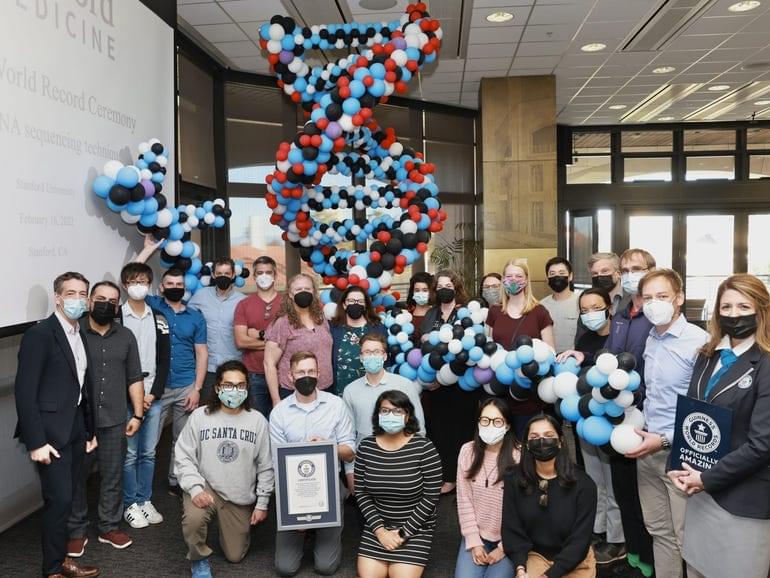
A Stanford University-led research team has set a new Guinness World Record for the fastest DNA sequencing technique using AI computing to accelerate workflow speed.
The research, led by Dr Euan Ashley, professor of medicine, genetics and biomedical data science at Stanford School of Medicine, in collaboration with Nvidia, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Google, Baylor College of Medicine, and the University of California, achieved sequencing in just five hours and two minutes.
The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, involved speeding up every step of genome sequencing workflow by relying on new technology. This included using nanopore sequencing on Oxford Nanopore’s PromethION Flow Cells to generate more than 100 gigabases of data per hour, and Nvidia GPUs on Google Cloud to speed up the base calling and variant calling processes.