Scientists have identified a new therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases by boosting a protein called PI31, which ensures proteasomes reach synapses to clear protein waste.


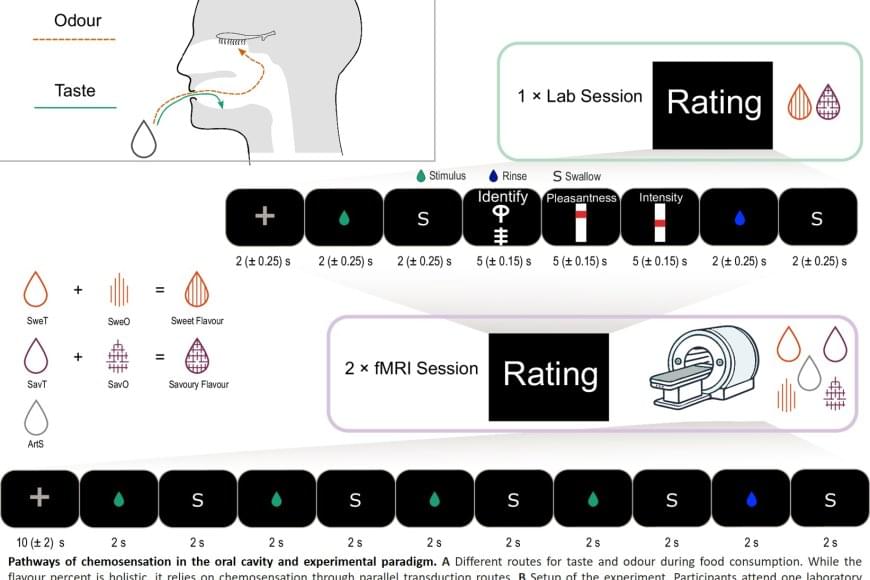
When we eat or drink, we don’t just experience taste, but rather a ‘flavor’. This taste experience arises from a combination of taste and smell, where aromas from food reach the nose via the oral cavity, known as retronasal odor. Researchers have now shown that the brain integrates these signals earlier than previously thought – already in the insula, a brain region known as the taste cortex – before the signals reach the frontal cortex, which controls our emotions and behavior.
“We saw that the taste cortex reacts to taste-associated aromas as if they were real tastes,” explains the lead author. “The finding provides a possible explanation for why we sometimes experience taste from smell alone, for example in flavored waters. This underscores how strongly odors and tastes work together to make food pleasurable, potentially inducing craving and encouraging overeating of certain foods.”
The study involved 25 healthy adults who were first taught to recognize both a sweet taste and a savory taste through combinations of taste and smell. This was followed by two brain imaging sessions using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), in which the participants were given either a tasteless aroma or a taste without smell. The researchers trained an algorithm to recognize patterns in brain activity for sweet and savory tastes, and then tested whether the same patterns could be identified when the participants were only given aromas.



Psilocybin, the active ingredient in magic mushrooms, might just revolutionize how depression and anxiety are treated in cancer patients. In a groundbreaking trial, a single dose combined with therapy significantly reduced emotional suffering, and these effects often lasted over two years. As follow-up studies expand the research to multiple doses and larger samples, scientists are eyeing a possible new standard of care that merges psychedelics with psychological support.

You probably think you’re listening to my voice right now. But what if I told you that you’re actually experiencing a sophisticated hallucination?
Perception isn’t the passive process that most of us imagine it to be, with our senses simply recording reality and sending it up to our brains for processing. Instead, our brains are constantly constructing theories about what’s going on around us—and sometimes our brains get reality wrong.
Here to explain this mind-bending way of looking at, well, the mind, is Daniel Yon, an associate professor of cognitive neuroscience and director of the Uncertainty Lab at Birkbeck, University of London. Daniel is also the author of a recent book called A Trick of the Mind: How the Brain Invents Your Reality.
Thank you so much for coming on to chat with us.
Thank you for having me.
So why don’t you start by telling me a little bit about your background and how it led you to write your latest book.
Yeah, so I’m an experimental psychologist and a cognitive neuroscientist, so that means my day job is to try and understand how your mind and brain work and how what happens inside your skull kind of makes the world that you live in.

Psychological problems such as depression and anxiety increase the risk of cognitive impairment in older adults. But mechanisms on the effect of psychological disorder on cognitive function is inconclusive. Repetitive negative thinking (RNT) is a core symptom of a number of common psychological disorders and may be a modifiable process shared by many psychological risk factors that contribute to the development of cognitive impairment. RNT may increase the risk of cognitive impairment. However, there are fewer studies related to RNT and cognitive function, and there is a lack of epidemiological studies to explore the relationship between RNT and cognitive function.
A cross-sectional study of 424 older adults aged 60 years or over was performed form May to November 2023 in hospital. To investigate the RNT level by using the Perseverative Thinking Questionnaire (PTQ), and investigate the cognitive function level by using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA). Multivariable linear regression and subgroup analyses were used to explore the relationship between RNT and cognitive function.
We categorized the total RNT scores into quartiles. The multivariable linear regression analysis showed that after adjusting for all covariates, the participants in the Q3 and Q4 groups exhibited lower cognition scores (Q3:β =-0.180, 95%CI-2.849~-0.860; Q4:β =-0.164, 95%-2.611~-0.666) compared to the Q1 group. The results of the subgroup analyses showed that individuals aged 60 ~ 79 years, junior high school and above are more prone to suffer from cognitive impairment with a high RNT score.