Researchers have identified mutations in the non-coding gene RNU2-2 as a cause of a newly defined neurodevelopmental disorder, often accompanied by severe epilepsy.

17K likes, — vaibhavsisinty on March 27, 2025: “Your Future Kids Might Be Genetically Engineered🤯… [genetic engineering, CRISPR, designer babies, IVF, in vitro gametogenesis, gene editing, human evolution, bioethics, futuristic science, AI in healthcare, medical advancements, artificial reproduction, skin cell gametes, future tech, DNA modification, biotechnology]”
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
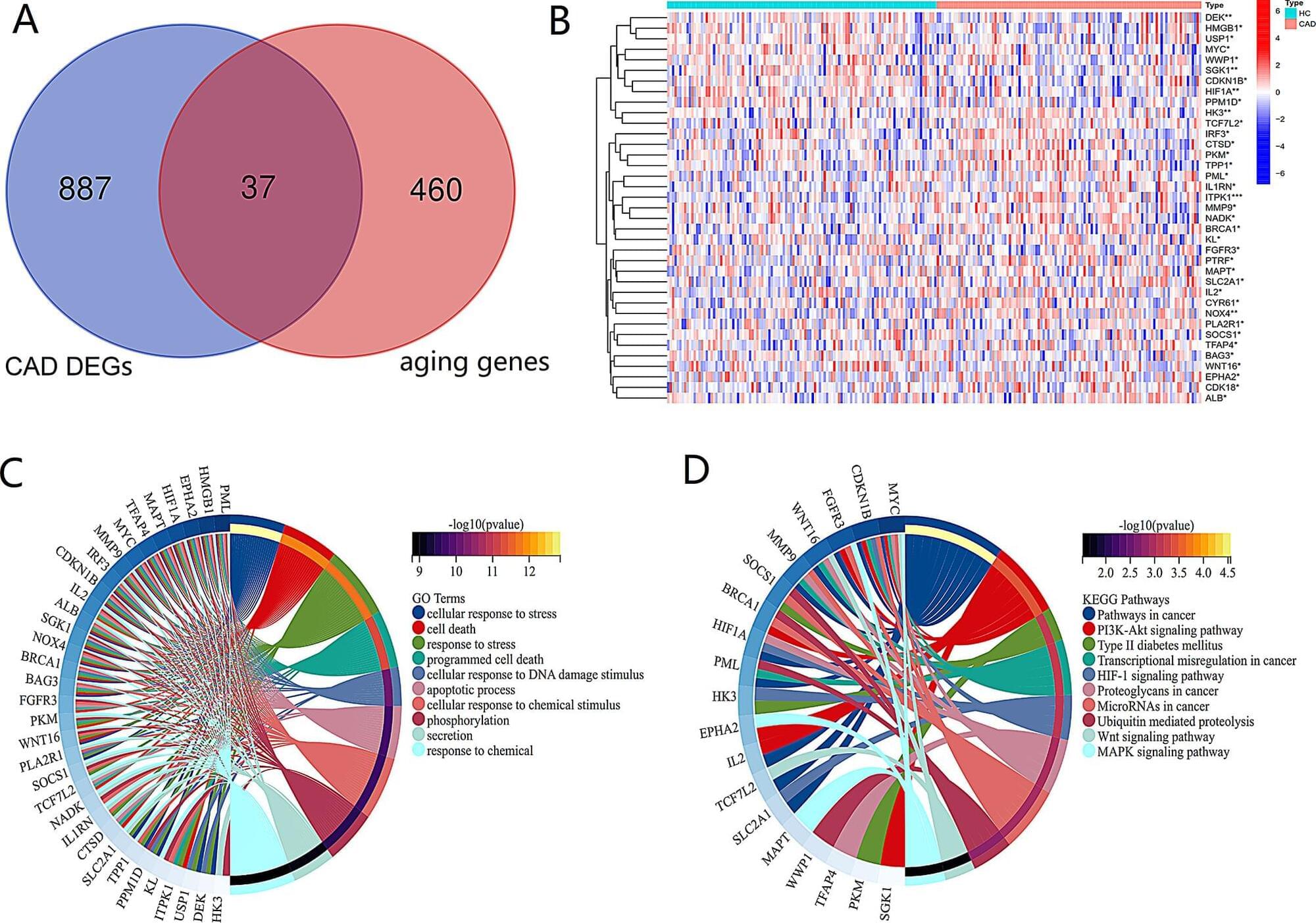
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the most common cardiovascular disease worldwide, threatening human health, quality of life and longevity. Aging is a dominant risk factor for CAD. This study aims to investigate the potential mechanisms of aging-related genes and CAD, and to make molecular drug predictions that will contribute to the diagnosis and treatment.
We downloaded the gene expression profile of circulating leukocytes in CAD patients (GSE12288) from Gene Expression Omnibus database, obtained differentially expressed aging genes through “limma” package and GenaCards database, and tested their biological functions. Further screening of aging related characteristic genes (ARCGs) using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and random forest, generating nomogram charts and ROC curves for evaluating diagnostic efficacy. Immune cells were estimated by ssGSEA, and then combine ARCGs with immune cells and clinical indicators based on Pearson correlation analysis. Unsupervised cluster analysis was used to construct molecular clusters based on ARCGs and to assess functional characteristics between clusters. The DSigDB database was employed to explore the potential targeted drugs of ARCGs, and the molecular docking was carried out through Autodock Vina.
Changes in brain connectivity before and after puberty may explain why some children with a rare genetic disorder have a higher risk of developing autism or schizophrenia, according to a UCLA Health study.
Developmental psychiatric disorders like autism and schizophrenia are associated with changes in brain functional connectivity. However, the complexity of these conditions make it difficult to understand the underlying biological causes. By studying genetically defined brain disorders, researchers at UCLA Health and collaborators have shed light on possible mechanisms.
The UCLA study examined a particular genetic condition called chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome—caused by missing DNA on chromosome 22—which is associated with a higher risk of developing neuropsychiatric conditions such as autism and schizophrenia. But the underlying biological basis of this association has not been well understood.

Pediatric neuroimmune disorders comprise a heterogeneous group of immune-mediated CNS inflammatory conditions. Some, such as multiple sclerosis, are well defined by validated diagnostic criteria. Others, such as anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis, can be diagnosed with detection of specific autoantibodies. This review addresses neuroimmune disorders that neither feature a diagnosis-defining autoantibody nor meet criteria for a distinct clinicopathologic entity. A broad differential in these cases should include CNS infection, noninflammatory genetic disorders, toxic exposures, metabolic disturbances, and primary psychiatric disorders. Neuroimmune considerations addressed in this review include seronegative autoimmune encephalitis, seronegative demyelinating disorders such as neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, and genetic disorders of immune dysregulation or secondary neuroinflammation.
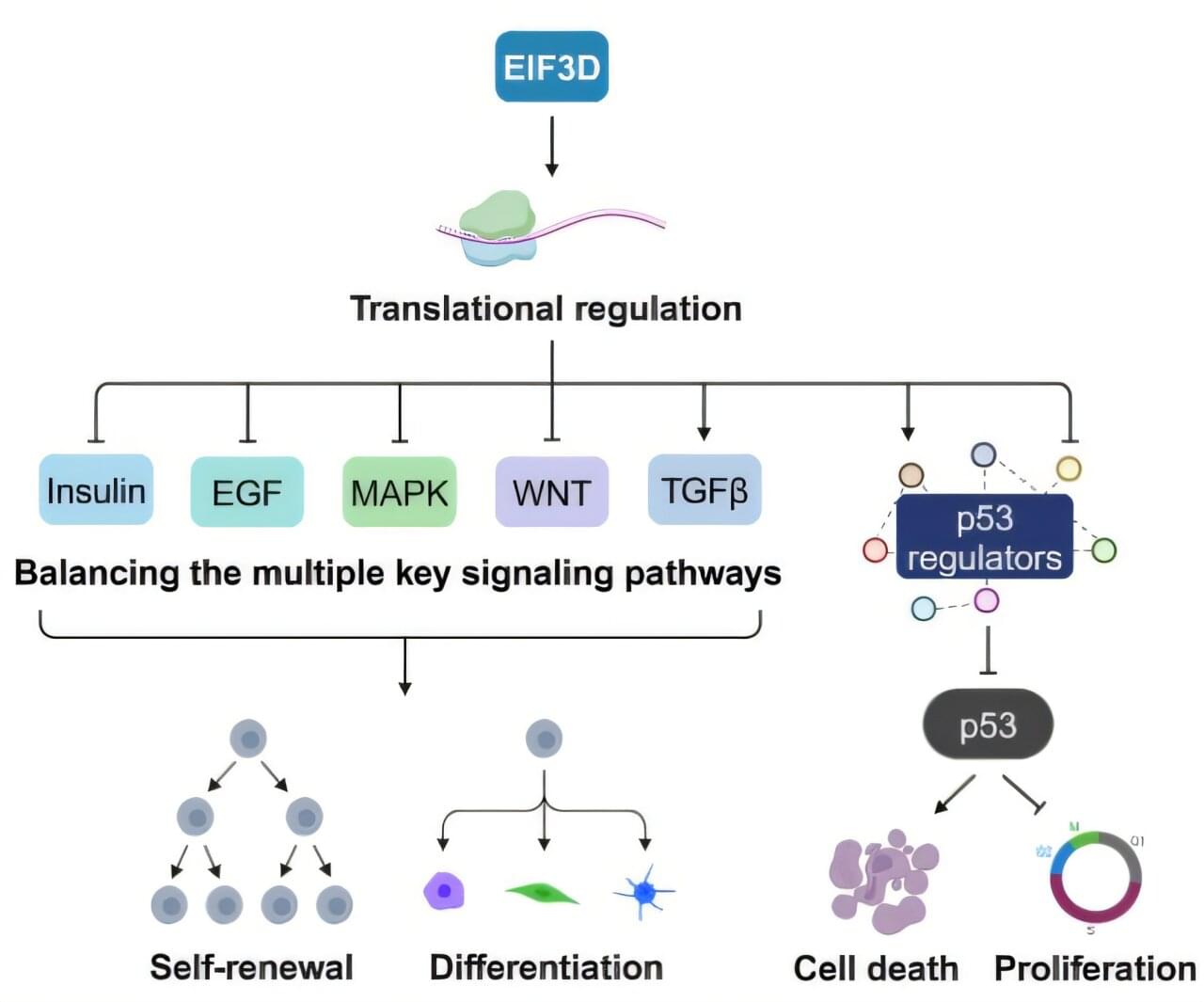
A team of CiRA researchers has uncovered the crucial role of EIF3D—a protein translational regulator—in primed pluripotency. The research is published in the journal Science Advances.
According to the central dogma of molecular biology, information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. While much is known about pluripotency —the ability to differentiate into any other cell type in the body and to divide indefinitely—in terms of transcriptional and epigenetic regulation, as well as signal transduction, how protein translation ties these control mechanisms together remains largely underexplored.
To identify genes important for maintaining primed pluripotency—a state poised for differentiating into various cell types in the body, the research team, led by Associate Professor Kazutoshi Takahashi and Assistant Professor Chikako Okubo, began with a genome-wide genetic screen based on CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) that systemically reduces the expression of every single gene in the genome of a pluripotent stem cell (PSC) line.
