With “each 10% increase in UPF contribution to total energy intake, there is a corresponding 2.7% rise in the risk of all-cause mortality,” the study says


The best solar company in Australia just installed my new solar system.
Check them out here: https://www.resinc.com.au/electricviking.
I use Starlink internet to upload all of my videos, use my referral link here: https://www.starlink.com/residential?referral=RC-392400-91086-9
👇👇 Buy something and support The Electric Viking Store 👇👇
https://shop.theelectricviking.com/
Size guide and other help for the store 👇
🔔 Subscribe and hit the notification bell! ►


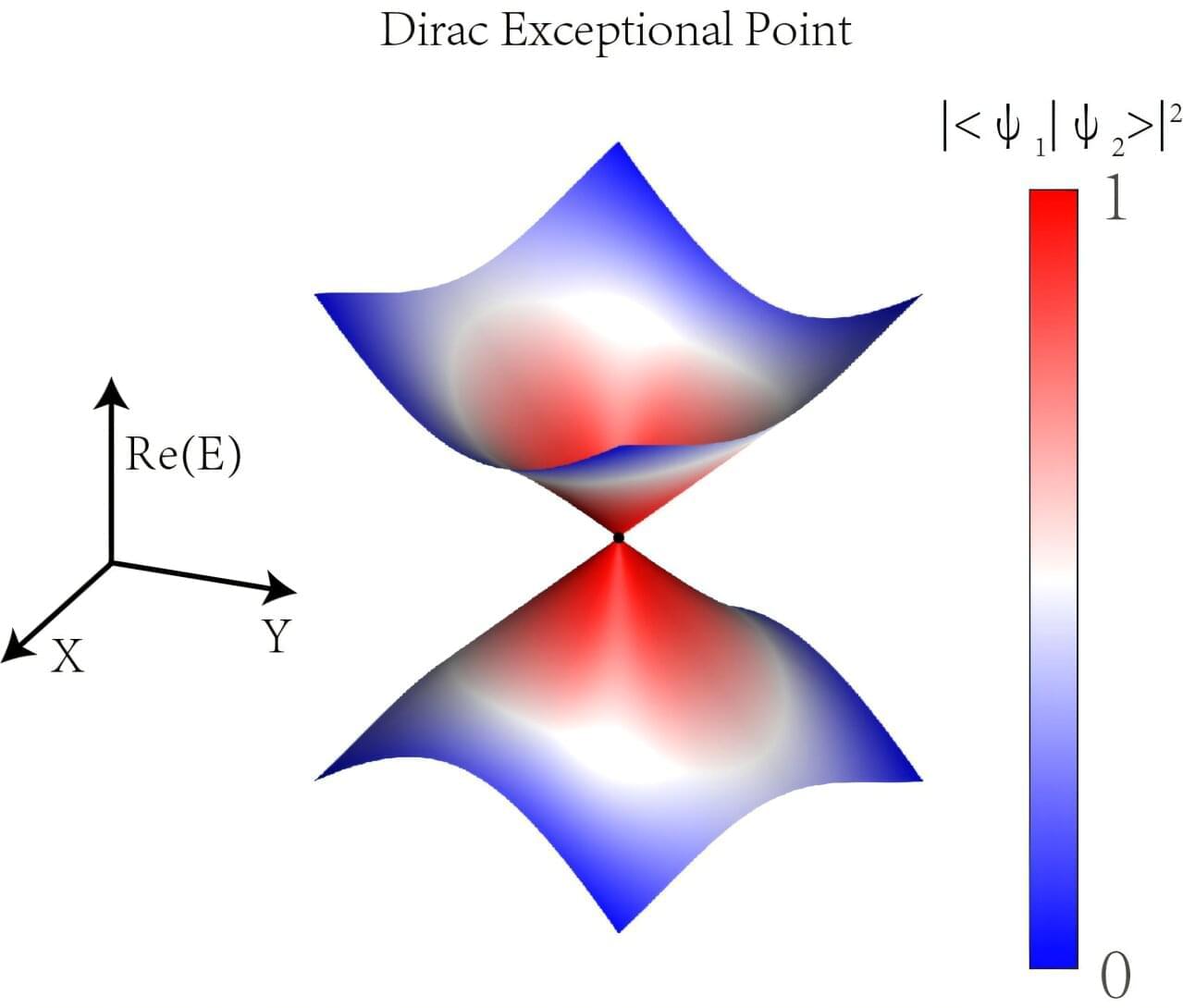
Exceptional points (EPs) are unique types of energy-level degeneracies that occur in non-Hermitian systems. Since their existence was first proposed more than a century ago, physicists have only been able to experimentally observe two types of EPs, both of which were found to give rise to exotic phases of matter in various materials, including Dirac and Weyl semimetals.
Building on recent theoretical studies, researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China recently set out to experimentally observe a new class of EPs, known as Dirac EPs. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, could open new exciting possibilities for the study of non-Hermitian dynamics and for the development of protocols to reliably control quantum systems.
“Our inspiration stemmed from a prior theoretical study that proposed a type of exceptional point (EP) termed Dirac EPs,” Xing Rong, senior author of the paper, told Phys.org. “We realized that this novel type of EP is distinct from all experimentally observed EPs over the past half-century. Our work aimed to transform this theoretical prediction into experimental reality.”

Understanding the origin of heavy elements on the periodic table is one of the most challenging open problems in all of physics. In the search for conditions suitable for these elements via “nucleosynthesis,” a Los Alamos National Laboratory-led team is going where no researchers have gone before: the gamma-ray burst jet and surrounding cocoon emerging from collapsed stars.
As proposed in an article in The Astrophysical Journal, high-energy photons produced deep in the jet could dissolve the outer layers of a star into neutrons, causing a series of physical processes that result in the formation of heavy elements.
“The creation of heavy elements such as uranium and plutonium necessitates extreme conditions,” said Matthew Mumpower, physicist at Los Alamos. “There are only a few viable yet rare scenarios in the cosmos where these elements can form, and all such locations need a copious amount of neutrons. We propose a new phenomenon where those neutrons don’t pre-exist but are produced dynamically in the star.”
A U of A engineering researcher is using sunlight and semiconductor catalysts to produce hydrogen by splitting apart water molecules into their constituent elements.
“The process to form the semiconductor, called thermal condensation polymerization, uses cheap and Earth-abundant materials, and could eventually lead to a more efficient, economical path to clean energy than existing solar technologies,” says project lead Karthik Shankar of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, an expert in the field of photocatalysis.
In a collaboration between the U of A and the Technical University of Munich, results of the research were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
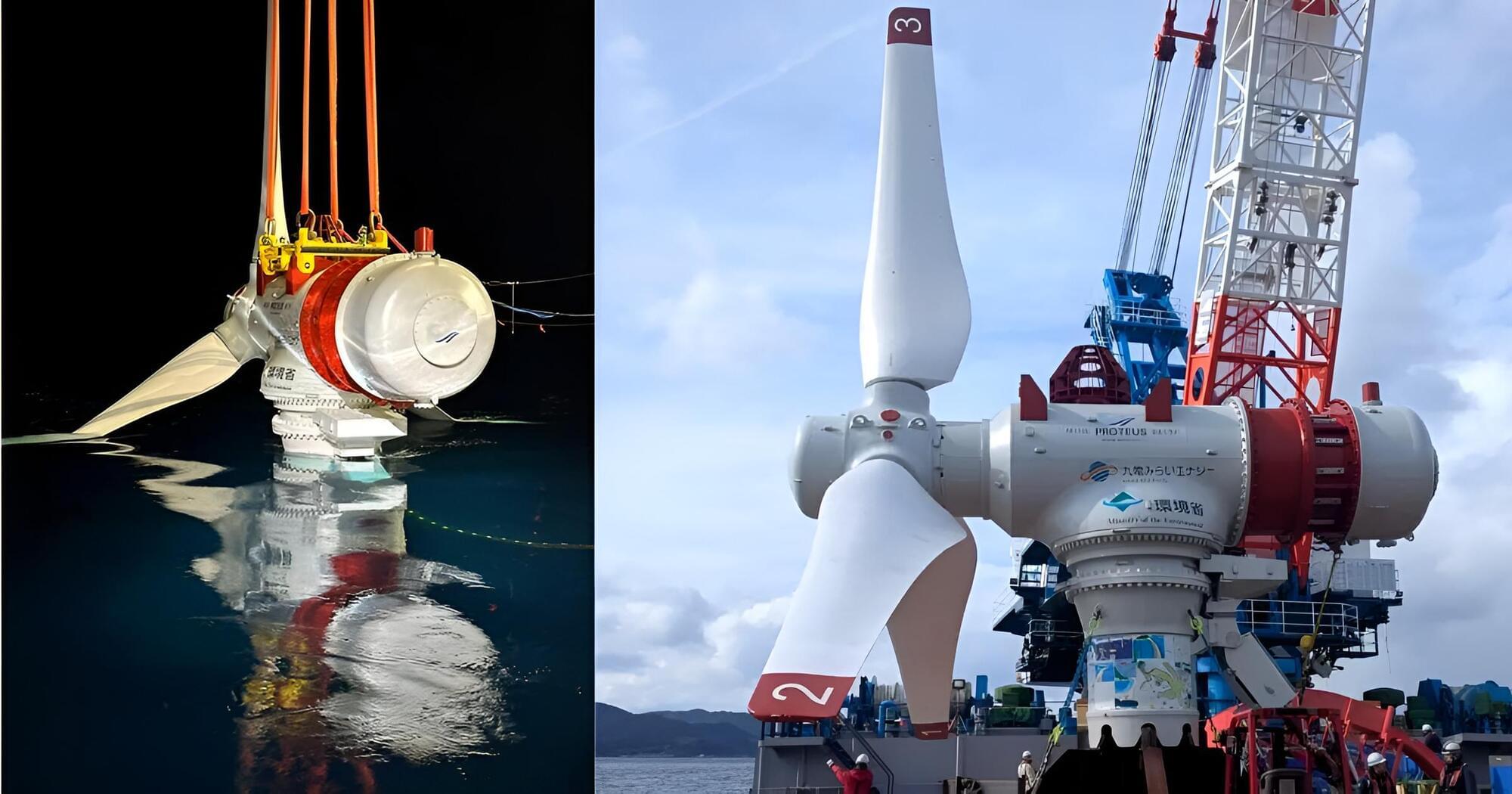
Japan has taken a significant step forward in renewable energy with the successful deployment of its first megawatt-scale tidal turbine, the AR1100. Installed in the Naru Strait, this 1.1 MW tidal turbine represents a major breakthrough in marine energy technology. As Japan moves towards a sustainable, fossil-fuel-free future, tidal energy is poised to play a crucial role in the country’s energy transition.
This latest achievement builds upon the success of the AR500 pilot project, which demonstrated the viability of tidal energy with a 97% availability rate. With the AR1100 now operational, Japan has entered the global race to harness ocean power on a large scale.
This article will explore how tidal energy works, the advantages of this technology, Japan’s commitment to renewable energy, and the impact of the AR1100 project on the future of clean power generation.

A research team has developed an innovative single-step laser printing technique to accelerate the manufacturing of lithium-sulfur batteries. Integrating the commonly time-consuming active materials synthesis and cathode preparation in a nanosecond-scale laser-induced conversion process, this technique is set to revolutionize the future industrial production of printable electrochemical energy storage devices. The team was led by Prof. Mitch Li Guijun, Assistant Professor from the Division of Integrative Systems and Design at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST).
The findings of this study are published in the journal Nature Communications.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are expected to supersede existing lithium-ion batteries due to sulfur cathodes’ high theoretical energy density. To ensure the rapid conversion of sulfur species, these cathodes are typically composed of active materials, host materials (or catalysts), and conductive materials.
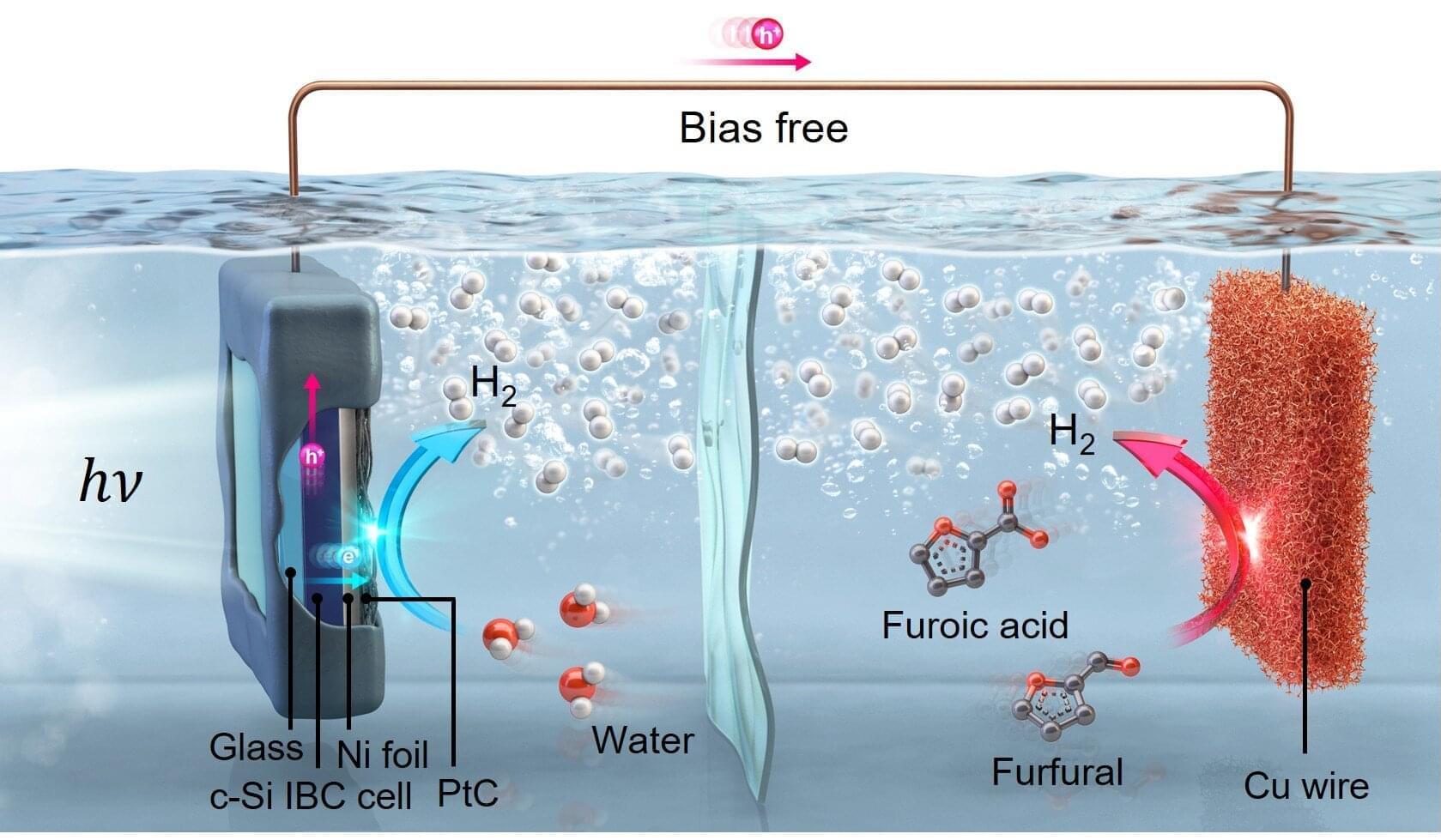
A technology for hydrogen (H2) production has been developed by a team of researchers led by Professors Seungho Cho and Kwanyong Seo from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Ji-Wook Jang’s team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST.
Their research is published in the journal Nature Communications.
This innovative method utilizes biomass derived from sugarcane waste and silicon photoelectrodes to generate H2 exclusively using sunlight, achieving a production rate four times higher than the commercialization benchmark set by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).