This technology will not only extend the lifespan of concrete structures, but also promote a circular economy.
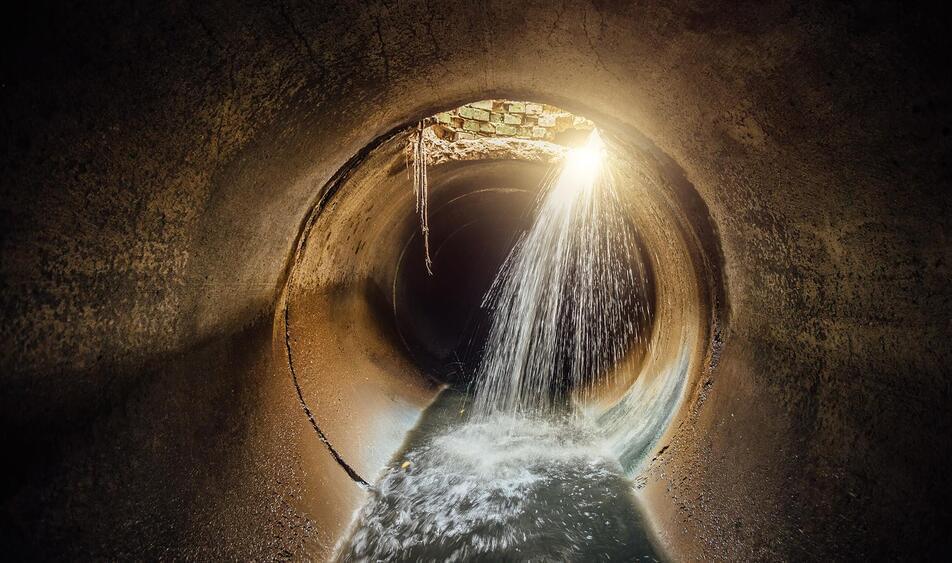
Sewer pipe corrosion, or crown corrosion, occurs when sewage pipe material comes into contact with sulphuric acid. The aging pipe material corrodes, and the pipes crack. Over the past few years, engineers have developed sewer bots to inspect sewage pipes and go to places unsafe for humans.
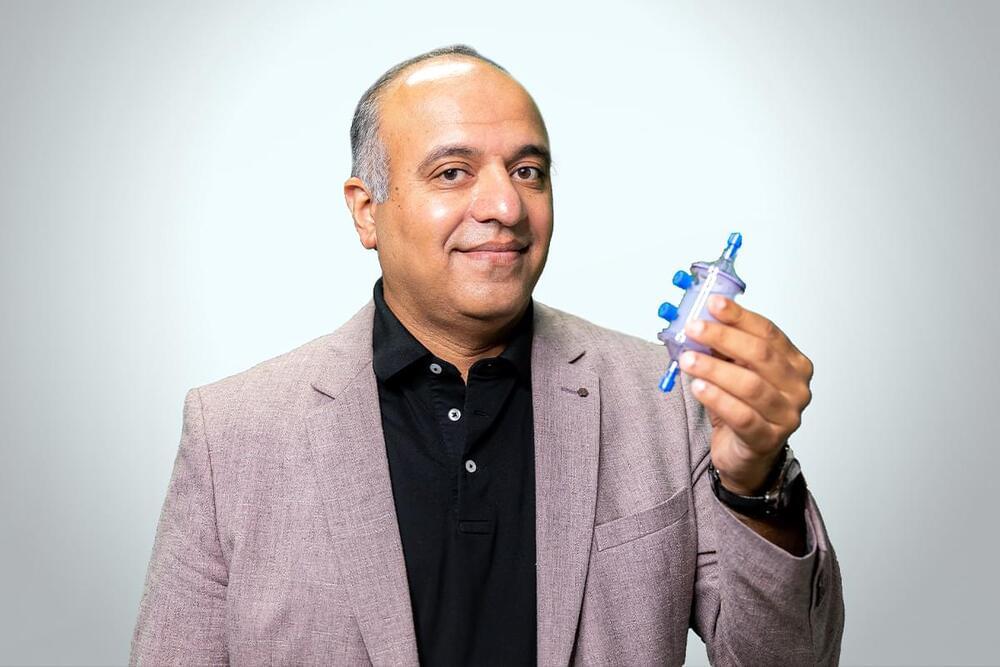
Professor Yan Zhuge, an engineering expert at the University of South Australia, is trialing a novel solution.
Vladimir Zapletin/iStock.
But that also means the robots would have to go to places where existing wireless communications cannot reach them. Hurdles are aplenty.