Many of us swing through gates every day—points of entry and exit to a space like a garden, park or subway. Electronics have gates too. These control the flow of information from one place to another by means of an electrical signal. Unlike a garden gate, these gates require control of their opening and closing many times faster than the blink of an eye.
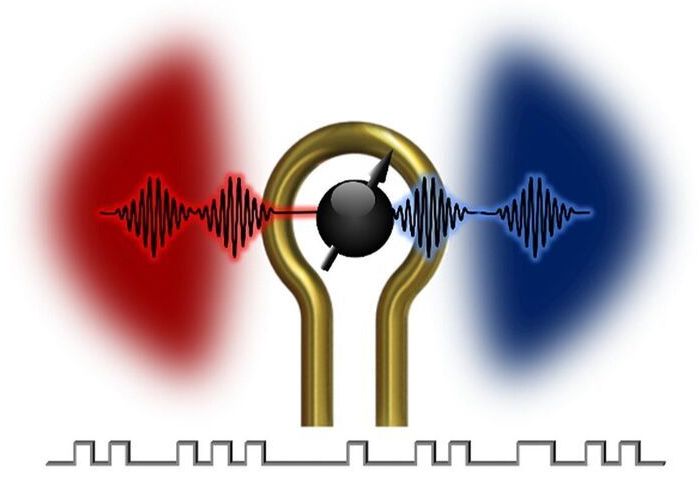
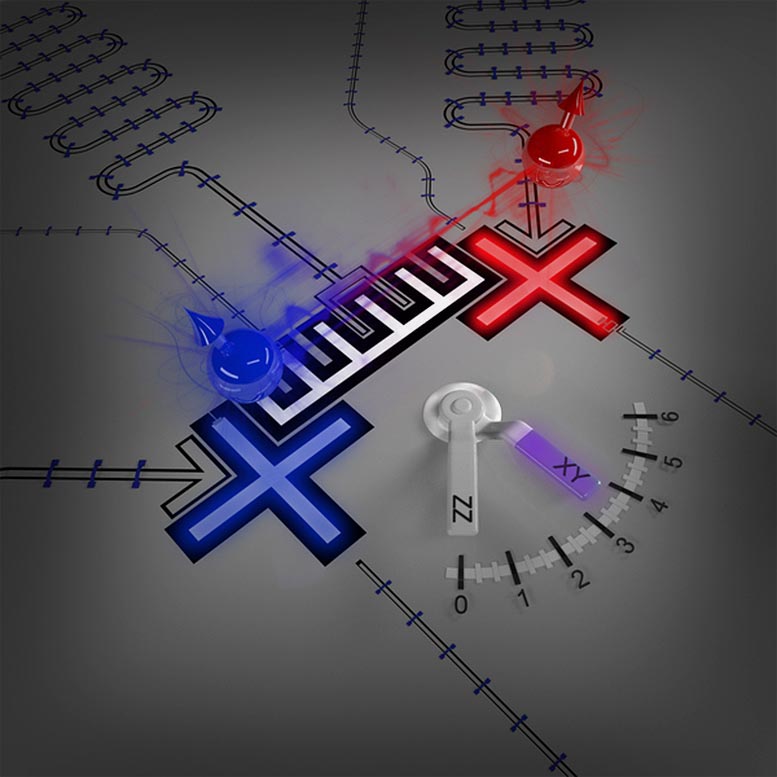
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering have devised a unique means of achieving effective gate operation with a form of information processing called electromagnonics. Their pivotal discovery allows real-time control of information transfer between microwave photons and magnons. And it could result in a new generation of classical electronic and quantum signal devices that can be used in various applications such as signal switching, low-power computing and quantum networking.
Microwave photons are elementary particles forming the electromagnetic waves employed in, for example, wireless communications. Magnons are the particle-like representatives of “spin waves.” That is, wave-like disturbances in an ordered array of microscopically aligned spins that occur in certain magnetic materials.