– (
The work, published today in Nature, marks a significant step forward in our ability to study how the human body takes shape during early development.
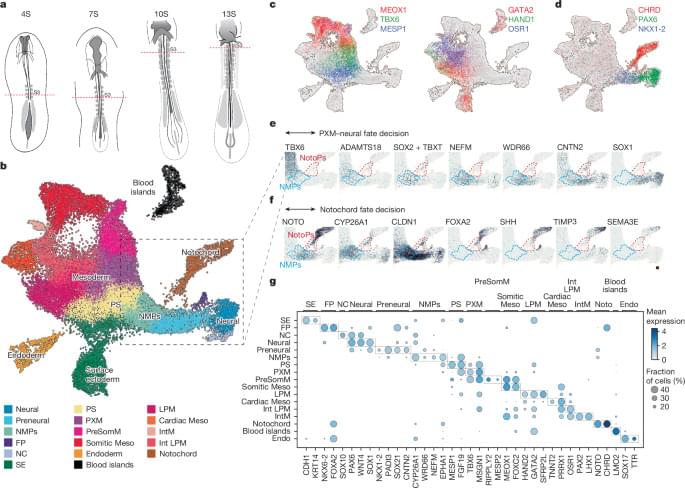
The notochord, a rod-shaped tissue, is a crucial part of the scaffold of the developing body. It is a defining feature of all animals with backbones and plays a critical role in organising the tissue in the developing embryo.
Despite its importance, the complexity of the structure has meant it has been missing in previous lab-grown models of human trunk development.
In this research, the scientists first analysed chicken embryos to understand exactly how the notochord forms naturally. By comparing this with existing published information from mouse and monkey embryos, they established the timing and sequence of the molecular signals needed to create notochord tissue.
With this blueprint, they produced a precise sequence of chemical signals and used this to coax human stem cells into forming a notochord.
The stem cells formed a miniature ‘trunk-like’ structure, which spontaneously elongated to 1–2 millimetres in length. It contained developing neural tissue and bone stem cells, arranged in a pattern that mirrors development in human embryos. This suggested that the notochord was encouraging cells to become the right type of tissue at the right place at the right time.