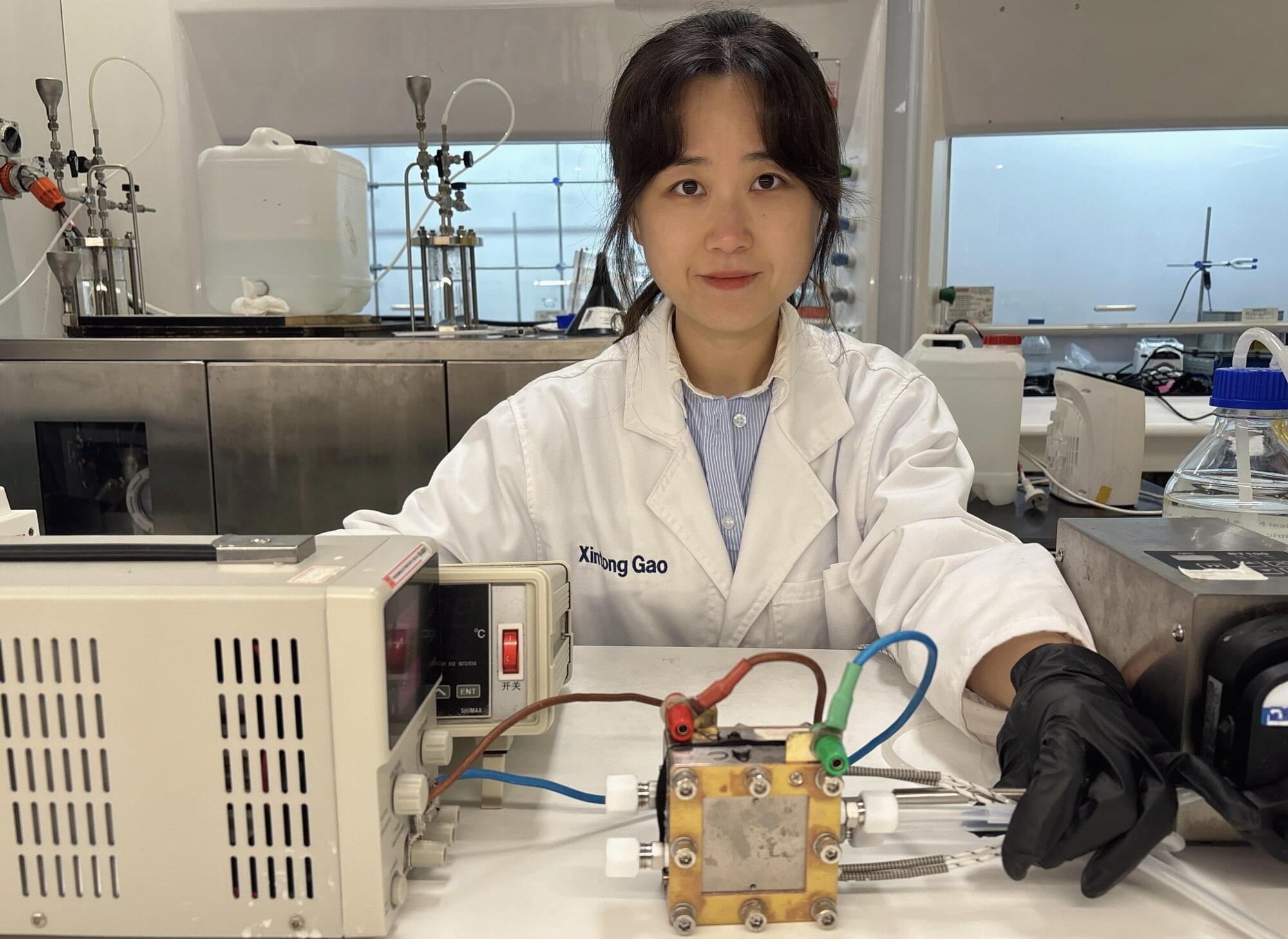
Researchers have developed two unique energy-efficient and cost-effective systems that use urea found in urine and wastewater to generate hydrogen.
The unique systems reveal pathways to economically generate “green” hydrogen, a sustainable and renewable energy source, and the potential to remediate nitrogenous waste in aquatic environments.
Typically, we generate hydrogen through the electrolysis of water where water is split into oxygen and hydrogen. It is a promising technology to help solve the global energy crisis, but the process is energy intensive, which renders it cost-prohibitive when compared to extracting hydrogen from fossil fuels (gray hydrogen), itself an undesirable process because of the carbon emissions it generates.