Learn More.
The Neuro-Network.
#Fetal #Brain begin to #experience #pain #neuroscience #science #Biology #consciousness
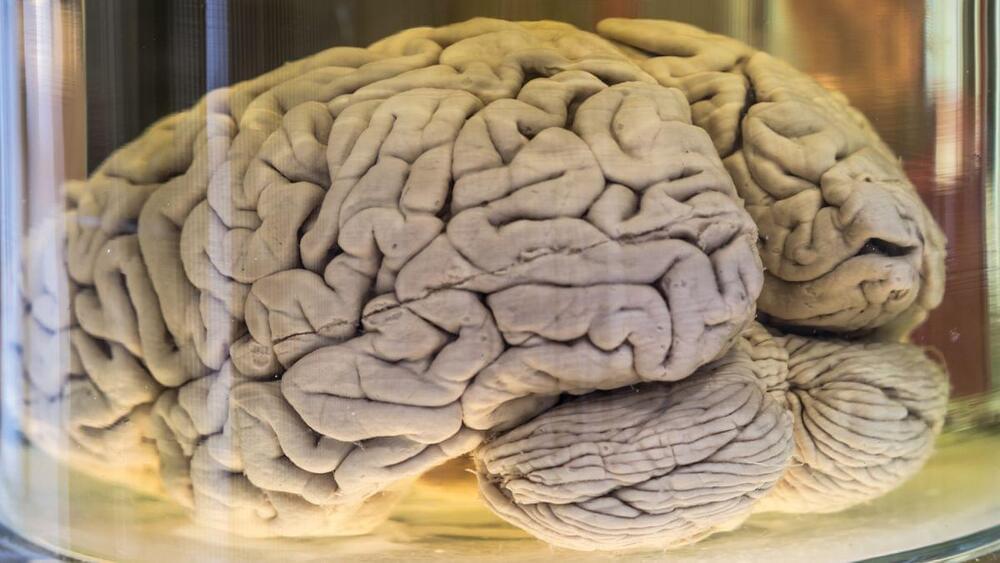
Context Proposed federal legislation would require physicians to inform women seeking abortions at 20 or more weeks after fertilization that the fetus feels pain and to offer anesthesia administered directly to the fetus. This article examines whether a fetus feels pain and if so, whether safe and effective techniques exist for providing direct fetal anesthesia or analgesia in the context of therapeutic procedures or abortion.
Evidence Acquisition Systematic search of PubMed for English-language articles focusing on human studies related to fetal pain, anesthesia, and analgesia. Included articles studied fetuses of less than 30 weeks’ gestational age or specifically addressed fetal pain perception or nociception. Articles were reviewed for additional references. The search was performed without date limitations and was current as of June 6, 2005.
Evidence Synthesis Pain perception requires conscious recognition or awareness of a noxious stimulus. Neither withdrawal reflexes nor hormonal stress responses to invasive procedures prove the existence of fetal pain, because they can be elicited by nonpainful stimuli and occur without conscious cortical processing. Fetal awareness of noxious stimuli requires functional thalamocortical connections. Thalamocortical fibers begin appearing between 23 to 30 weeks’ gestational age, while electroencephalography suggests the capacity for functional pain perception in preterm neonates probably does not exist before 29 or 30 weeks. For fetal surgery, women may receive general anesthesia and/or analgesics intended for placental transfer, and parenteral opioids may be administered to the fetus under direct or sonographic visualization.