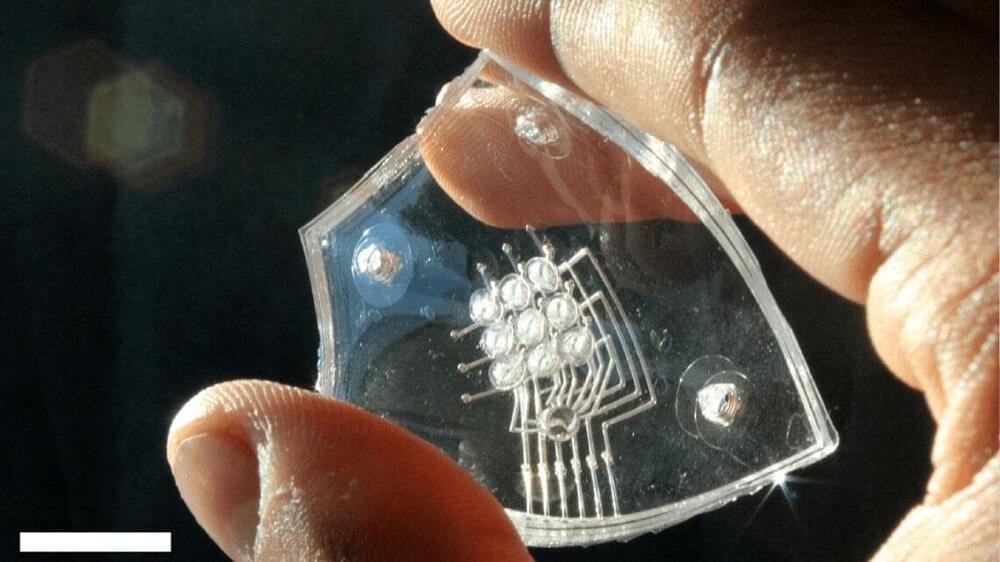
Imagine an iPad or a Kindle for the blind, with inflatable Braille that changes shape under a user’s touch. A Cornell-led collaboration has made a crucial component for such a technology: A haptic array of densely packed actuators that cause silicone membrane “dots” to pop up when triggered by combustion.
The team’s paper, “Valveless Microliter Combustion for Densely Packed Arrays of Powerful Soft Actuators,” published Sept. 28 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The lead author is doctoral student Ronald Heisser.
One of the major hurdles for designing a dynamic Braille display for electronics is figuring out how to apply the necessary amount of force for each dot. Previous attempts have usually involved motors, hydraulics or tethered pumps, all of which are cumbersome, complex and expensive, according to Rob Shepherd, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering in the College of Engineering and the paper’s senior author.