Ed Boyden is a professor at the MIT Media Lab working on the most advanced brain-computer interfacing technology currently available, optogenetics. At Singularity Summit 2009.
Category: neuroscience – Page 341
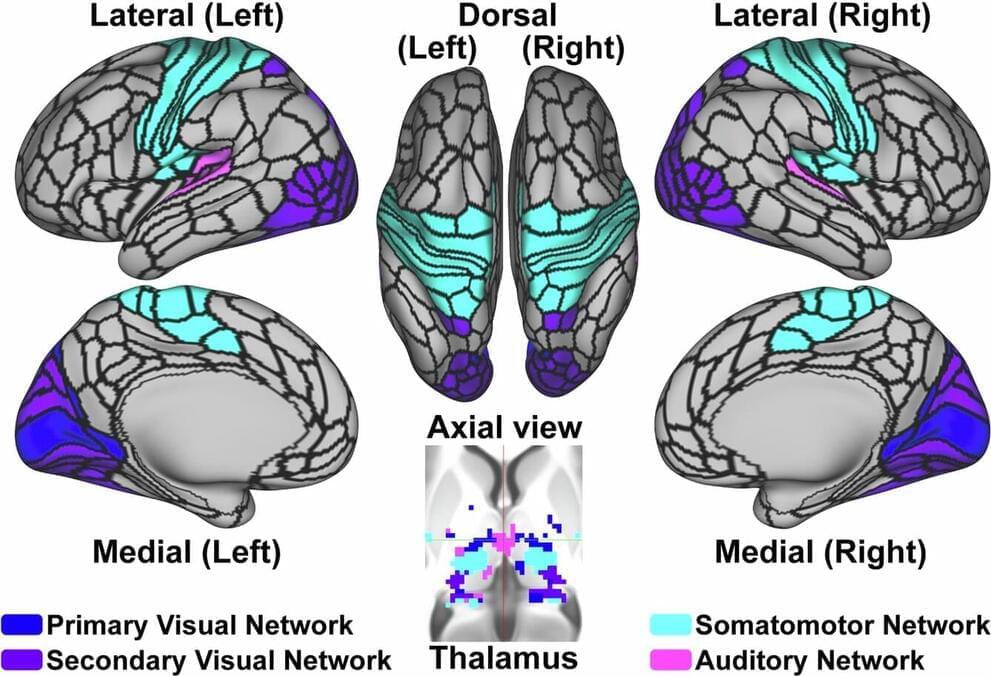
Researchers uncover potential new biomarker for psychosis diagnosis
The current standard of care for psychosis is a diagnostic interview, but what if it could be diagnosed before the first symptom emerged? Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester are pointing toward a potential biomarker in the brain that could lead to more timely interventions and personalized care.
“Establishing such biomarkers could provide a key step in changing how we care for, treat, and offer interventions to people with psychosis,” said Brian Keane, Ph.D., assistant professor of Psychiatry, Center for Visual Science, and Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center.
Keane recently co-authored an article in Molecular Psychiatry that identifies how MRI scans could reveal brain differences in people with psychosis.
Comparative prospects of imaging methods for whole-brain mammalian connectomics
Neuroscience aficionados may enjoy my preprint that compares leading imaging technologies for whole-brain mammalian connectomics, now with major updates/improvements: Link: arxiv.org/abs/2405.
Mammalian whole-brain connectomes at nanoscale synaptic resolution are a crucial ingredient for holistic understanding of brain function. Imaging these connectomes at sufficient resolution to densely reconstruct cellular morphology and synapses represents a longstanding goal in neuroscience. Although the technologies needed to reconstruct whole-brain connectomes have not yet reached full maturity, they are advancing rapidly enough that the mouse brain might be within reach in the near future. Detailed exploration of these technologies is warranted to help plan projects with varying goals and requirements. Whole-brain human connectomes remain a more distant goal yet are worthy of consideration to orient large-scale neuroscience program plans. Here, we quantitatively compare existing and emerging imaging technologies that have potential to enable whole-brain mammalian connectomics.
The Thrill and Threat of Mind Hacking | Posthuman with Emily Chang
From brain implants that allow paralyzed patients to communicate to the wearable devices enhancing our capabilities, brain-computer interfaces could change the way we use our minds forever.
——-
Like this video? Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_…
Get unlimited access to Bloomberg.com for $1.99/month for the first 3 months: https://www.bloomberg.com/subscriptio…
Bloomberg Originals offers bold takes for curious minds on today’s biggest topics. Hosted by experts covering stories you haven’t seen and viewpoints you haven’t heard, you’ll discover cinematic, data-led shows that investigate the intersection of business and culture. Exploring every angle of climate change, technology, finance, sports and beyond, Bloomberg Originals is business as you’ve never seen it.
Subscribe for business news, but not as you’ve known it: exclusive interviews, fascinating profiles, data-driven analysis, and the latest in tech innovation from around the world.
Visit our partner channel Bloomberg Quicktake for global news and insight in an instant.
The illusionist View of Consciousness
Non-personalized content and ads are influenced by things like the content you’re currently viewing and your location (ad serving is based on general location). Personalized content and ads can also include things like video recommendations, a customized YouTube homepage, and tailored ads based on past activity, like the videos you watch and the things you search for on YouTube. We also use cookies and data to tailor the experience to be age-appropriate, if relevant.
Select “More options” to see additional information, including details about managing your privacy settings. You can also visit g.co/privacytools at any time.
Early adult binge drinking has lasting impact on aging brain in mice
In a new work, a team from the University of Pennsylvania tracked the impact of alcohol consumption from the age of 20 on brain health and came to disappointing conclusions.
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Binge drinking in early adults can lead to long-lasting and potentially permanent dysregulation in the brain, according to a new study in mice, led by researchers at Penn State. They found that neurons, cells that transmit information in the brain via electrical and chemical signals, showed changes following binge drinking were similar in many ways to those seen with cognitive decline.
These findings, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, reveal that binge drinking early in life may have lasting impacts that are predictive of future health issues, like Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, the researchers said. The work could inform the development of therapeutics to help combat these changes — particularly in aging populations who may have given up alcohol decades earlier, according to Nikki Crowley, director of the Penn State Neuroscience Institute at University Park, Huck Early Career Chair in Neurobiology and Neural Engineering, assistant professor of biology in the Eberly College of Science, and the leader of the research team.
“We know from previous studies that there are immediate effects of binge drinking on the brain, but we didn’t have any sense of if these changes were long-lasting, or reversible over time,” said Crowley, who is also an assistant professor of biomedical engineering and of pharmacology. “We were interested in understanding if binge drinking during early adulthood may have lasting consequences that are not revealed until later in life — even if drinking had stopped for a very long period of time. This allows us to consider the effects of alcohol on an individual’s holistic health, in terms of their entire life history.”
New Platform Overcomes Blood-Brain Barrier for Drug Delivery
Summary: Researchers have developed a breakthrough system to deliver large therapeutic molecules into the brain, overcoming the challenges of the blood-brain barrier. The innovative blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugate (BCC) platform utilizes a biological process called γ-secretase-mediated transcytosis to safely transport drugs like oligonucleotides and proteins into the central nervous system via intravenous injection.
In mouse models and human brain tissue, the system effectively silenced harmful genes linked to diseases such as ALS and Alzheimer’s without causing significant side effects. This advancement could revolutionize treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders, solving a critical challenge in brain research.

Tiny Implant Aims to Treat Depression in Your Brain
Neurotech startup Motif says it has built a pea-sized brain chip that can treat mental illnesses, including depression, without the side effects of conventional drugs. Watch Posthuman with Emily Chang to learn more about the power of brain-computer interfaces.
——-
Like this video? Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_…
Get unlimited access to Bloomberg.com for $1.99/month for the first 3 months: https://www.bloomberg.com/subscriptio…
Bloomberg Originals offers bold takes for curious minds on today’s biggest topics. Hosted by experts covering stories you haven’t seen and viewpoints you haven’t heard, you’ll discover cinematic, data-led shows that investigate the intersection of business and culture. Exploring every angle of climate change, technology, finance, sports and beyond, Bloomberg Originals is business as you’ve never seen it.
Subscribe for business news, but not as you’ve known it: exclusive interviews, fascinating profiles, data-driven analysis, and the latest in tech innovation from around the world.
Visit our partner channel Bloomberg Quicktake for global news and insight in an instant.
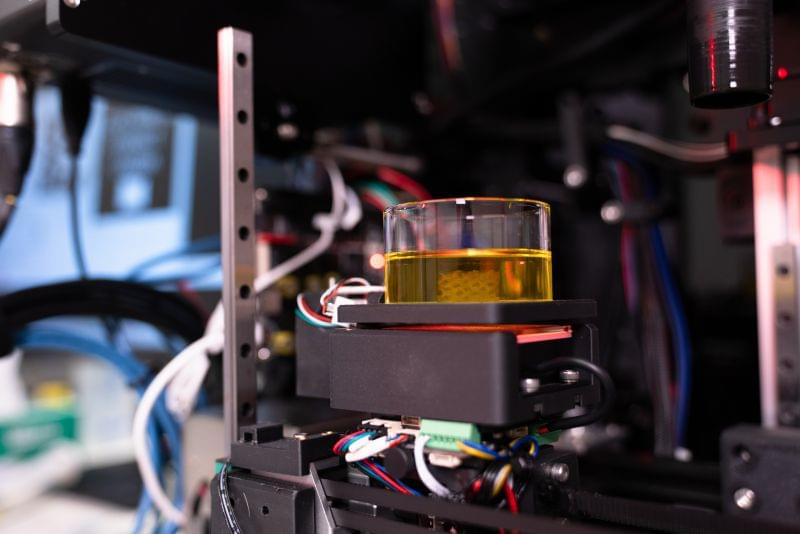
Revolutionary High-Speed 3D Bioprinter hailed a Gamechanger for Drug Discovery
Biomedical engineers from the University of Melbourne have invented a 3D printing system, or bioprinter, capable of fabricating structures that closely mimic the diverse tissues in the human body, from soft brain tissue to harder materials like cartilage and bone.
This cutting-edge technology offers cancer researchers an advanced tool for replicating specific organs and tissues, significantly improving the potential to predict and develop new pharmaceutical therapies. This would pave the way for more advanced and ethical drug discovery by reducing the need for animal testing.
Head of the Collins BioMicrosystems Laboratory at the University of Melbourne, Associate Professor David Collins said: In addition to drastically improving print speed, our approach enables a degree of cell positioning within printed tissues. Incorrect cell positioning is a big reason most 3D bioprinters fail to produce structures that accurately represent human tissue.