Insights from the 1st World Longevity Summit show how social ties, daily movement, plant-forward meals, and purpose improve healthy life expectancy.

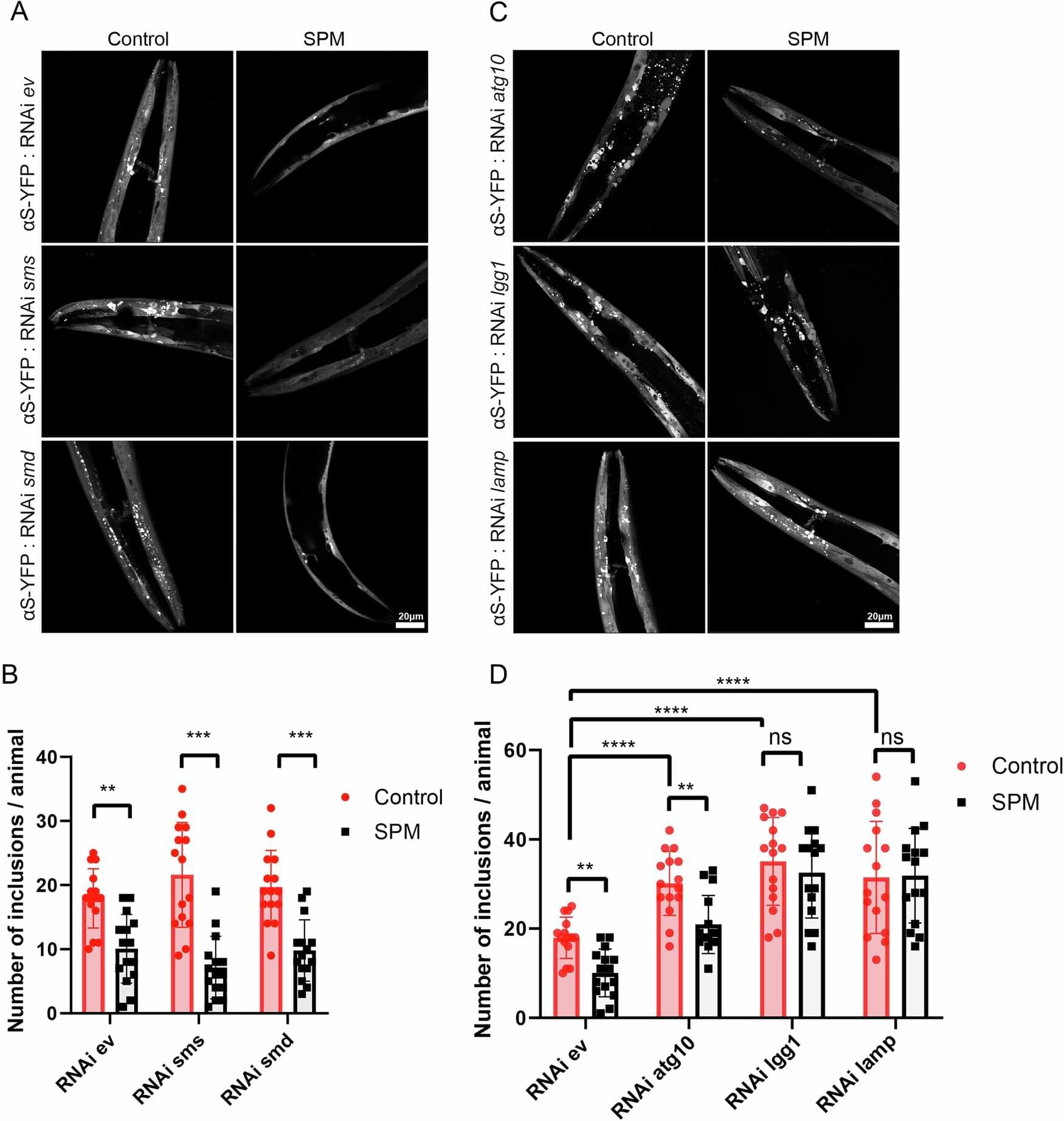
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have clarified how spermine—a small molecule that regulates many processes in the body’s cells—can guard against diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s: It renders certain proteins harmless by acting a bit like cheese on noodles, making them clump together. This discovery could help combat such diseases. The study has now been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Our life expectancy keeps rising—and as it does, age-related illnesses, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are becoming increasingly common. These diseases are caused by accumulations in the brain of harmful protein structures consisting of incorrectly folded amyloid proteins. Their shape is reminiscent of fibers or spaghetti. To date, there is no effective therapy to prevent or eliminate such accumulations.
Yet a naturally occurring molecule in the body called spermine offers hope. In experiments, researchers led by study leader Jinghui Luo, in the Center for Life Sciences at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, have discovered that this substance is capable of extending the lifespan of small nematode worms, improving their mobility in old age, and strengthening the powerhouses of their cells—the mitochondria. Specifically, the researchers observed how spermine helps the body’s immune system eliminate nerve-damaging accumulations of amyloid proteins.

A study by the Leibniz Institute on Aging – Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) in Jena shows that the chemical composition of proteins in the brain undergoes fundamental changes with aging. In particular, ubiquitylation—a process that marks proteins and thus controls their activity and degradation—undergoes drastic changes in the aging brain. Interestingly, a change in nutrition, such as short-term dietary restriction, can partially revert some of these molecular patterns. These findings open up new opportunities to better understand the aging process of the brain and related diseases.
Two recently published studies led by Brazilian scientists reveal the key roles of multifunctional proteins, STIP1 and Maspin, in vital cellular processes.
The results demonstrate new protein functions that help clarify how cells maintain their shape, communicate, and renew themselves. These findings contribute to new studies on cancer, embryogenesis, and potential applications in regenerative medicine.
According to one of the studies, STIP1 plays a central role in embryonic development and maintaining pluripotency, or the ability of cells to multiply and give rise to other cell types.
In this epsiode of the Cryosphere chat we discuss:
● The research proposal we submitted to BRLS
● Why slow growth could be an existential risk to cryonics.
● Our review of the Fixation vs. Vitrification discussion.
● Why there are so many autistic cryonicists.
Links:
Fixation vs. Virtification Discussion: https://youtu.be/gvu8P9D6p0g?si=2KOSESeOndtVl33V
Biostasis Pacific Northwest: https://www.reddit.com/r/cryonics/comments/1ozxslv/announcin…northwest/
I’ll see ya later mom… Reddit post: https://www.reddit.com/r/cryonics/comments/1owgnk0/ill_see_ya_later_mom/
Cryosphere Discord: https://discord.gg/ndshSfQwqz

Join our LONGEVITY and ANTI-AGING Skool Community: https://www.skool.com/youthspan-society-9710/
Timestamps:
00:00 Intro.
00:41 DNA damage and aging.
01:37 Why bowhead whales live so long.
03:13 Cold shock proteins and lifespan.
04:43 Body temperature and longevity.
06:50 Acute cold exposure benefits.
08:10 Takeaway.
100 Health Biomarkers Ranked: https://youtu.be/SgKp5mm0ALI?si=M7YkYo6Lelci7kOQ
Start rewinding your biological clock: https://www.siimland.co/course.
P.S. This is not professional medical advice and should not be taken as such. The creator of this video is not held accountable for your health. Consult your doctor first.
Multicellular organisms (animals, plants, humans) all have the ability to methylate the cytosine base in their DNA. This process, a type of epigenetic modification, plays an important role in conditions such as cancer and processes such as aging.
In a paper appearing in Nature Genetics, researchers discover that in more “primitive” unicellular organisms, both the adenine and the cytosine bases are methylated. This would suggest that in some ways, these unicellular organisms are more complex than their multicellular peers.
The team also found that methylation of the adenine base was, in the case of many of these unicellular organisms, vital for controlling which genes are switched on, which is important for their viability.
Not only can the drug metformin help to effectively manage type 2 diabetes, but it may also give older women a better chance of living to the grand old age of 90, according to recent research – thanks, it seems, to a variety of anti-aging effects.
Scientists in the US and Germany used data from a long-term US study of postmenopausal women. Records on a total of 438 people were picked out – half of whom took metformin to treat diabetes, and half who took a different diabetes drug, called sulfonylurea.
While there are some caveats and asterisks to the study, those in the metformin group were calculated to have a 30 percent lower risk of dying before the age of 90 than those in the sulfonylurea group.
