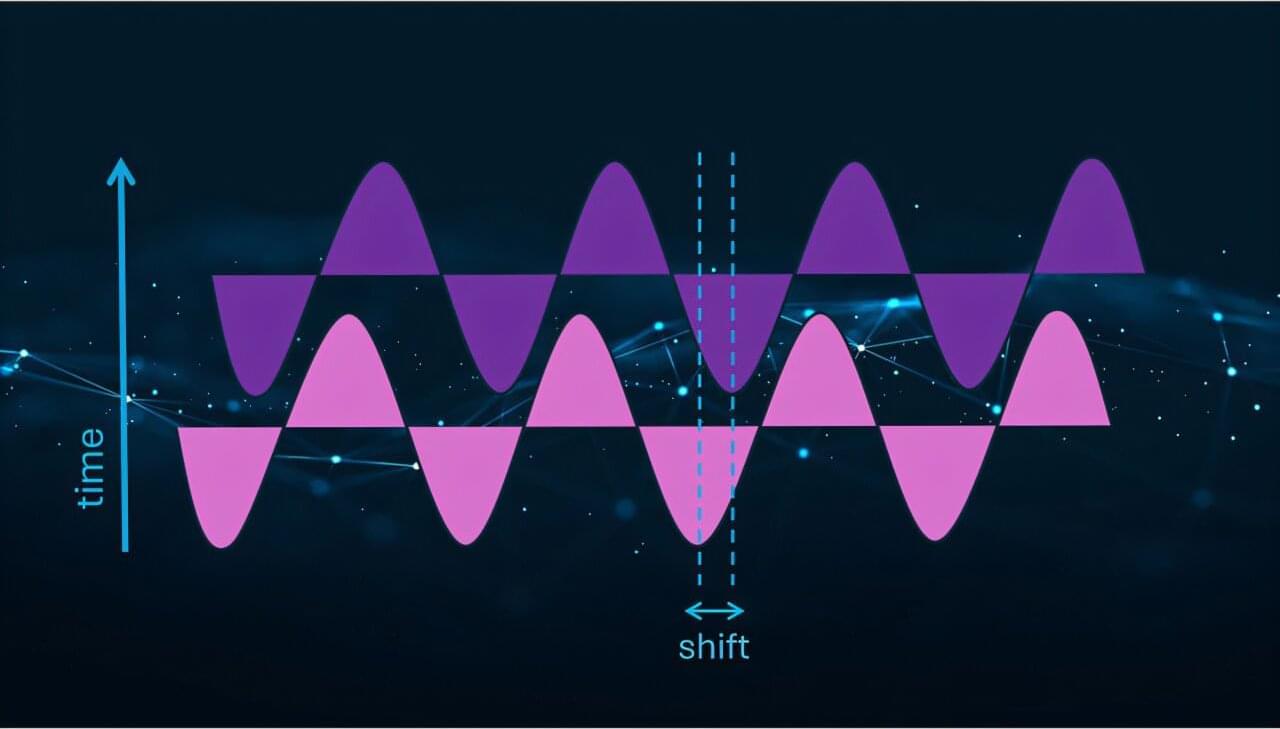
Scattering takes place across the universe at large and miniscule scales. Billiard balls clank off each other in bars, the nuclei of atoms collide to power the stars and create heavy elements, and even sound waves deviate from their original trajectory when they hit particles in the air.
Understanding such scattering can lead to discoveries about the forces that govern the universe. In a recent publication in Physical Review C, researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the InQubator for Quantum Simulations and the University of Trento developed an algorithm for a quantum computer that accurately simulates scattering.
“Scattering experiments help us probe fundamental particles and their interactions,” said LLNL scientist Sofia Quaglioni. “The scattering of particles in matter [materials, atoms, molecules, nuclei] helps us understand how that matter is organized at a microscopic level.”
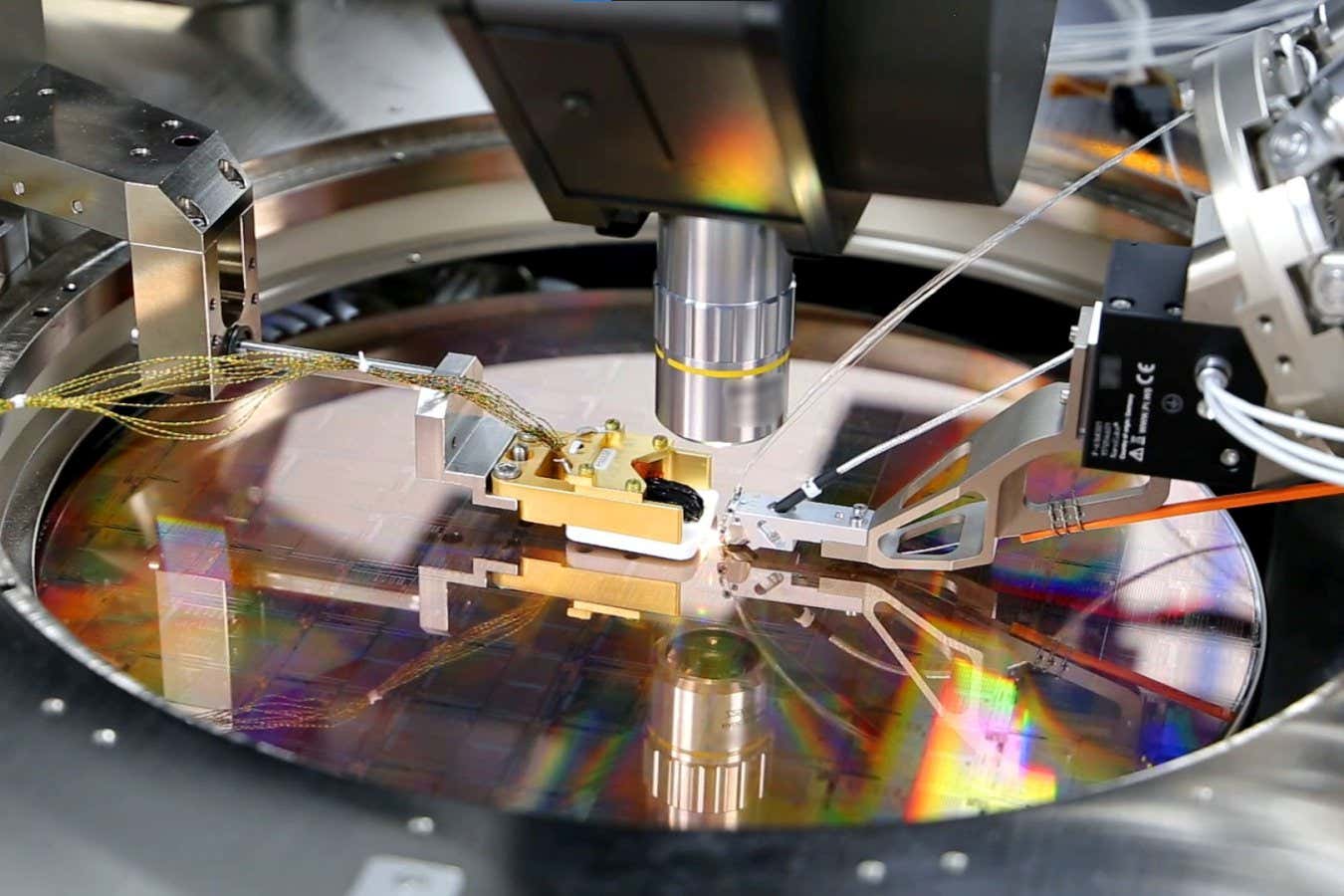
With an investment of AU$1 billion, PsiQuantum is planning to build a photonic quantum computer with a million qubits, far larger than any in existence today — and the firm says it will be ready in just two years.
Qubits—the building blocks of quantum computing—are driving advancements across the tech industry. Among them, superconducting qubits hold great promise for large-scale quantum computers. However, they rely on electrical signals, making them challenging to scale.
In a breakthrough, physicists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) have successfully developed a fully optical readout for superconducting qubits, overcoming a key technological hurdle. Their findings, recently published in Nature Physics.
<em>Nature Physics</em> is a prestigious, peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes high-quality research across all areas of physics. Launched in 2005, it is part of the Nature family of journals, known for their significant impact on the scientific community. The journal covers a wide range of topics, including fundamental physics, applied physics, and interdisciplinary research that bridges physics with other scientific disciplines. Nature Physics aims to highlight the most impactful and cutting-edge research in the field, providing insights into theoretical, experimental, and applied physics. The journal also features reviews, news, and commentary on major advances and issues affecting the physics community.


Hundreds of quantum computing firms around the world are racing to commercialise these once-exotic devices, but the jury is still out on who is going to pull ahead and produce a machine that actually does something useful.