How the Japanese manufacturer YKK has stayed at the top of its industry.



Reward maximisation is one strategy that works for reinforcement learning to achieve general artificial intelligence. However, deep reinforcement learning algorithms shouldn’t depend on reward maximisation alone.
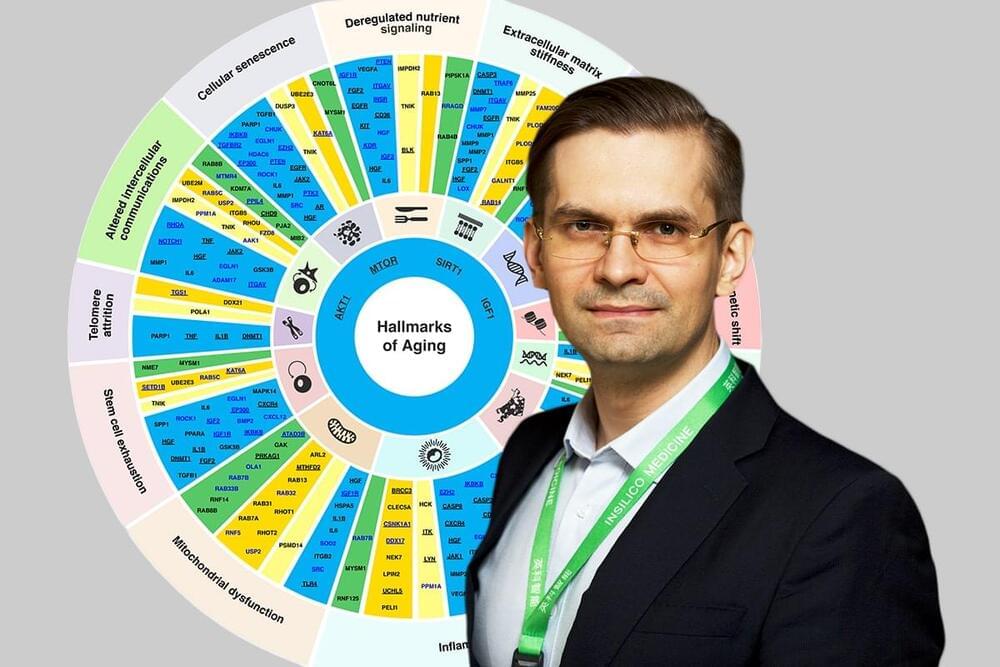
Identifying dual-purpose therapeutic targets implicated in aging and disease will extend healthspan and delay age-related health issues.
AI is all that matters now, and reaching Agi before 2030 is all that matters for this decade.
A substantial percentage of the human clinical trials, including those evaluating investigational anti-aging drugs, fail in Phase II, a phase where the efficacy of the drug is tested. This poor success is in part due to inadequate target choice and the inability to identify a group of patients who will most likely respond to specific agents. This challenge is further complicated by the differences in the biological age of the patients, as the importance of therapeutic targets varies between the age groups. Unfortunately, most targets are discovered without considering patients’ age and being tested in a relatively younger population (average age in phase I is 24). Hence, identifying potential targets that are implicated in multiple age-associated diseases, and also play a role in the basic biology of aging, may have substantial benefits.
Identifying dual-purpose targets that are implicated in aging and disease at the same time will extend healthspan and delay age-related health issues – even if the target is not the most important in a specific patient, the drug would still benefit that patient.
“When it comes to targets identification in chronic diseases, it is important to prioritize the targets that are implicated in age-associated diseases, implicated in more than one hallmark of aging, and safe,” said Zhavoronkov. “So that in addition to treating a disease, the drug would also treat aging – it is an off-target bonus.”
Great article by the great Steve Hill. One little thing:
“The life extension community unfortunately does have a reputation for being long on promises and short on delivery. With what is now decades of research, there are still no effective therapies against aging.”
Well, George Church commented recently that life extension does exist for mice and worms. And there is one human trial underway via plasma dilution and another one later this year.
It seems bizarre that in 2022, some biotech companies interested in doing something about aging are still saying that they are not. Cellular rejuvenation seems to be the latest buzzword and an attempt to rebrand and escape the stigma of anti-aging.
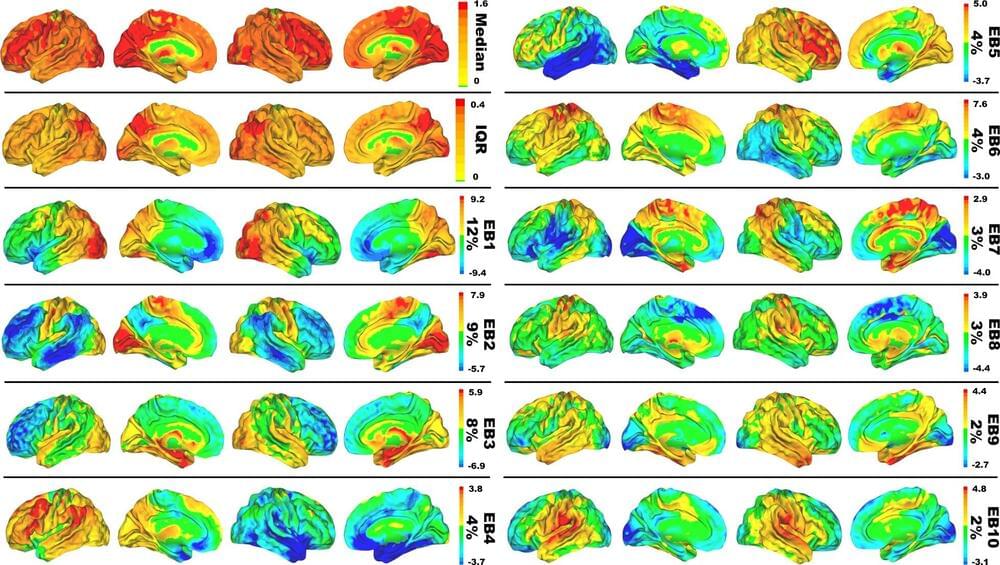
Mayo Clinic researchers have proposed a new model for mapping the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease to brain anatomy. This model was developed by applying machine learning to patient brain imaging data. It uses the entire function of the brain rather than specific brain regions or networks to explain the relationship between brain anatomy and mental processing. The findings are reported in Nature Communications.
“This new model can advance our understanding of how the brain works and breaks down during aging and Alzheimer’s disease, providing new ways to monitor, prevent and treat disorders of the mind,” says David T. Jones, M.D., a Mayo Clinic neurologist and lead author of the study.
Alzheimer’s disease typically has been described as a protein-processing problem. The toxic proteins amyloid and tau deposit in areas of the brain, causing neuron failure that results in clinical symptoms such as memory loss, difficulty communicating and confusion.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease caused by a type of bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually affect the lungs, but also can invade other organs.
In 2018, tuberculosis bacteria infected 1.7 billion people — roughly 23% of the world’s population, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In 2020, the CDC reported 7,174 TB cases and 13 million people living with a latent tuberculosis infection (the germs are in the body but do not cause sickness) in the United States.
Even after successful therapy for tuberculosis, survivors of the disease have an increased risk of recurrent infection and death. A new study published recently by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine found that the cells of humans and animals who have recovered from tuberculosis had prematurely aged up to 12 to 14 years.
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Levine’s Biological age calculator is embedded as an Excel file in this link from my website:
Papers referenced in the video:
Inter-and intra-individual variability in daily resting heart rate and its associations with age, sex, sleep, BMI, and time of year: Retrospective, longitudinal cohort study of 92,457 adults.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32023264/
Heart rate variability with photoplethysmography in 8 million individuals: a cross-sectional study.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33328029/

Boston medical researchers in a new groundbreaking study have discovered a “vicious cycle” between daytime napping and Alzheimer’s dementia.
The Brigham and Women’s Hospital researchers found a link between the two: Excessive daytime napping predicted an increased future risk of Alzheimer’s dementia, and a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s dementia sped up the increase in daytime napping during aging.
Daytime napping is common among older adults, but researchers have not known the relationship between daytime napping and cognitive aging.
How Will Nanotechnologies Transform Humanity?
#WomenOfImpact #Nanotech #WeLoveScience #Immortality
Immortalists Magazine is an experimental project by multi-media, conceptual artist, Dinorah Delfin.
Inspinspired by Trans-, Post-, and Meta-Humanist philosophy & innovations. The aim is to bring greater awareness to Transhumanism & the science of Radical Life Extension. Immortalists Magazine reflects the personal opinions of the artist.

Technique allows researchers to toggle on individual genes that regulate cell growth, development, and function.
By combining CRISPR technology with a protein designed with artificial intelligence, it is possible to awaken individual dormant genes by disabling the chemical “off switches” that silence them. Researchers from the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle describe this finding in the journal Cell Reports.
The approach will allow researchers to understand the role individual genes play in normal cell growth and development, in aging, and in such diseases as cancer, said Shiri Levy, a postdoctoral fellow in UW Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine (ISCRM) and the lead author of the paper.