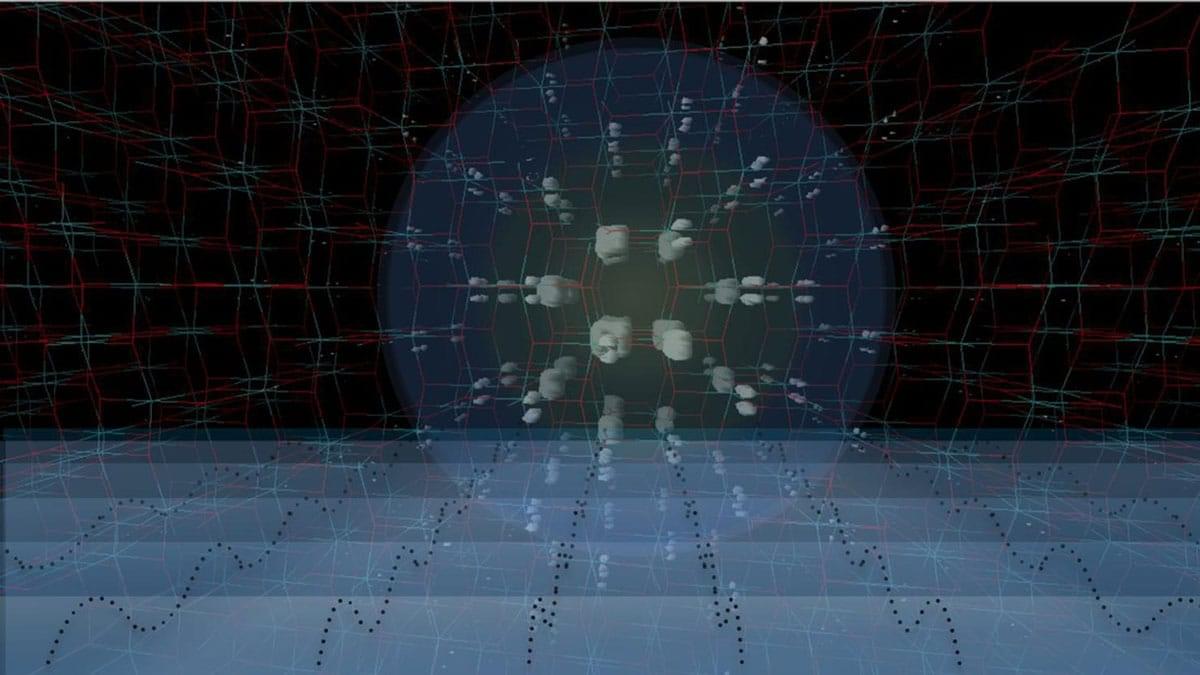
Superconductivity—the ability of some materials to conduct electricity with no energy loss—holds immense promise for new technologies from lossless power grids to advanced quantum devices.
A publication in Physical Review Letters by researchers at the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory sheds light on an outstanding mystery in the study of superconductivity: high-temperature superconductivity in cuprates.
Doubling down on results from a previous SLAC study, the paper provides further evidence that the Hubbard model—the leading theory for describing strong correlations between electrons in quantum materials—fails to explain electron dynamics in cuprates, even in simplified, one-dimensional systems.