Colossal Biosciences claims three pups born recently are dire wolves, but they are actually grey wolves with genetic edits intended to make them resemble the lost species
Category: genetics – Page 82
Specialized Recycling System Eliminates Faulty Mitochondrial DNA
Damage to the mitochondria, the “power plants” of the cells, contributes to many diseases. Researchers from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the University of Cologne led by HHU professor of medicine Dr David Pla-Martín, now describe in the scientific journal Science Advances how cells with defective mitochondria activate a special recycling system to eliminate damaged genetic material.
Damage to the genetic material of mitochondria – the mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA for short – can lead to diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Such damage also speeds up the ageing process. However, the cells are normally capable of identifying such damage and reacting.
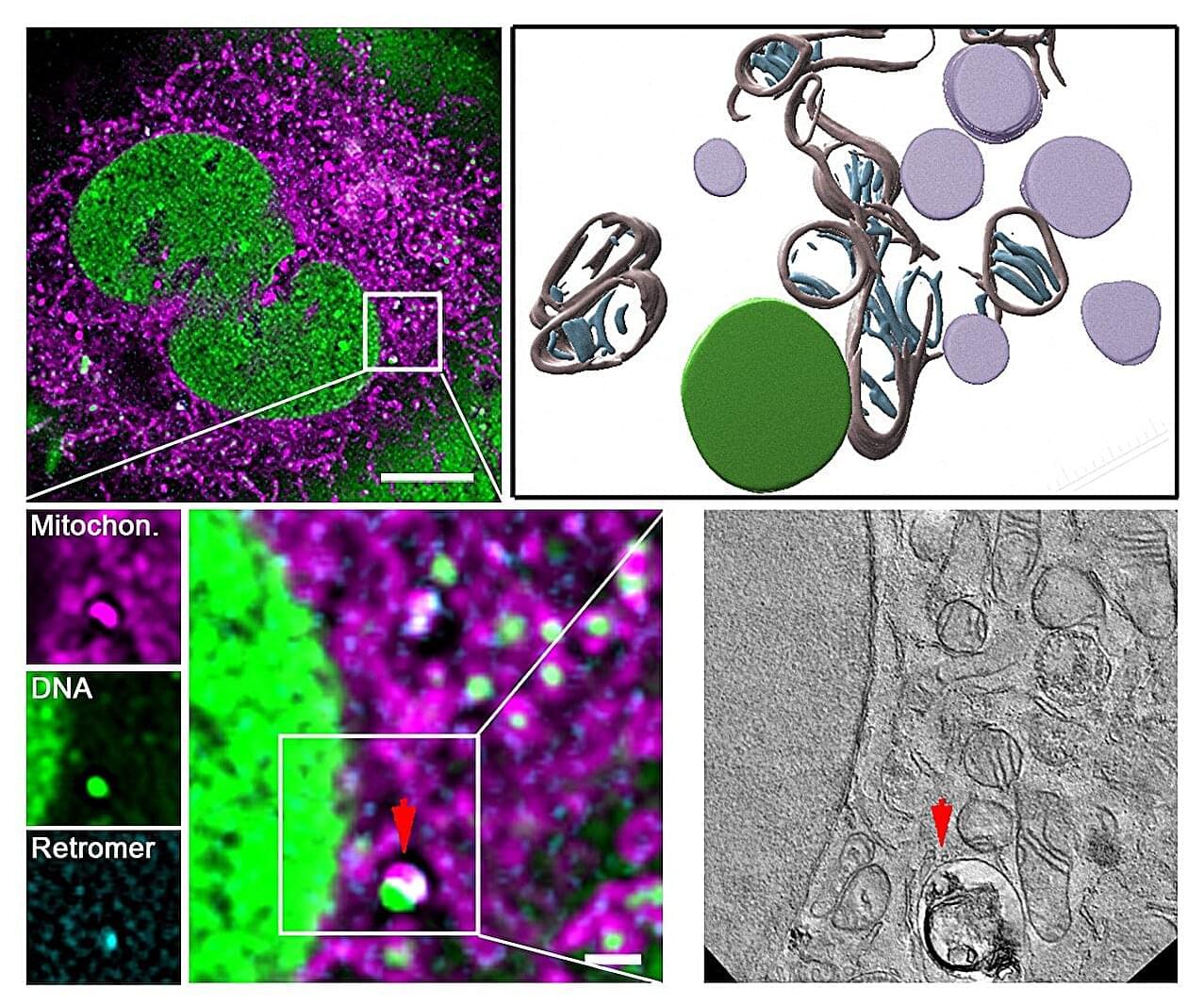
How cells repair their mitochondria: Research uncovers a specialized recycling system
Damage to the genetic material of mitochondria—the mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA for short—can lead to diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Such damage also speeds up the aging process. However, the cells are normally capable of identifying such damage and reacting.
Scientists from University Hospital Düsseldorf and HHU have—in collaboration with the University of Cologne and the Center for Molecular Medicine Cologne (CMMC)—discovered a mechanism which protects and repairs the mitochondria. The research team, headed by Professor Pla-Martín from the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology I at HHU, has identified a specialized recycling system, which cells activate when they identify damage to the mtDNA.
According to the authors in Science Advances, this mechanism relies on a protein complex known as retromer and the lysosomes—cell organelles containing digestive enzymes. These special cellular compartments act like recycling centers, eliminating the damaged genetic material.
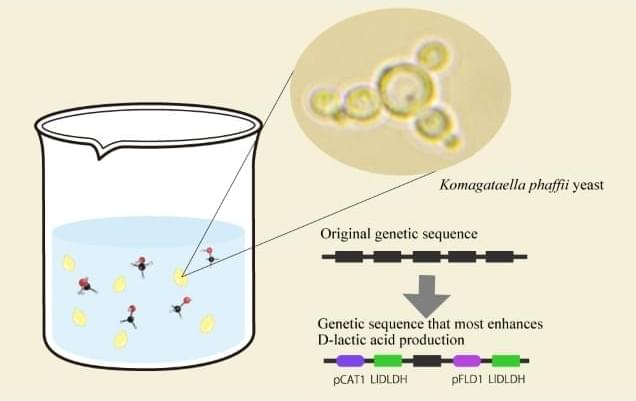
Green recipe: Engineered yeast boosts D-lactic acid production
Constructed strain achieves record-high yield from methanol, advancing ecofriendly biomanufacturing. Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered the ideal genetic “recipe” to turn yeast into a tiny yet powerful eco-friendly factory that converts methanol into D-lactic acid, a key compound used in biodegradable plastics and pharmaceuticals.
This approach could help reduce reliance on petroleum-based processes and contribute to more sustainable chemical production.
Lactic acid is widely used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and bioplastics.
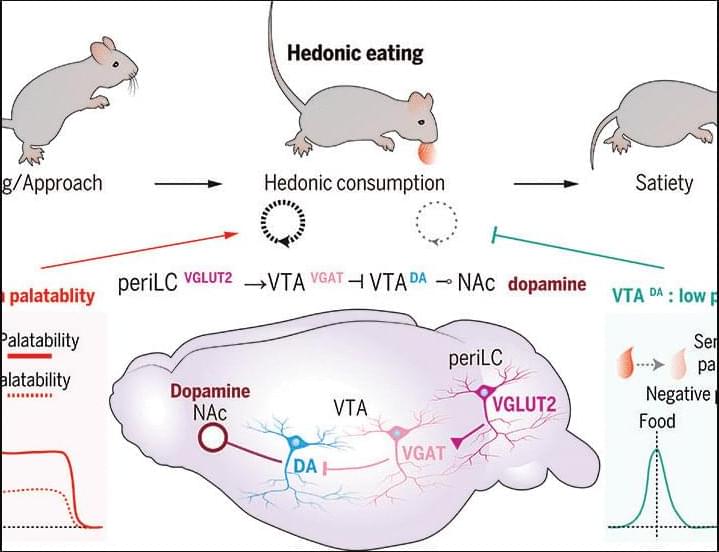
Hedonic eating is controlled by dopamine neurons that oppose GLP-1R satiety
Hedonic eating is defined as food consumption driven by palatability without physiological need. However, neural control of palatable food intake is poorly understood. We discovered that hedonic eating is controlled by a neural pathway from the peri–locus ceruleus to the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Using photometry-calibrated optogenetics, we found that VTA dopamine (VTADA) neurons encode palatability to bidirectionally regulate hedonic food consumption. VTADA neuron responsiveness was suppressed during food consumption by semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide receptor 1 (GLP-1R) agonist used as an antiobesity drug. Mice recovered palatable food appetite and VTADA neuron activity during repeated semaglutide treatment, which was reversed by consumption-triggered VTADA neuron inhibition.
Does Methylene Blue Impact Lifespan?
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
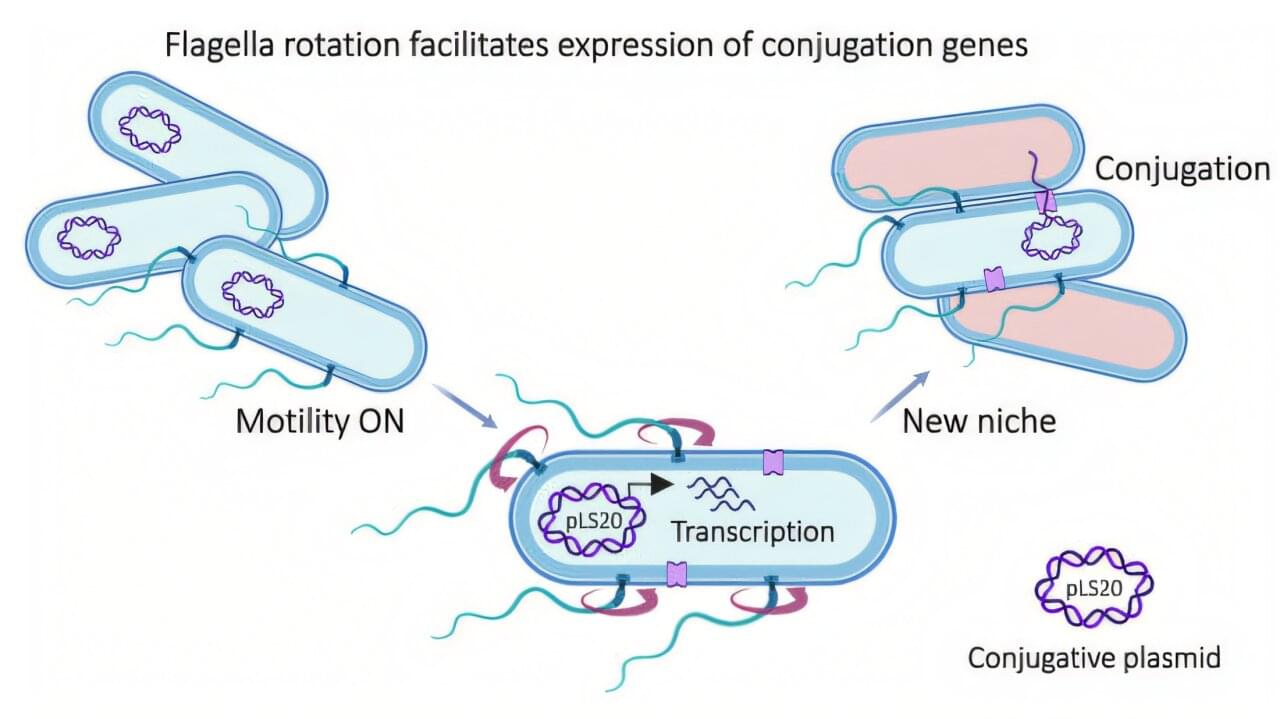
Spinning into antibiotic resistance: The flagella’s hidden role
A new study from the Faculty of Medicine at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem sheds light on how bacterial motion influences the spread of antibiotic resistance. Led by Professor Sigal Ben-Yehuda and Professor Ilan Rosenshine from the Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, the research uncovers a direct connection between the rotation of bacterial flagella—structures used for movement—and the activation of genes that enable bacteria to transfer DNA to one another.
This process, known as bacterial conjugation, is a key mechanism by which genetic traits, particularly antibiotic resistance, are shared among bacterial populations. While conjugation has traditionally been associated with bacteria attaching to solid surfaces, the team investigated pLS20, a widespread conjugative plasmid in Bacilli species, which behaves differently. The study shows that in liquid environments, where bacteria rely on movement to navigate, the rotation of flagella acts as a mechanical signal that turns on a set of genes required for DNA transfer.
The researchers discovered that this signal triggers gene expression in a specific subset of donor cells, which then form clusters with recipient bacteria. These multicellular clusters bring the two types of cells into close contact, facilitating the transfer of genetic material.

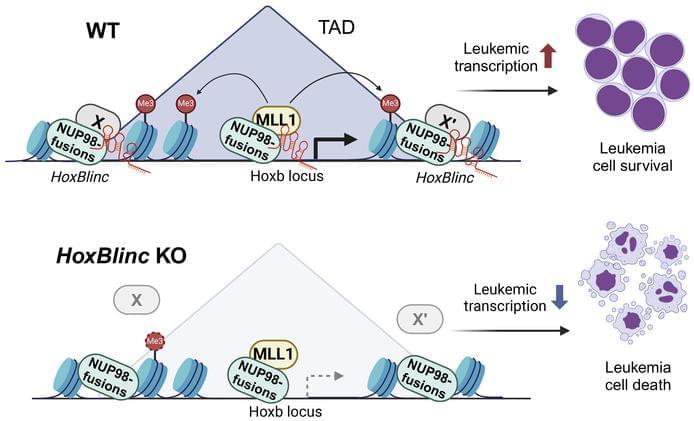
Abstract: Understanding the pathogenesis of NUP98-fusion mediated leukemia—
Suming Huang & team show the HoxBlin c long non-coding RNA serves as an oncogenic regulator that controls 3D nuclear organization, chromatin accessibility and gene transcription related to leukemogenesis.
The figure shows H&E staining of sternum and spleen from WT and B-ALL HoxBlin c Tg mice.
1Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, Department of Pediatrics, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA.
2Department of Molecular Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA.
3Genetics Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute (NCI), NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.
