T1 Energy, an energy solutions and manufacturing company based in Austin, is doubling down on the Lone Star State with a new plant.


The large-scale renewable energy storage sphere is set to get a massive boost with the development of a 1 GWh molten salt storage system, which will be capable of powering approximately 100,000 homes for 10 hours with an efficiency of up to 90%.
This breakthrough is the result of a collaboration between Danish thermal energy storage developer Hyme Energy and Swiss fluid engineering specialist Sulzer.
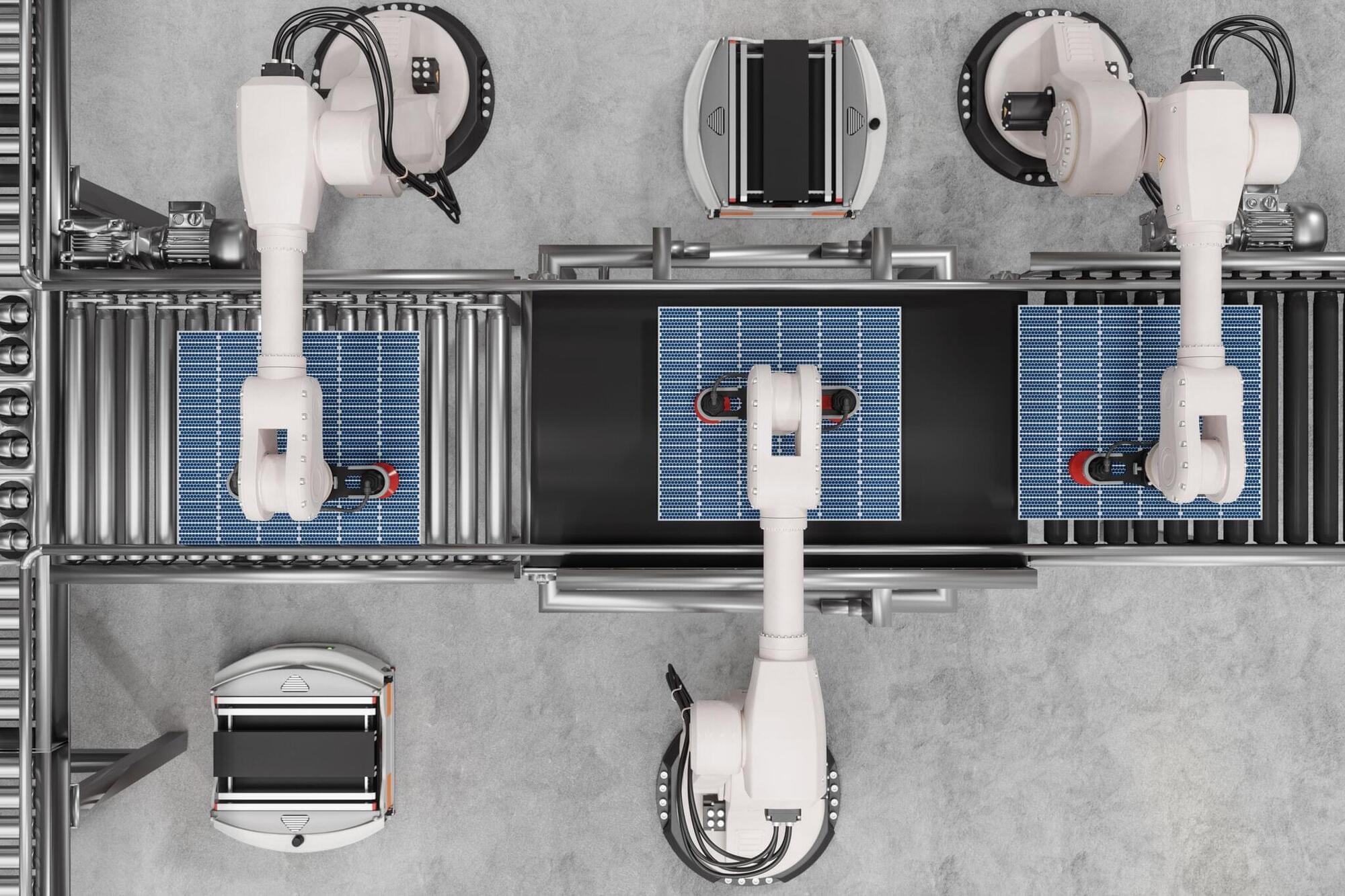
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have unlocked new insights into the turbulent behavior of hypersonic flows by using advanced 3D simulations.
Leveraging supercomputing power and custom-built software, they discovered unexpected instabilities and flow breaks around cone-shaped models at Mach 16, disturbances never seen before in previous 2D or experimental studies. These findings could significantly impact the design of future hypersonic vehicles by helping engineers understand how extreme speeds interact with surface geometries in new ways.
Hypersonic Flows and New Discoveries.

Scientists have long sought to unravel the mysteries of strange metals—materials that defy conventional rules of electricity and magnetism. Now, a team of physicists at Rice University has made a breakthrough in this area using a tool from quantum information science. Their study, published recently in Nature Communications, reveals that electrons in strange metals become more entangled at a crucial tipping point, shedding new light on the behavior of these enigmatic materials. The discovery could pave the way for advances in superconductors with the potential to transform energy use in the future.
Unlike conventional metals such as copper or gold that have well-understood electrical properties, strange metals behave in much more complex ways, making their inner workings beyond the realm of textbook description. Led by Qimiao Si, the Harry C. and Olga K. Wiess Professor of Physics and Astronomy, the research team turned to quantum Fisher information (QFI), a concept from quantum metrology used to measure how electron interactions evolve under extreme conditions, to find answers. Their research shows that electron entanglement, a fundamental quantum phenomenon, peaks at a quantum critical point: the transition between two states of matter.
“Our findings reveal that strange metals exhibit a unique entanglement pattern, which offers a new lens to understand their exotic behavior,” Si said. “By leveraging quantum information theory, we are uncovering deep quantum correlations that were previously inaccessible.”
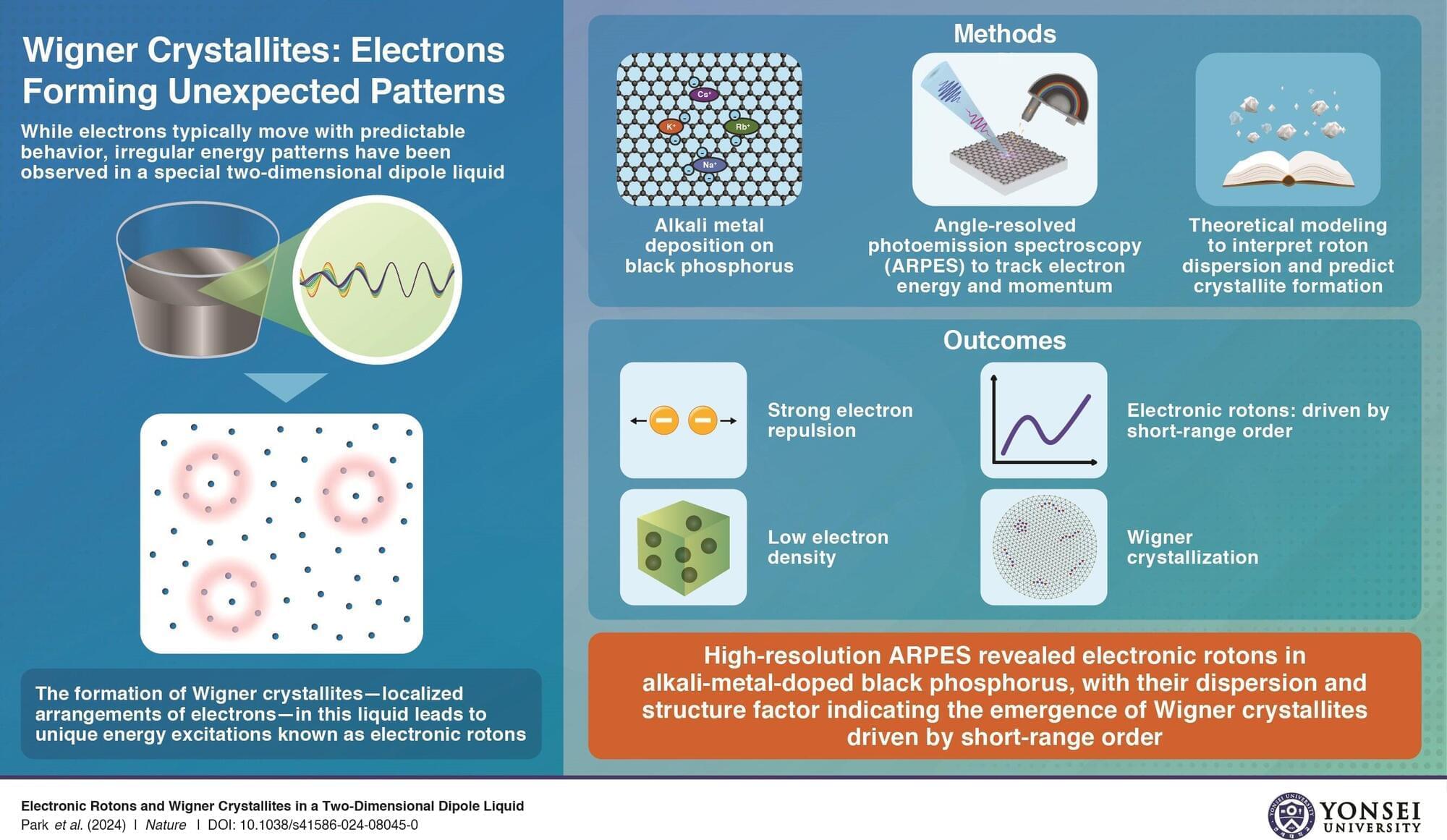
For decades, researchers have explored how electrons behave in quantum materials. Under certain conditions, electrons interact strongly with each other instead of moving independently, leading to exotic quantum states. One such state, first proposed by Nobel laureate Eugene Wigner, is the Wigner crystal—a structured electron arrangement caused by their mutual repulsion. Although widely theorized, experimental proof has been rare.
Researchers at Yonsei University have now provided evidence of Wigner crystallization and the associated electronic rotons. In a study published in the journal Nature, Prof. Keun Su Kim and his team used angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) to analyze black phosphorus doped with alkali metals. Their data revealed aperiodic energy variations, a hallmark of electronic rotons.
Crucially, as they decreased the dopant density within the material, the roton energy gap shrank to zero. This observation confirmed a transition from a fluid-like quantum state to a structured electron lattice, characteristic of Wigner crystallization.
A new solid-state laser produces 193-nm light for precision chipmaking and even creates vortex beams with orbital angular momentum – a first that could transform quantum tech and manufacturing.
Deep ultraviolet (DUV) lasers, which emit high-energy light at very short wavelengths, play a vital role in areas like semiconductor manufacturing, high-resolution spectroscopy, precision material processing, and quantum technology. Compared to traditional excimer or gas discharge lasers, DUV lasers offer better coherence and lower power consumption, making it possible to build smaller, more efficient systems.
Breakthrough in Solid-State Laser Development.

Is there a cleaner and more environmentally friendly way for scientists to create lithium-6, which is a primary component in creating nuclear fusion fuel? This is what a recent study published in Chem hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated safer methods for separating lithium-6 from lithium-7, which is a common procedure for creating nuclear fusion fuel. However, this procedure has long-required liquid mercury, whose exposure often results in sever neurodevelopmental disorders, including memory loss, along with lung, kidney, and nervous system damage.
For the study, the researchers discovered their novel method purely by accident while they were working with “produced water”, which is groundwater that is forced to the surface during drilling processes for gas and oil that needs cleaning before it’s pumped back underground, and this process repeats. To accomplish this cleaning process, a membrane is used to filter out unwanted components, during which the researchers found they were filtering lithium within this now-surface groundwater.
“We saw that we could extract lithium quite selectively given that there was a lot more salt than lithium present in the water,” said Dr. Sarbajit Banerjee, who is a professor of chemistry at ETH Zurich and a co-author on the study. “That led us to wonder whether this material might also have some selectivity for the 6-lithium isotope.”

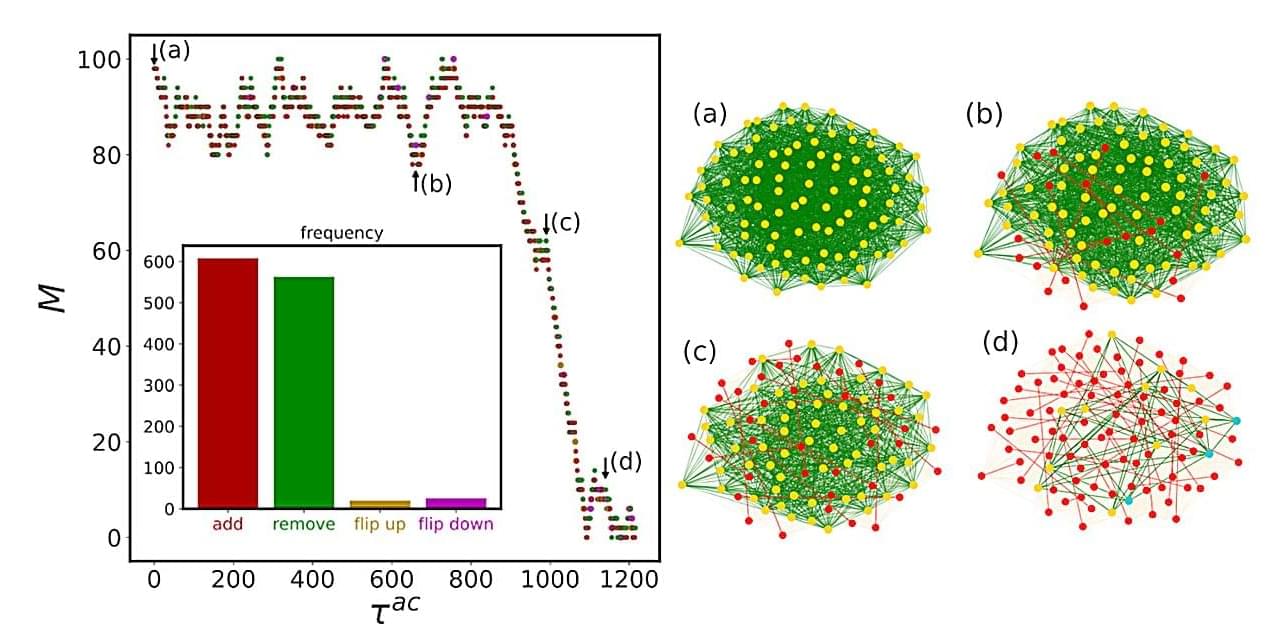
Many systems in nature—and in society—can suddenly change their properties: Water freezes at normal pressure at 32°F, a power grid collapses when a central substation fails, or a society splits into opposing factions following a major event. All of these processes are examples of so-called phase transitions—tipping points where a system abruptly shifts into a new state.
“Often, we can predict these transitions easily. We know at what temperature water freezes. But sometimes, it is extremely difficult to foresee when and how these changes will occur,” explains CSH researcher Jan Korbel, one of the authors of the study, which was published in Nature Communications.