An amazing paper (link:) where functional ultrasound imaging (fUSI) is used to explore how brain activity in the lateral intraparietal cortex (LIP) can predict visual saccades (eye movements) in two monkeys. An impressive array of computational analyses are used to extract insights from the imaged regions. Indeed, predictive models developed by the authors remained fairly stable over the course of up to 900 days! I happen to know two of the authors (Sumner L Norman and Mikhail Shapiro): congratulations to them and their colleagues on this excellent publication!
Our results demonstrate that PPC contains subregions tuned to different directions. These tuned voxels were predominately within LIP and grouped into contiguous mesoscopic subpopulations. Multiple subpopulations existed within a given coronal plane, i.e., there were multiple preferred directions in each plane. A rough topography exists where anterior LIP had more voxels tuned to contralateral downwards saccades and posterior LIP had more voxels tuned to contralateral upwards saccades. These populations remained stable across more than 100–900 days.
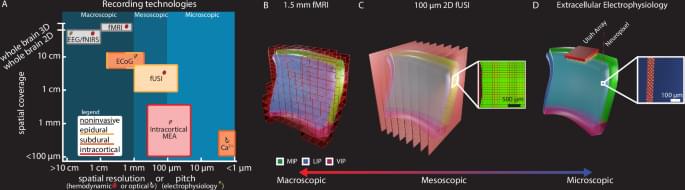
We observed large effect sizes with changes in CBV on the order of 10–30% from baseline activity (Fig. 3). This is much larger than observed with BOLD fMRI where the effect size was ~0.4–2% on similar saccade-based event-related tasks27,32. Our results support a growing evidence base that establishes fUSI as a sensitive neuroimaging technique for detecting mesoscopic functional activity in a diversity of model organisms, including pigeons, rats, mice, nonhuman primates, ferrets, and infant and adult humans23,24,25,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40.
Several studies have reported a patchiness in direction selectivity with many neighboring neurons tuned to approximately the same direction followed by an abruption to a patch of a different preferred direction13,14,41. These results match very closely with the results observed in this study where we found clusters within LIP tightly tuned to one direction with differently tuned clusters in close proximity within a given plane. These results further emphasize the high spatial resolution of fUSI for functional mapping of neuronal activity. These results also closely match a previous study that used fUSI to identify the tonotopic mapping of the auditory cortex and inferior colliculus in awake ferrets where the authors found a functional resolution of 100 µm for voxel responsiveness and 300 µm for voxel frequency tuning34.