For scientists searching for the brain’s ‘control room, an area called the claustrum has emerged as a compelling candidate. This little-studied deep brain structure is thought to be the place where multiple senses are brought together, attention is controlled, and consciousness arises. Observations in mice now support the role of the claustrum as a hub for coordinating activity across the brain. New research from the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) shows that slow-wave brain activity, a characteristic of sleep and resting states, is controlled by the claustrum. The synchronization of silent and active states across large parts of the brain by these slow waves could contribute to consciousness.
A serendipitous discovery actually led Yoshihiro Yoshihara, team leader at CBS, to investigate the claustrum. His lab normally studies the sense of smell and the detection of pheromones, but they chanced upon a genetically engineered mouse strain with a specific population of brain cells that was present only in the claustrum. These neurons could be turned on using optogenetic technology or selectively silenced through genetic manipulation, thus enabling the study of what turned out to be a vast, claustrum-controlled network. The study by Yoshihara and colleagues was published in Nature Neuroscience on May 11.
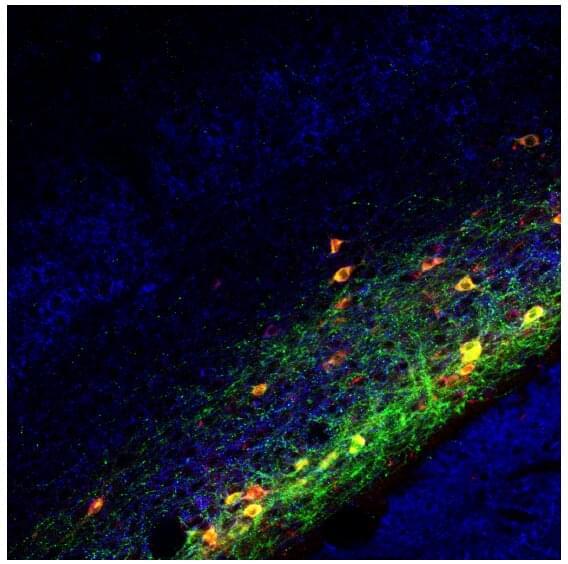
They started out by mapping the claustrum’s inputs and outputs and found that many higher-order brain areas send connections to the claustrum, such as those involved in sensation and motor control. Outgoing connections from the claustrum were broadly distributed across the brain, reaching numerous brain areas such as prefrontal, orbital, cingulate, motor, insular, and entorhinal cortices. “The claustrum is at the center of a widespread brain network, covering areas that are involved in cognitive processing,” says co-first author Kimiya Narikiyo. “It essentially reaches all higher brain areas and all types of neurons, making it a potential orchestrator of brain-wide activity.”