Virginia Tech study shows gentle electric pulses can modify tumors, making them more accessible to immune cells.

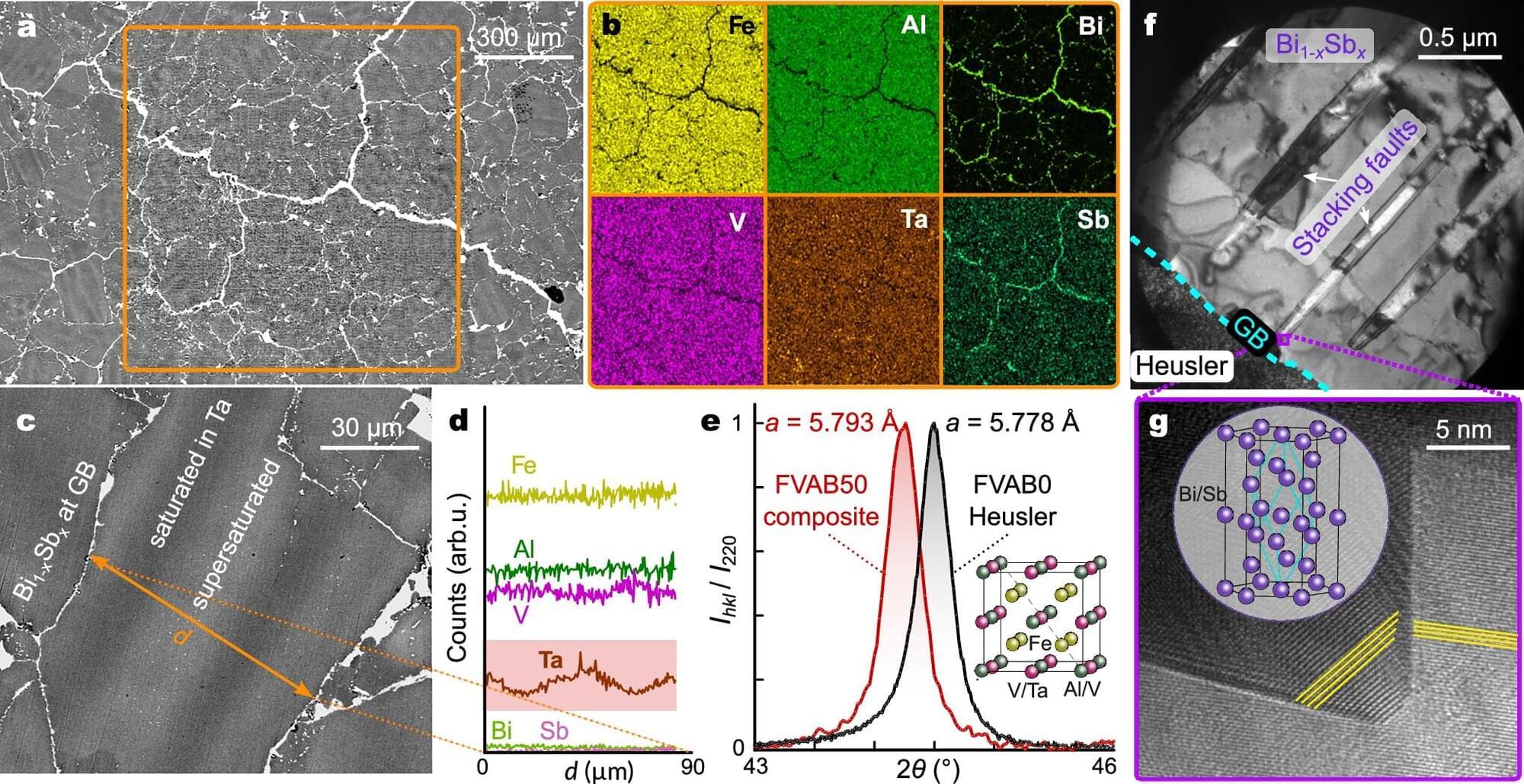
Thermoelectric materials enable the direct conversion of heat into electrical energy. This makes them particularly attractive for the emerging Internet of Things. For example, for the autonomous energy supply of microsensors and other tiny electronic components.
In order to make the materials more efficient, at the same time, heat transport via the lattice vibrations must be suppressed and the mobility of the electrons increased—a hurdle that has often hindered research until now.
An international team led by Fabian Garmroudi has now succeeded in using a new method to develop hybrid materials that achieve both goals—reduced coherence of the lattice vibrations and increased mobility of the charge carriers. The key: a mixture of two materials with fundamentally different mechanical but similar electronic properties.

A recent study found that the Hubbard model failed to accurately predict the behavior of a simplified one-dimensional cuprate system. According to scientists at SLAC, this suggests the model is unlikely to fully account for high-temperature superconductivity in two-dimensional cuprates.
Superconductivity, the phenomenon where certain materials can conduct electricity without any energy loss, holds great potential for revolutionary technologies, from ultra-efficient power grids to cutting-edge quantum devices.
A recent study published in Physical Review Letters.

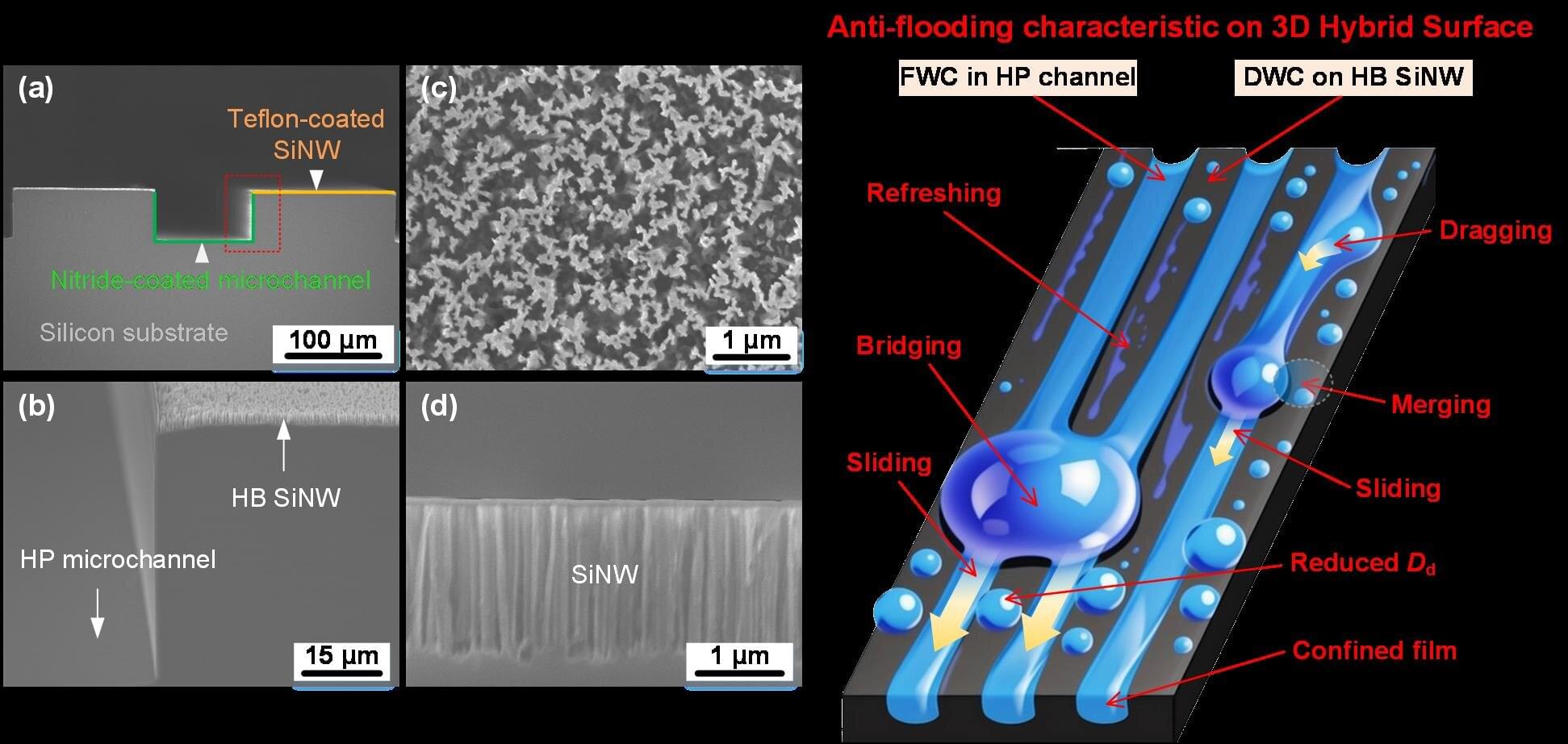
Condensation is critical for applications like power generation, water harvesting, and cooling systems. However, traditional surfaces suffer from a drop in performance under high subcooling, when the surface temperature is much lower than the surrounding vapor. This leads to water flooding and reduced heat transfer.
To tackle this long-standing challenge, researchers at National Taiwan University and National Chung Hsing University have developed a novel three-dimensional (3D) hybrid surface that significantly enhances condensation performance and avoids flooding, even at high subcooling. The paper is published in Small Structures.
The new surface integrates short hydrophobic nanowires and hydrophilic microchannels in a structured pattern. This combination helps guide water droplets efficiently off the surface, preventing the accumulation of water that typically hampers heat transfer.
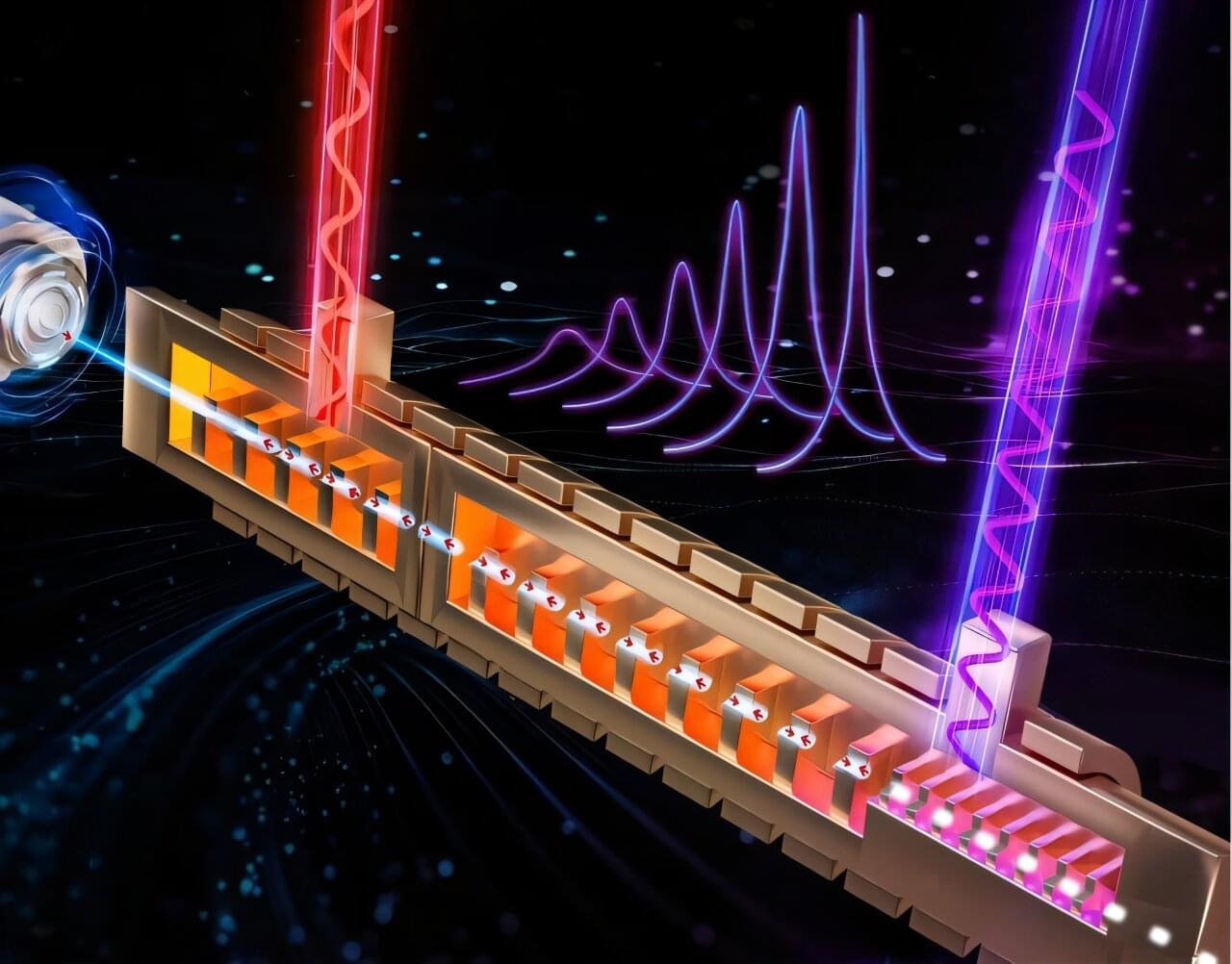
Superradiant Smith-Purcell radiation (S-SPR) is a kind of free electron radiation with a train of free electron bunches passing over a periodic grating. In theory, the ultra-narrow spectral linewidth of S-SPR could be realized, which would be greatly beneficial to various applications such as imaging, sensing and communication.
However, in the free electron accelerators, customized setups and orotrons, the instability of electron kinetic energy, coulomb effect and the finite number of electron bunches worsened the radiation linewidth, and the large size of equipment limits the application scenarios.
In a new paper published in eLight, a team of scientists, led by Professor Fang Liu and Yidong Huang from the Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, China, have developed the first compact S-SPR device with ultra-narrow and continuously tunable spectral linewidth.
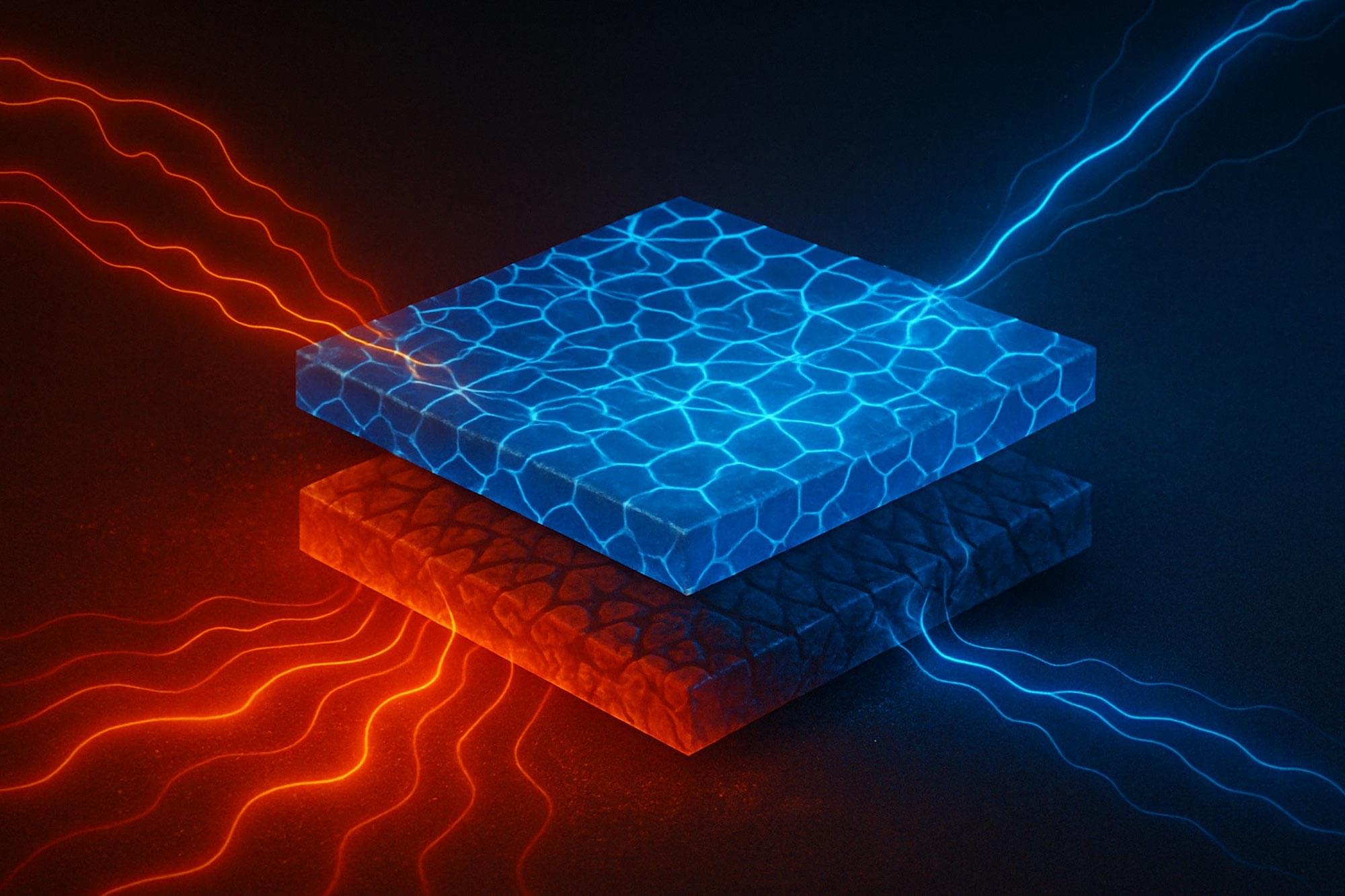
Scientists have found a clever way to double the efficiency of thermoelectric materials — those that convert heat into electricity — by mixing two substances with contrasting mechanical properties but similar electronic traits.
The result is a hybrid that blocks heat at microscopic interfaces while allowing electricity to flow freely, bringing us closer to cheaper, more stable alternatives to today’s gold-standard materials used in the Internet of Things and beyond.
Boosting thermoelectrics for the internet of things.

For more than a century, electricity has flowed through wires, powering everything from the smallest gadgets to entire cities. However, what seemed like a distant dream—wireless energy transmission—may soon become a reality. This breakthrough technology, known as “power beaming”, promises to eliminate the need for physical infrastructure, delivering power directly from one point to another using electromagnetic waves.